Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Displacement of Halogens
Displacement of Halogens
Uploaded by
Edelstein Tommy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesA more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive one from its compounds in solution because the more reactive halogen is able to accept the extra electron from the metal ion. For example, when sodium chloride solution is mixed with fluorine, fluorine replaces chloride to form sodium fluoride because fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine and able to pull the electron away from chlorine. A table shows that chlorine will displace bromide and iodide from their salts but bromine only displaces iodide because reactivity decreases down the halogen group.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive one from its compounds in solution because the more reactive halogen is able to accept the extra electron from the metal ion. For example, when sodium chloride solution is mixed with fluorine, fluorine replaces chloride to form sodium fluoride because fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine and able to pull the electron away from chlorine. A table shows that chlorine will displace bromide and iodide from their salts but bromine only displaces iodide because reactivity decreases down the halogen group.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesDisplacement of Halogens
Displacement of Halogens
Uploaded by
Edelstein TommyA more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive one from its compounds in solution because the more reactive halogen is able to accept the extra electron from the metal ion. For example, when sodium chloride solution is mixed with fluorine, fluorine replaces chloride to form sodium fluoride because fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine and able to pull the electron away from chlorine. A table shows that chlorine will displace bromide and iodide from their salts but bromine only displaces iodide because reactivity decreases down the halogen group.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
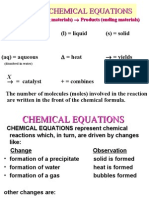
If a halogen is added to a solution of a compound containing a less reactive halogen, it will react with the compound and form
a new one. This is called displacement. sodium chloride 2NaCl (aq) sodium fluoride 2NaF (aq)
fluorine
+ +
+ +
chlorine
F2 (aq)
Cl2 (aq)
A more reactive halogen will always displace a less reactive halide from its compounds in solution.
Why will a halogen always displace a less reactive halogen?
If a metal halide is mixed with a more reactive halogen, the extra electron will be transferred from the less reactive to the more reactive halogen.
+
sodium Na Cl
chlori e chloride
fluori e fluoride F
The reactions between solutions of halogens and metal halides (salts) can be summarised in a table: salt (aq) halogen chlorine potassium chloride potassium bromide 2KCl + Br2 potassium iodide 2KCl + I2 2KBr + I2
bromine
no reaction no reaction no reaction
iodine
You might also like
- HalogensDocument70 pagesHalogensKSINo ratings yet
- Halogens Power Point NotesDocument74 pagesHalogens Power Point NotesgajenraoNo ratings yet
- Group 7 HalogensDocument59 pagesGroup 7 HalogensHisham Jafar AliNo ratings yet
- HalogensDocument15 pagesHalogensDuplexNo ratings yet
- Group 17Document18 pagesGroup 17Muhammad KalimNo ratings yet
- A Level Group 7 NotesDocument8 pagesA Level Group 7 NotesBarry HowarthNo ratings yet
- Group Vii: The HalogensDocument9 pagesGroup Vii: The HalogensromiifreeNo ratings yet
- Group 17 Elements - F, CL, BR, ..Document36 pagesGroup 17 Elements - F, CL, BR, ..Looi Chui YeanNo ratings yet
- Group 7 The Halogens KLASS AnswersDocument4 pagesGroup 7 The Halogens KLASS AnswersKimberly Linderholm100% (1)
- Group VII Elements Lecture NotesDocument14 pagesGroup VII Elements Lecture NotesTerry LimNo ratings yet
- 06 Reaksi Dalam Larutan BerairDocument89 pages06 Reaksi Dalam Larutan BerairIrfan Setya BasithNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - Group 7Document3 pagesCHEMISTRY - Group 7annabelbithellNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Part 2: Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryDocument37 pagesUnit 5 - Part 2: Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryBibha KumariNo ratings yet
- Group VII NotesDocument6 pagesGroup VII NotesA LEVEL TOPNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions NotesDocument13 pagesRedox Reactions NotesmoiiifitbituserNo ratings yet
- The HalogensDocument5 pagesThe HalogensDoc_Croc100% (1)
- Mod 2 Revision Guide 5. Halogens PDFDocument3 pagesMod 2 Revision Guide 5. Halogens PDFDarian BurkettNo ratings yet
- 10407-Lecture N4Document24 pages10407-Lecture N4ggogitidze052No ratings yet
- F321 Group 7Document5 pagesF321 Group 7Doc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Inorganic: GROUP 17 CL, BR, IDocument31 pagesChemistry-Inorganic: GROUP 17 CL, BR, IHenfin AuNo ratings yet
- A. Electrolysis of Acidified Water (Dilute Sulphuric Acid) : Notes Myp 5 ChemistryDocument10 pagesA. Electrolysis of Acidified Water (Dilute Sulphuric Acid) : Notes Myp 5 Chemistrywama ojhaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Powerpoint PresentationDocument52 pagesChemistry Powerpoint Presentationjjjobson jobsonNo ratings yet
- 11 Halogens: Redox Reactions and Reactivity of Halogens and Their CompoundsDocument4 pages11 Halogens: Redox Reactions and Reactivity of Halogens and Their CompoundsGbadamosiNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument26 pagesChemical ReactionsEvernim Ompacan100% (1)
- Halogens 2Document53 pagesHalogens 2tik-tok worldNo ratings yet
- Oxidation - Reduction ReactionsDocument29 pagesOxidation - Reduction Reactionsademola rufaiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Chemical ReactionsDocument12 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Chemical ReactionsSahil SweNo ratings yet
- Unit 12 - Group 17Document44 pagesUnit 12 - Group 17Sahana KumarNo ratings yet
- Test Tube Reactions For Topic 6 1) Halogen Displacement ReactionsDocument2 pagesTest Tube Reactions For Topic 6 1) Halogen Displacement ReactionsXiandan AyjNo ratings yet
- Group Trends: Prepared by K. Walker-DawkinsDocument36 pagesGroup Trends: Prepared by K. Walker-DawkinsZae ZayNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Sem2Document12 pagesExperiment 8 Sem2Fatin NurhudaNo ratings yet
- Jahiem Nembhard Inorganic Lab 5Document6 pagesJahiem Nembhard Inorganic Lab 5Jahiem NembhardNo ratings yet
- Poster RevisionDocument3 pagesPoster RevisionAnonymous fvw90RTQ7No ratings yet
- HalogensDocument21 pagesHalogensPaul TinarwoNo ratings yet
- The HalogensDocument9 pagesThe HalogensAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction Is Related To Gain or Loss of Electrons PDFDocument4 pagesRedox Reaction Is Related To Gain or Loss of Electrons PDFClarence B. MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Sodium Hypochlorite / Essay / PaperDocument5 pagesChemistry of Sodium Hypochlorite / Essay / PaperAssignmentLab.comNo ratings yet
- Group 17Document13 pagesGroup 17hernaniabdullah100% (1)
- iGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 2Document67 pagesiGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 2G8. 15 Reet SinghviNo ratings yet
- Notes MAINDocument22 pagesNotes MAINFarhan TanveerNo ratings yet
- 9halogens Group PresentationDocument31 pages9halogens Group PresentationQueen GeminiNo ratings yet
- Displacement ReactionDocument3 pagesDisplacement ReactionFatmata Haja KamaraNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table - 9.3 LessonDocument5 pagesThe Periodic Table - 9.3 LessonSri Charitha ANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical ReactionsDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Chemical ReactionsHema lathaNo ratings yet
- Group 17: Prepared By: Gracia & NazirahDocument21 pagesGroup 17: Prepared By: Gracia & NazirahGracia Blessina FrancisNo ratings yet
- Chem121-Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsDocument87 pagesChem121-Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsberkitenberkanNo ratings yet
- 5333 Chlorine and Other HalogensDocument8 pages5333 Chlorine and Other Halogensbilldanit4fitzNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document3 pagesUnit 7api-282526559No ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument80 pagesRedox ReactionsShashwatNo ratings yet
- 2.07.2 Group 7Document7 pages2.07.2 Group 7Bryan YeohNo ratings yet
- 11.3 Some Reactions of The Halide IonsDocument6 pages11.3 Some Reactions of The Halide Ionstajwaar0506No ratings yet
- Ch5 Redox Reaction Shobhit NirwanDocument22 pagesCh5 Redox Reaction Shobhit NirwanPROFESSOR0% (1)
- Redox Reaction Shobhit NirwanDocument22 pagesRedox Reaction Shobhit NirwanBhavya Goyal XI Non med100% (7)
- Genchem Pre-MidtermDocument5 pagesGenchem Pre-MidtermhjNo ratings yet
- 12.3 HalogensDocument16 pages12.3 HalogensPuja DhawanNo ratings yet
- The HalogensDocument11 pagesThe Halogensmukwellerenefavour27No ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument27 pagesRedox ReactionsRakesh SNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) Chemical ReactionsDocument32 pages(CHEM) Chemical Reactionssodiumboyupinthishoe100% (2)
- Catalytic Activity of Transition ElementsDocument47 pagesCatalytic Activity of Transition ElementsNeen Naaz100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet