Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A JVM
A JVM
Uploaded by
rmuthusamiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A JVM
A JVM
Uploaded by
rmuthusamiCopyright:
Available Formats
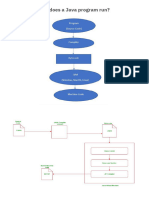
A JVM is a piece of software that is implemented on non-virtual hardware and on standard operating systems.
A JVM provides an environment in which Java bytecode can be executed, enabling such features as automated exception handling, which provides "root-cause" debugging information for every software error (exception), independent of the source code. A JVM is distributed along with a set of standard class libraries that implement the Java application programming interface (API). Appropriate APIs bundled together form the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms. The use of the same bytecode for all JVMs on all platforms allows Java to be described as a "compile once, run anywhere" programming language, as opposed to "write once, compile anywhere", which describes cross-platform compiled languages. Thus, the JVM is a crucial component of the Java platform. Java bytecode is an intermediate language which is typically compiled from Java, but it can also be compiled from other programming languages. For example, Ada source code can be compiled to Java bytecode and executed on a JVM. Oracle, the owner of Java, produces a JVM, but JVMs using the "Java" trademark may be developed by other companies as long as they adhere to the JVM specification published by Oracle and to related contractual obligations.
You might also like
- Java Virtual MachineDocument2 pagesJava Virtual MachineSaravana Kumar RNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Java Introduction To JavaDocument2 pages1.1 Introduction To Java Introduction To JavaAnonymous Atg05gpbNo ratings yet
- By Vagish Kirubaharan COL/A-051935Document29 pagesBy Vagish Kirubaharan COL/A-051935Vagish KirubaharanNo ratings yet
- About Java: The Java Programming LanguageDocument3 pagesAbout Java: The Java Programming LanguageMan RunnerNo ratings yet
- Java Set-1 AnswersDocument9 pagesJava Set-1 AnswersMounika MouniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To JavaDocument3 pagesIntroduction To JavaROHIT DSUZANo ratings yet
- Core Java With JSP Unit - 1 Chapter - 1. Introduction HistoryDocument13 pagesCore Java With JSP Unit - 1 Chapter - 1. Introduction HistoryMarsha KhanNo ratings yet
- Assign 5Document1 pageAssign 5MirNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document40 pagesUnit 1Prabesh KarkiNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL About The Java TechnologyDocument3 pagesTUTORIAL About The Java Technologylaura vanesaNo ratings yet
- JDB - Java Debugger, Which Help Us To Find Errors in Our ProgramsDocument6 pagesJDB - Java Debugger, Which Help Us To Find Errors in Our ProgramsJoel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- ) What Is Difference Between JDK, JRE and JVM?: More Details..Document3 pages) What Is Difference Between JDK, JRE and JVM?: More Details..premaNo ratings yet
- 2.what Is JVMDocument1 page2.what Is JVMjaikumar_22No ratings yet
- JDK, Jre, JVMDocument2 pagesJDK, Jre, JVMpandivenkatesh nNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument22 pagesJavasasik98395No ratings yet
- Java Virtual MachineDocument6 pagesJava Virtual MachineNaveen TibbaNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument59 pagesJavaApoorva Karvariya11 bNo ratings yet
- Java NotesDocument7 pagesJava NotesPraveen VyasNo ratings yet
- Java Notes - Part 1Document39 pagesJava Notes - Part 1Daniel JoshuaNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument5 pagesJavakarunyaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionlearnjava2052No ratings yet
- ComputerDocument1 pageComputerJoel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Java Virtual Machine - Wiki.Document6 pagesJava Virtual Machine - Wiki.prasad357No ratings yet
- Java LanguageDocument17 pagesJava LanguageAna RamonaNo ratings yet
- History of JavaDocument3 pagesHistory of JavaudayahariNo ratings yet
- 3 JavaDocument5 pages3 JavaBibhas PalNo ratings yet
- Java Compiler: Rearrange or Rewrite (Data, Software, Etc.) To Improve Efficiency of Retrieval or ProcessingDocument3 pagesJava Compiler: Rearrange or Rewrite (Data, Software, Etc.) To Improve Efficiency of Retrieval or ProcessingrakiNo ratings yet
- Assignment AcpDocument3 pagesAssignment AcpMuhammad MohsinNo ratings yet
- Explaining Java TechnologyDocument16 pagesExplaining Java TechnologyjackNo ratings yet
- JVM JRE JDK Data Types PDFDocument4 pagesJVM JRE JDK Data Types PDFশেখ মিশারNo ratings yet
- Plat FrameDocument1 pagePlat Frameamanbaba1No ratings yet
- JDK JVMDocument2 pagesJDK JVManuragNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document40 pagesUnit 1ranajitsenkoNo ratings yet
- Core JavaDocument266 pagesCore JavaAjay KaruppusamyNo ratings yet
- Example: C, C++, C#, JavaDocument1 pageExample: C, C++, C#, JavaeddieNo ratings yet
- Java Virtual Machine2Document6 pagesJava Virtual Machine2Abhishek Kavi100% (1)
- Introduction To Java ProgrammingDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Java ProgrammingRamakant UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document18 pagesLecture 01Oluwapelumi EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Chap1-Introduction To JavaDocument10 pagesChap1-Introduction To JavaVarsha KalagiNo ratings yet
- Programming With JAVADocument32 pagesProgramming With JAVAGovind UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- JAVA End Term QuestionsDocument60 pagesJAVA End Term QuestionsVandana GariaNo ratings yet
- My Java Notes BasicDocument31 pagesMy Java Notes BasicDivya PawarNo ratings yet
- Java Terminology-3157Document5 pagesJava Terminology-3157CEO OF BOLLYWOODNo ratings yet
- Phase 1: Creating A Program: Editor Program Editor Source CodeDocument9 pagesPhase 1: Creating A Program: Editor Program Editor Source CodeshimelisNo ratings yet
- 220245-MSBTE-22412-Java (Unit 1)Document40 pages220245-MSBTE-22412-Java (Unit 1)Nomaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 9.introduction To JavaDocument46 pages9.introduction To JavadoneyNo ratings yet
- Java Full Notes Unit 1-6 V2V by Rajan SirDocument156 pagesJava Full Notes Unit 1-6 V2V by Rajan SirYash GawareNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java: Java Virtual Machine (JVM)Document9 pagesIntroduction To Java: Java Virtual Machine (JVM)Ayush VermaNo ratings yet
- 2 IntroToJavaDocument26 pages2 IntroToJavaAZRI HADIF A21EC0054No ratings yet
- What Is Java Bytecode?: How Does It Works?Document1 pageWhat Is Java Bytecode?: How Does It Works?RASHMI DABRENo ratings yet
- Adv Java24Document102 pagesAdv Java24Rohit AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- JavaNotes1 F11Document15 pagesJavaNotes1 F11tshr2323No ratings yet
- Differences Between Augmented Reality Vs Virtual RealityDocument3 pagesDifferences Between Augmented Reality Vs Virtual RealityDivyansh Agrawal (Epigrammatic)No ratings yet
- Introduction To Programming: Sheikh Qaisar Ayub, Sulma RashidDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Programming: Sheikh Qaisar Ayub, Sulma RashidQaisar Ayub SheikhNo ratings yet
- CH1Introduction PDFDocument20 pagesCH1Introduction PDFAshik MahmudNo ratings yet
- Java SE 8 Programmer 1 (IZO-808) Study Material PDFDocument408 pagesJava SE 8 Programmer 1 (IZO-808) Study Material PDFsandesh singhalNo ratings yet
- Difference Between JDK, JRE and JVMDocument4 pagesDifference Between JDK, JRE and JVMArijit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Programación Orientada A ObjetosDocument31 pagesProgramación Orientada A ObjetosPablito Quispe RuizNo ratings yet
- JAVA: Java Programming for beginners teaching you basic to advanced JAVA programming skills!From EverandJAVA: Java Programming for beginners teaching you basic to advanced JAVA programming skills!No ratings yet