Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bubble
Uploaded by
Natalie JonesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bubble
Uploaded by
Natalie JonesCopyright:
Available Formats
BUBBLE (Question 1) Breasts: Assess the breasts for signs of engorgement, including fullness around postpartum days 3 and
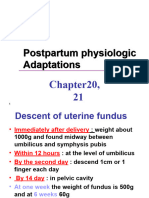
4; assess for hot, red, painful and edematous areas which could indicate mastitis; assess nipple condition for patients who are breastfeeding. Uterus: Assess fundus for firmness; by approximately one hour post delivery the fundus is firm and at the level of the umbilicus. The fundus continues to descend into the pelvis at the rate of approximately 1cm per day and should be nonpalpable by 10 days postpartum. Bladder: Assess for return of urination, which should occur within 6-8 hours of delivery. Patients should void a minimum of 150ml per void. Bowel Function: Assessment of bowel is important, it is vital for patient following cesarean section. Assess the patient s bowel sounds, return of bowel function, and flatus. Include color and consistency of stools. Lochia: Note any excessive amount, any large blood clots, or any foul odors emitted from the lochia. Saturating 1 pad in less than an hour, a constant trickle, or the presence of large blood clots is indicative of more serious complications. Lochia should progress from rubra to serosa to alba. Episiotomy: REEDA (red, edema, ecchymosis, discharge, and approximation); Perineal pain should be assessed and treated. Nurses should assess the rectal area for hemorrhoids.
You might also like
- Postpartum Maternal Physical Assessment SummaryDocument6 pagesPostpartum Maternal Physical Assessment SummaryAlyanna Evangelista100% (2)
- New NORMAL PUERPERIUMDocument21 pagesNew NORMAL PUERPERIUMvarshaNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Assessment NCM 107 Care of Mother Child Adolescent Well Client Rle Skills LabDocument10 pagesPost Partum Assessment NCM 107 Care of Mother Child Adolescent Well Client Rle Skills Labskz19914No ratings yet
- Postpartum Car1Document11 pagesPostpartum Car1Claire Alvarez OngchuaNo ratings yet
- Script - Agito Reniel A - BubbleplebDocument7 pagesScript - Agito Reniel A - BubbleplebReniel AgitoNo ratings yet
- Signs Indicating Possible Complications of PregnancyDocument6 pagesSigns Indicating Possible Complications of Pregnancygerald polopotNo ratings yet
- Assigment VDocument4 pagesAssigment VJoey ParkNo ratings yet
- 3.2 PuerperiumDocument8 pages3.2 PuerperiumTrisha Mae BalladNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Changes Postpartal Period (Puerperium) - Refers To The 6 Weeks Period After ChildbirthDocument12 pagesPostpartum Changes Postpartal Period (Puerperium) - Refers To The 6 Weeks Period After ChildbirthGrace CruzNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Assessment and CareDocument14 pagesPostpartum Assessment and CareGail Chantel Spring PerlasNo ratings yet
- Postpartal CareDocument48 pagesPostpartal CareGladys YaresNo ratings yet
- NRSE 3900 Exam 3 Study GuideDocument15 pagesNRSE 3900 Exam 3 Study GuideNelson MandelaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Nursing Care Fa 10 Nur 263Document63 pagesPostpartum Nursing Care Fa 10 Nur 263EddogawaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum LectureDocument64 pagesPostpartum LectureStephen Gabriel TitoNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument13 pagesPostpartum CareChristian100% (11)
- Postpartum Woman Slide NotesDocument13 pagesPostpartum Woman Slide NotesyolondanicNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Health TeachingDocument8 pagesPostpartum Health TeachingMsOrange96% (24)
- Postpartum: Competency Appraisal - OBDocument54 pagesPostpartum: Competency Appraisal - OBkimalli92No ratings yet
- Post Partal Care 7Document36 pagesPost Partal Care 7Christian OpinaldoNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Care ReportDocument57 pagesPostpartum Care ReportCutay Cristene Mae OrmidoNo ratings yet
- Puerperum Notes 1Document7 pagesPuerperum Notes 1Google SecurityNo ratings yet
- Normal PuerperiumDocument23 pagesNormal Puerperiumnaga maniNo ratings yet
- Assessment PostPARTUMDocument4 pagesAssessment PostPARTUMKariza PerdidoNo ratings yet
- Puerperium Perineal RuptureDocument27 pagesPuerperium Perineal RuptureNovia RizqiNo ratings yet
- Puerperium: DR - Dona Wirniaty, Mked (Og), SpogDocument30 pagesPuerperium: DR - Dona Wirniaty, Mked (Og), SpogMila AnriyaniNo ratings yet
- OB Study Guide #4Document18 pagesOB Study Guide #4lpirman05No ratings yet
- Forceps Delivery (Management) & Puerperium (Postpartum) Stage PDFDocument5 pagesForceps Delivery (Management) & Puerperium (Postpartum) Stage PDFTandingco, Olivia Mari H.No ratings yet
- M. Post PartumDocument65 pagesM. Post PartumRosenda CruzNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument56 pagesPostpartum CareJan Oliver YaresNo ratings yet
- Management of PuerperiumDocument22 pagesManagement of Puerperiumannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Postpartum CareDocument5 pagesModule 4 - Postpartum CareKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Period 1Document93 pagesPostpartum Period 1Angela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- 4physiologyofpuerperium 180930161559Document54 pages4physiologyofpuerperium 180930161559annu panchalNo ratings yet
- PostpartumDocument52 pagesPostpartumAdlehcyer Airod OtanodNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Period 1Document93 pagesPostpartum Period 1Angela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- PuerperiumDocument58 pagesPuerperiumYazeed AsrawiNo ratings yet
- Physical-Assessment-of-Post-Partum-Mother-MIDTERM NotesDocument27 pagesPhysical-Assessment-of-Post-Partum-Mother-MIDTERM NotesAudrie Allyson Gabales100% (1)
- Assessment and Management of Women During Post-Natal PeriodDocument82 pagesAssessment and Management of Women During Post-Natal Periodsweta0% (1)
- PostnatalDocument99 pagesPostnatalPlain GerlNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Physiology of PuerperiumDocument15 pagesSeminar On Physiology of Puerperiumvarshasharma05100% (3)
- The PuerperiumDocument41 pagesThe PuerperiumblatchujosephNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Normal PuerperiumDocument52 pagesCase Study On Normal PuerperiumPiyush Dutta100% (1)
- 7-Physiology of Normal PuerperiumDocument24 pages7-Physiology of Normal Puerperiumhade elNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Physical AssessmentDocument60 pagesPostpartum Physical Assessmentalmyr_rimandoNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Health TeachingDocument6 pagesPostpartum Health TeachingAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14postpartum Physiology Postpartum AdaptationsDocument18 pagesLecture 14postpartum Physiology Postpartum AdaptationsSulaiman SanusiNo ratings yet
- OB NotesDocument9 pagesOB NotesDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Health Teachng - PostpartumDocument15 pagesHealth Teachng - PostpartumMercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- Puerperium and ManagementDocument38 pagesPuerperium and ManagementWadhha AlsenaidiNo ratings yet
- Puerperium and Its Management 1Document35 pagesPuerperium and Its Management 1Elvis100% (2)
- Postpartum Period and ComplicationsDocument63 pagesPostpartum Period and ComplicationsSharmaineAnnePoliciosNo ratings yet
- GyneDocument10 pagesGyneyohannes zerubabelNo ratings yet
- At I Maternal NewbornDocument24 pagesAt I Maternal NewbornEunice Cortés100% (2)
- Postpartum Physical AssessmentDocument60 pagesPostpartum Physical AssessmentJhgrace Mary Pacaña Gallo100% (1)
- PRO Post Natal AssessmentDocument9 pagesPRO Post Natal AssessmentMali KanuNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Postpartum AssessmentDocument2 pagesGuidelines Postpartum Assessmentgrad_nurse_2015100% (1)
- Post Partum Assessment CiDocument5 pagesPost Partum Assessment CiSupremo Manuel M DeluaoNo ratings yet
- PostpartumDocument10 pagesPostpartumEdsylaine BumatayNo ratings yet