Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Islcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Pre Intermediate A2 Elementary School Tenses Present Perfect 319954e35a70c8ab893 72786782
Islcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Pre Intermediate A2 Elementary School Tenses Present Perfect 319954e35a70c8ab893 72786782
Uploaded by
Марија К.Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Islcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Pre Intermediate A2 Elementary School Tenses Present Perfect 319954e35a70c8ab893 72786782
Islcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Pre Intermediate A2 Elementary School Tenses Present Perfect 319954e35a70c8ab893 72786782
Uploaded by
Марија К.Copyright:
Available Formats
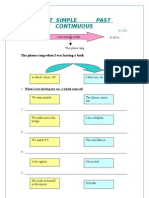
Past Simple tense is used: - Use the Simple Past to express the idea that an action started and
finished at a specific time in the past. Sometimes, the speaker may not actually mention the specific time, but they do have one specific time in mind. E.g. I saw a movie yesterday.
We use the Simple Past to list a series of completed actions in the past. E.g. I finished work, walked to the beach, and found a nice place to swim. The Simple Past can be used with a duration which starts and stops in the past. E.g. He studied Japanese for 5 years SUBJECT + VERB (-ed (regular)/ irregular verbs (2nd Column)) + COMPLEM. SUBJECT + DIDNT + VERB (-infinitive) + COMPLEMENTS. (WH-) + DID+ SUBJECT + VERB (Infinitive) + COMPLEMENTS + ? YES/NO, SUBJECT + DID/DIDNT + COMPLEMENTS SPELLING RULES: - Consonant after after short stressed vowel at the end of the word. o We double the consonant. STOP- STOPPED. - One e at the end of the word. o We only add a d. SAVE- SAVED. - Verbs ending in y. o Preceded by a vowel (add ed). PLAY-PLAYED. o Preceded by a consonant (change y to i and add ed). HURRYHURRIED. PRONUNCIATION OF THE VERBS FINISHED IN ED.
In the Simple Past we add -ed to regular verbs. Be careful pronuncing the verbs: 1) verbs ending in -ed preceded by a voiceless consonant [p, k, f, , , s, ] -> speak [t]. The -e is silent. Example: I stop - I stopped [stpt] 2) verbs ending in -ed preceded by a voiced consonant [b, g, v, , , z, , l, m, n] or a vowel -> speak [d]. The -e is silent. Example: I clean - I cleaned [kli:nd] 3) verbs ending in -ed preceded by [t] or [d] -> speak [d]. The -e changes to []. Example: I visit - I visited [vztd]
(+) (-) (?) (A)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Articles of Indian Constitution in Telugu LanguageDocument3 pagesArticles of Indian Constitution in Telugu Languagefacebookcontactme46% (24)
- Celta Lesson FrameworksDocument2 pagesCelta Lesson FrameworksIryna Shymanovych100% (3)
- Past Simple Vs Past Continuous Fun Activities Games Warmers Coolers 7889Document1 pagePast Simple Vs Past Continuous Fun Activities Games Warmers Coolers 7889Claudia Kerekes33% (3)
- Educ4748 Assessment 1Document10 pagesEduc4748 Assessment 1api-359895239100% (1)
- Eurolingua English 2 PDFDocument2 pagesEurolingua English 2 PDFJuanNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Messages 1Document4 pagesTest 1 Messages 1emcesssNo ratings yet
- I. Complete The Sentences. Use The Adverb and The Correct Form of The Verbs in BracketsDocument2 pagesI. Complete The Sentences. Use The Adverb and The Correct Form of The Verbs in BracketsМарија К.No ratings yet
- FacebookDocument2 pagesFacebookМарија К.No ratings yet
- Where Are They From? Answer The Questions: Test On Unit 1 Welcome BackDocument4 pagesWhere Are They From? Answer The Questions: Test On Unit 1 Welcome BackМарија К.No ratings yet
- Go GreenPledgeDocument1 pageGo GreenPledgeМарија К.No ratings yet
- English For Hospitality: GreetingDocument15 pagesEnglish For Hospitality: GreetingМарија К.100% (1)
- The Frog PrinceDocument6 pagesThe Frog PrinceМарија К.No ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs in The Past Simple Tense Gap Fill Ig14+Document1 pageIrregular Verbs in The Past Simple Tense Gap Fill Ig14+Марија К.No ratings yet
- Islcollective Worksheets Beginner Prea1 Elementary A1 Adu Talking About Your Family The Simpsons 110484df9b0c86db5f2 71292192Document2 pagesIslcollective Worksheets Beginner Prea1 Elementary A1 Adu Talking About Your Family The Simpsons 110484df9b0c86db5f2 71292192Марија К.No ratings yet
- Educators Calendar 2011Document13 pagesEducators Calendar 2011Марија К.No ratings yet
- Islcollective S Family Puzzle 143854d8a17f3d4aa18 13324993Document1 pageIslcollective S Family Puzzle 143854d8a17f3d4aa18 13324993Марија К.No ratings yet
- Islcollective Family Tree 253904cf8e66b4f7689 27184719Document1 pageIslcollective Family Tree 253904cf8e66b4f7689 27184719Марија К.No ratings yet
- Islcollective Worksheets Beginner Prea1 Elementary A1 Adu Talking About Your Family The Simpsons 110484df9b0c86db5f2 71292192Document2 pagesIslcollective Worksheets Beginner Prea1 Elementary A1 Adu Talking About Your Family The Simpsons 110484df9b0c86db5f2 71292192Марија К.No ratings yet
- Family Members: Study This Family Tree and Write The Correct WordsDocument3 pagesFamily Members: Study This Family Tree and Write The Correct WordsBiljana Oliveroska-Trajkovska0% (1)
- Look at The Picture, Read The Sentences and Write The Name in The Right BoxDocument3 pagesLook at The Picture, Read The Sentences and Write The Name in The Right BoxМарија К.No ratings yet
- 35394ad9eecb1f6c74 31956412meet My FamilyDocument2 pages35394ad9eecb1f6c74 31956412meet My FamilyМарија К.No ratings yet
- Islcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Pre Intermediate A2 Adult Elementary SC Past Simple Revision 15774e2194acd48c92 96055585Document2 pagesIslcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Pre Intermediate A2 Adult Elementary SC Past Simple Revision 15774e2194acd48c92 96055585Марија К.No ratings yet
- Islcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Elementary School Past Simple Continuous Gramm Past Simple 86694e39d0ccde8282 50910769Document1 pageIslcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Elementary School Past Simple Continuous Gramm Past Simple 86694e39d0ccde8282 50910769Марија К.No ratings yet
- Islcollective Tenses Past Simple Past Continuous 66234da343650df3f6 07178842Document3 pagesIslcollective Tenses Past Simple Past Continuous 66234da343650df3f6 07178842Марија К.No ratings yet
- Islcollective Worksheets Beginner Prea1 Elementary A1 Pre Inter Media Past Simple or Past Continuous 81454e5016727be6c4 63527033Document1 pageIslcollective Worksheets Beginner Prea1 Elementary A1 Pre Inter Media Past Simple or Past Continuous 81454e5016727be6c4 63527033Марија К.No ratings yet
- 171644af54de60b7eb8 96203816 Simple Past Past ContDocument2 pages171644af54de60b7eb8 96203816 Simple Past Past ContМарија К.No ratings yet
- English Unit 1 Lesson 5 9Document134 pagesEnglish Unit 1 Lesson 5 9Gianna Gayle S. FondevillaNo ratings yet
- Cockney English - Main FeaturesDocument3 pagesCockney English - Main FeaturesIván Doval Méndez0% (1)
- English Is Too Hard To Read For Children (Ss Copy)Document3 pagesEnglish Is Too Hard To Read For Children (Ss Copy)Manh TranNo ratings yet
- A Reflection ViewDocument4 pagesA Reflection ViewChem VathoNo ratings yet
- Early BlazonDocument572 pagesEarly Blazonisenhand37490% (1)
- Language Is The Ability To Acquire and Use Complex Systems ofDocument2 pagesLanguage Is The Ability To Acquire and Use Complex Systems ofLakshanmayaNo ratings yet
- My Dreams Is ThisDocument10 pagesMy Dreams Is ThissandeshkunnathNo ratings yet
- Isaac Pitman S Short Isaac Pitman Black and White (Ebooksread - Com)Document328 pagesIsaac Pitman S Short Isaac Pitman Black and White (Ebooksread - Com)numanashiq100% (5)
- Vowel and Consonant SoundsDocument4 pagesVowel and Consonant Soundslaura100% (1)
- Formulario RH-117 Novedades Docentes ANDREADocument444 pagesFormulario RH-117 Novedades Docentes ANDREAAndrea NolascoNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of The Critical Period Research (Scovel 2000)Document11 pagesA Critical Review of The Critical Period Research (Scovel 2000)Eduardo100% (2)
- HBX 6516DS VTMDocument2 pagesHBX 6516DS VTMRoma Zurita100% (1)
- This Is My Family: VocabularyDocument54 pagesThis Is My Family: VocabularyARMANDO JRNo ratings yet
- Japanese, Korean and AltaicDocument20 pagesJapanese, Korean and Altaicchaoxian82416100% (1)
- SYLLABLE Learning MaterialDocument3 pagesSYLLABLE Learning MaterialIrina MitkevichNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentation RubricDocument2 pagesOral Presentation RubricDavid MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Jamaican EnglishDocument13 pagesJamaican EnglishRaquelNo ratings yet
- Translatic Theory - TouDocument25 pagesTranslatic Theory - TouFaiidjahIdaaFatmawatiiNo ratings yet
- Workplace Communication Skills U3Document161 pagesWorkplace Communication Skills U3Foo Chuat MengNo ratings yet
- Silabus Mata Kuliah Language Testing IDocument2 pagesSilabus Mata Kuliah Language Testing IRahma AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Research On Listening Comprehension Problems PDFDocument10 pagesResearch On Listening Comprehension Problems PDFYerbua Onas LptNo ratings yet
- PDF Arabic Alphabet - Compress PDFDocument1 pagePDF Arabic Alphabet - Compress PDFJakub WyrwińskiNo ratings yet
- Grammar Translation MethodDocument4 pagesGrammar Translation MethodnilsusudeNo ratings yet
- Lesson V LanguageDocument5 pagesLesson V LanguageNina UyadNo ratings yet
- Mother Tongue Based-Multilingual EducationDocument167 pagesMother Tongue Based-Multilingual EducationSAMANTHA L. POLICARPIO100% (2)
- George O. Holbrooke - Âryan Word-Building PDFDocument476 pagesGeorge O. Holbrooke - Âryan Word-Building PDFKeep CalmNo ratings yet