Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CMAP
Uploaded by
Jaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CMAP
Uploaded by
Jaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahCopyright:
Available Formats
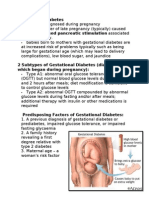
PREGNANCY
Late gestation
Adipose Tissue accretion
Formation of the placenta
Increased levels of resistin Adipose tissue depot decline Obesity FFA increases Increased cortisol, estrogen and progesterone Insulin mediated glucose disposal worsens Interferes with post insulin receptors Ethnicity
Stimulation of placenta for hormonal production
Increased production of hCG
Placental insulinase
Increased HPL and hPGH
Accelerates insulin degredation
Decreased peripheral resistance to insulin
Decreased tissue sensitivity To insulin
Family Hx Pancreas produces more insulin to compensate
Exercise
Age
Fails to compensate or produce enough insulin
Glucose remains in the blood
1.
NCP Trauma, Risk for Injury related to presence of macrosomia or IUGR. Risk for maternal Injury related to inadequate diabetic control secondary to Gestational Diabetes. Anxiety related to situational crisis/ threat to health status (maternal or fetal) secondary to Gestational Diabetes. Risk for impaired parent/infant / child attachment related to Interruption in bonding process, physical illness/changes in physical abilities secondary to Gestational Diabetes. Knowledge deficit regarding condition, prognosis and treatment needs related to lack of exposure, misinterpretation of the disease process secondary to Gestational Diabetes.
Energy depletion on body cells
Increased blood glucose concentration
Crosses placental barrier and enters the fetus
2.
Oxidation of fats and protein
Increased glucose levels Osmotic pressure pulls H2O from cells to blood Increased insulin production Cellular dehydration Fetal hyperinsulism and hyperglycemia Glycosuria Polydipsia Macrosomia Polyuria Preterm Birth
5. 3.
Wasting of muscle fats and protein
4.
Prevents H2O reabsorption in the kidney tubules
Weakness
Fatigue Disease process Risk Factor Manifestation CS
Hypoglycemia
You might also like
- Assessment of High-Risk PregnancyDocument23 pagesAssessment of High-Risk PregnancyNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes 97-03Document9 pagesGestational Diabetes 97-03jaenaroseNo ratings yet
- Edited To Include Report 1Document16 pagesEdited To Include Report 1allanrnmanalotoNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition - Less Than Body Requirements 01Document6 pagesImbalanced Nutrition - Less Than Body Requirements 01AgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- Fetal Issues: Table 25.16Document3 pagesFetal Issues: Table 25.16CristinaNo ratings yet
- 12-05-2021-1620815054-8-Ijgmp-3. Ijgmp - Management of Infertility in Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeDocument18 pages12-05-2021-1620815054-8-Ijgmp-3. Ijgmp - Management of Infertility in Polycystic Ovarian Syndromeiaset123No ratings yet
- Diseases Affecting Pregnancy HODocument10 pagesDiseases Affecting Pregnancy HORasco, Allen jayNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document5 pagesLec 3mudassir qazalbashNo ratings yet
- 109 Pregestational Nov2019Document68 pages109 Pregestational Nov2019Sean kevinNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Gestasional Diabetes MellitusDocument24 pagesPathogenesis of Gestasional Diabetes MellitusNadya Meilinar SamsonNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Infertility: Behind The Medical HeadlinesDocument4 pagesObesity and Infertility: Behind The Medical HeadlinesKurnia Sari SyaifulNo ratings yet
- Management of Hyperemesis Gravidarum PDFDocument10 pagesManagement of Hyperemesis Gravidarum PDFResi Lystianto PutraNo ratings yet
- Documents For ScribdDocument15 pagesDocuments For ScribdAishaNo ratings yet
- Rev 05 (02-26 PP) - Gestational DiabetesDocument1 pageRev 05 (02-26 PP) - Gestational DiabetesSaya MenangNo ratings yet
- Complicated Midwifery - 1Document28 pagesComplicated Midwifery - 1nafisatmuhammed452No ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacy (Chapter 1) : Drug Use in Pregnancy & LactationDocument40 pagesClinical Pharmacy (Chapter 1) : Drug Use in Pregnancy & LactationAnonymous DgPsK0oQNo ratings yet
- Drug Use During Pregnancy and LactationDocument93 pagesDrug Use During Pregnancy and Lactation2012100% (2)
- Resistencia A La Insulina Madre y FetoDocument10 pagesResistencia A La Insulina Madre y FetoNorma AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Obs PresentationDocument19 pagesObs PresentationAliNo ratings yet
- Adult Sequelae of Intrauterine Growth RestrictionDocument6 pagesAdult Sequelae of Intrauterine Growth RestrictionAnca AdamNo ratings yet
- Life Span Health PromotionDocument67 pagesLife Span Health Promotion22bgu0727msNo ratings yet
- Res Lounge Infant of Diabetic MotherDocument19 pagesRes Lounge Infant of Diabetic MotherYong Kui ChooNo ratings yet
- Fetal Origin of Adult Disease: New HorizonsDocument5 pagesFetal Origin of Adult Disease: New HorizonsHervi LaksariNo ratings yet
- 10b. Paper Enfermedades Gastrointestinales en El EmbarazoDocument17 pages10b. Paper Enfermedades Gastrointestinales en El EmbarazoPaloma ErazoNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes - ppt12Document59 pagesGestational Diabetes - ppt12tanseem88% (8)
- Association Between Weight Gain and PCOSDocument3 pagesAssociation Between Weight Gain and PCOSAstrid SitohangNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in Pregnancy: Ryan Agema MS IIIDocument23 pagesDiabetes in Pregnancy: Ryan Agema MS IIIAkshat Goel100% (1)
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum PresentationDocument22 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum PresentationMaricar Sanson FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Type1Diabetesinpregnancy: David R. Mccance,, Claire CaseyDocument15 pagesType1Diabetesinpregnancy: David R. Mccance,, Claire Caseyjose ricardo escalante perezNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes IrDocument10 pagesGestational Diabetes IrChikezie OnwukweNo ratings yet
- Ob PrelimsDocument13 pagesOb PrelimseliNo ratings yet
- Human Chorionic GonadotropinDocument2 pagesHuman Chorionic GonadotropinCharissa de LeonNo ratings yet
- Growth PDFDocument69 pagesGrowth PDFSiselle FajardoNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes and Maternal ObesityDocument2 pagesGestational Diabetes and Maternal Obesitydr.vidhyaNo ratings yet
- High-Risk Pregnancy: The Internet Journal of Gynecology and ObstetricsDocument16 pagesHigh-Risk Pregnancy: The Internet Journal of Gynecology and ObstetricsWidelmark FarrelNo ratings yet
- HEGDocument23 pagesHEGSamer SaoumaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Hypertension: Maternal Health Care-ClinicalDocument10 pagesGestational Hypertension: Maternal Health Care-ClinicalIbrahim W. HassanNo ratings yet
- 06 - 213the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome-A Systematic ReviewDocument4 pages06 - 213the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome-A Systematic ReviewAnni SholihahNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid: Influence On The Outcome of Pregnancy: Theresa O Scholl and William G JohnsonDocument9 pagesFolic Acid: Influence On The Outcome of Pregnancy: Theresa O Scholl and William G JohnsonKeylLaNo ratings yet
- Past Year ReproDocument4 pagesPast Year ReproThulasi tootsieNo ratings yet
- Obesity in ChildrenDocument52 pagesObesity in Childrenjournaldaily82No ratings yet
- FTT SeminarDocument16 pagesFTT SeminarAmy Lalringhluani ChhakchhuakNo ratings yet
- Attachment Filename Merging ResultDocument127 pagesAttachment Filename Merging Resultmaqma.1453No ratings yet
- Fetal Origins of Adult DiseaseDocument9 pagesFetal Origins of Adult DiseaseMuljadi HartonoNo ratings yet
- PCOSDocument15 pagesPCOSAndyan Adlu PrasetyajiNo ratings yet
- Infants of Diabetic MothersDocument19 pagesInfants of Diabetic MothersGaby AldamaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition During Pregnancy Part2Document17 pagesNutrition During Pregnancy Part222bgu0727msNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Care of at RiskDocument38 pagesNCM 109 Care of at RiskMia Fe Cuaya LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Perinatal MedicineDocument7 pagesPerinatal MedicineMerna MahrousNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders During Pregnancy 2006Document223 pagesEndocrine Disorders During Pregnancy 2006STEPHANIE TALILAHNo ratings yet
- 353 PregnancyDocument88 pages353 PregnancyLeofe CorregidorNo ratings yet
- Infant of A Diabetic MotherDocument31 pagesInfant of A Diabetic MotherDatulna Benito Mamaluba Jr.No ratings yet
- Placenta: P. Pantham, I.L.M.H. Aye, T.L. PowellDocument7 pagesPlacenta: P. Pantham, I.L.M.H. Aye, T.L. PowellrismaNo ratings yet
- Script Pedia 1Document38 pagesScript Pedia 1Jessy Arcaina BañagaNo ratings yet
- Neet PGDocument39 pagesNeet PGKartik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Insulin Resistance Eating Plan: A Beginner's 2-Week Step-by-Step Guide for Women to Manage PCOS and Prediabetes, With Sample Curated RecipesFrom EverandInsulin Resistance Eating Plan: A Beginner's 2-Week Step-by-Step Guide for Women to Manage PCOS and Prediabetes, With Sample Curated RecipesNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Diabetes: Symptoms; Causes; Treatment; PreventionFrom EverandA Guide to Diabetes: Symptoms; Causes; Treatment; PreventionNo ratings yet
- Insulin Resistance Cookbook: Your Guide to Beating Insulin Resistance with 20 Go-To Recipes!: Diabetes and Blood Sugar LevelFrom EverandInsulin Resistance Cookbook: Your Guide to Beating Insulin Resistance with 20 Go-To Recipes!: Diabetes and Blood Sugar LevelNo ratings yet
- Smoothies for Diabetics: Reverse Diabetes and Lower Blood Sugar with 36 Quick & Easy Delicious Diabetic Smoothie RecipesFrom EverandSmoothies for Diabetics: Reverse Diabetes and Lower Blood Sugar with 36 Quick & Easy Delicious Diabetic Smoothie RecipesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Form No. 232 Complaint With Preliminary InjunctionDocument3 pagesForm No. 232 Complaint With Preliminary InjunctionJaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahNo ratings yet
- Torts DigestsDocument7 pagesTorts DigestsJaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Witness Hotel ManagerDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Witness Hotel ManagerJaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahNo ratings yet
- Prohibitions Against HomeworkDocument4 pagesProhibitions Against HomeworkJaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahNo ratings yet
- Report Notes: Employment of Industrial Homeworkers (Article 151-153 of Labor Code) Definition of TermsDocument4 pagesReport Notes: Employment of Industrial Homeworkers (Article 151-153 of Labor Code) Definition of TermsJaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahNo ratings yet
- Report Notes (Arts. 141-152, Labor Code of The Philippines, in Relation To R.A. No. 10361 (Batas Kasambahay) ) Definition of TermsDocument7 pagesReport Notes (Arts. 141-152, Labor Code of The Philippines, in Relation To R.A. No. 10361 (Batas Kasambahay) ) Definition of TermsJaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahNo ratings yet
- Antiola, Nina Marie Ramos, Rozzini October 5, 2018 Vidal, KC Quiapo, Fatima Toledo, Joyce ElpieDocument1 pageAntiola, Nina Marie Ramos, Rozzini October 5, 2018 Vidal, KC Quiapo, Fatima Toledo, Joyce ElpieJaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahNo ratings yet
- Philippine Lawyer'S Association vs. Celedonio Agrava: FactsDocument6 pagesPhilippine Lawyer'S Association vs. Celedonio Agrava: FactsJaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahNo ratings yet
- Case Digest On Corporation LawDocument30 pagesCase Digest On Corporation LawJaeho Sani Dalidig Sabdullah100% (1)
- Philippine Lawyer'S Association vs. Celedonio Agrava: FactsDocument14 pagesPhilippine Lawyer'S Association vs. Celedonio Agrava: FactsJaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahNo ratings yet
- BibliographyDocument1 pageBibliographyJaeho Sani Dalidig SabdullahNo ratings yet