Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stacks and Queues
Uploaded by
api-3711790Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stacks and Queues
Uploaded by
api-3711790Copyright:
Available Formats
Stacks & Queue
Week 6
Faezeh Seyedarabi www.faezeh.co.uk 1
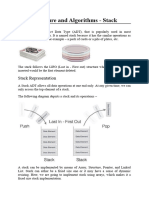
Stacks
A stack is one of the methods used to insert and delete items from a linear list. For example, pile of plates in
a canteen. After washing up the plates, the last plate will be placed on to the top of the stack. The next plate
to be used will be taken from the top of the stack (i.e. LIFO stack)
We refer to the ‘top of the stack’ or the ‘buttom of the stack’, thus the number will be set out vertically, to
reinforce this point visually.
We also have the phrase ‘pushed on the top of the stack’ to indicate that an item of data has been added to
the stack.
Moreover, we have the phrase ‘popped off the stack’ to indicate that the ‘last number in’ is always the ‘first
number out’
The system of storing this list of numbers is called LIFO stack (Last In First Out).
A Pointer System
In practice a stack would be built up in the computer’s memory using a pointer system. This is a number
used to pint to an item of interest, so it may be used to point to the memory location inside the computer that
indicates the top of the stack. (called Stack Pointer)
Faezeh Seyedarabi www.faezeh.co.uk 2
For example, consider the numbers in the list:
23 Add number 77
77
54 (PUSH) 23
10 54
90 10
90
Stack _pointer variable used to indicate the current top
of the stack.
Maximum used to determine when the stack is full.
Minimum used to determine if the stack is empty.
Data item in data to be pushed or popped.
STACK general name for the stack contained in
memory.
STACK(Stack_pointer) subscripted variable representing the
data at the current stack pointer, i.e. it is
an identifier for the data on the stack.
Faezeh Seyedarabi www.faezeh.co.uk 3
Pseudocode to PUSH a new item of data on to the top of the STACK
Note: if there is no room to add a new item then a error message must be generated, as an overflow has
occurred. Example: (Let’s assume that an array STACK(N) has been already set up.)
PUSH (Stack_pointer, Maximum, Data) Calling the procedure
The actual Pseudocode for the PUSH procedure:
PROCEDURE PUSH (Stack_pointer, Maximum, Data)
(*Check if the stack is already full*)
IF Stack_pointer=Maximum THEN
PRINT No room on the stack
EXIT PROCEDURE
ELSE
(*Push data item on the stack*)
SET Stack_pointer= Stack_pointer+1
SET Stack_pointer= Data
END IF
END PROCEDURE
Faezeh Seyedarabi www.faezeh.co.uk 4
Pseudocode to POP a new item of data on to the top of the STACK
Note: here the stack cannot overflow from this operation. However, there might be no items of data on the
stack, in which case cannot remove any more data.
POP (Stack_pointer, Maximum, Data) Calling the procedure
The actual Pseudocode for the POP procedure:
PROCEDURE POP (Stack_pointer, Maximum, Data)
(*Check if the stack is already empty*)
IF Stack_pointer=Minimum THEN
PRINT the stack is already empty
EXIT PROCEDURE
ELSE
(*Pop data off of stack and adjust pointer*)
SET Data= STACK (Stack_pointer)
SET Stack_pointer= Stack_pointer - 1
END IF
END PROCEDURE
Faezeh Seyedarabi www.faezeh.co.uk 5
Queues
A queue is very similar in principle to the operation of a stack, a queue is often called a FIFO stack (First In
First Out). E.g. normal queue, waiting to be served in a shop, where the first person in the queue is expected
to get served first and thus will be first person out.
Note: in this operation the data does not move, it is just the pointers that have been altered. We have the
start pointer (indicating to the head of the queue) and stop pointer (indicating to the end of the queue).
Start _pointer variable used to indicate the start of the queue.
Stop_pointer variables used to indicate the end of the queue.
Size variables that represents the size of the queue. (Data elements in the queue)
Data item in data to be pushed or popped.
QUEUE general name for the queue contained in memory.
QUEUE(pointer) subscripted variable representing the data at the current pointer position, i.e. an
identifier for the data on the queue.
Faezeh Seyedarabi www.faezeh.co.uk 6
Summery
What does a stack mean?
A stack is an area of memory set up as a temporary storage for data. A stack has a logical top and bottom,
which represent the places at which the beginning and end of the data can be found.
How might a stack be implemented?
Stacks are implemented by pointers which point to specific areas of memory.
What is a pointer?
A pointer is simply a data element that indicates the position of some other data element (e.g. the data
element that points to the top of the stack).
What does the term ‘push’ mean?
Push is the term used to indicate that data has been placed on the stack.
What does the term ‘pop’ mean?
Pop is the term used to indicate that data has been removed from the stack.
What is LIFO stack?
A LIFO stack is a Last-In-First-Out stack.
Faezeh Seyedarabi www.faezeh.co.uk 7
What is FIFO stack?
A FIFO is a First-In-First-Out stack.
What is an Overflow?
A queue or a stack may have a maximum size. An attempt to add a new element to a queue or stack which
is already full will result in an overflow error.
What is an Underflow?
An attempt to remove an item from an empty queue or stack will result in an underflow.
Faezeh Seyedarabi www.faezeh.co.uk 8
You might also like
- Data Structures and Algorithms in Swift: Implement Stacks, Queues, Dictionaries, and Lists in Your AppsFrom EverandData Structures and Algorithms in Swift: Implement Stacks, Queues, Dictionaries, and Lists in Your AppsNo ratings yet
- Stack: Presented By: Maritess Tolentino Maricris Z.Alemania Charmaine Delos TriosDocument22 pagesStack: Presented By: Maritess Tolentino Maricris Z.Alemania Charmaine Delos Triosjay-ar andradaNo ratings yet
- StackDocument16 pagesStackkktamang09No ratings yet
- What Is Stack Data Structure?Document3 pagesWhat Is Stack Data Structure?ذیشان چودھریNo ratings yet
- DS - Unit IDocument32 pagesDS - Unit IMuthu ManiyaNo ratings yet
- StackDocument11 pagesStackShreyansh MauryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 STACKDocument55 pagesChapter 4 STACKfitsum tekaNo ratings yet
- Printed StackDocument16 pagesPrinted StackRajNo ratings yet
- StackDocument18 pagesStackadiraihajaNo ratings yet
- Data Structures AssDocument11 pagesData Structures AssFiraol TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Stack FinalDocument17 pagesStack FinalAmar SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 - Dsa Lab FileDocument10 pagesExp 3 - Dsa Lab Fileparamita.chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Data Structure and Algorithms - StackDocument3 pagesData Structure and Algorithms - StackBharti PatelNo ratings yet
- Name Id NumberDocument65 pagesName Id NumberBiniyam TeketelNo ratings yet
- Stack Data StructureDocument7 pagesStack Data StructurehassaniftikharlapiNo ratings yet
- STACKDocument124 pagesSTACKRajNo ratings yet
- Abstract Data Types (Linked List and Stack)Document30 pagesAbstract Data Types (Linked List and Stack)MOSES ALLENNo ratings yet
- Stack: LIFO (Last in First Out)Document13 pagesStack: LIFO (Last in First Out)GAUTAMI UPPADANo ratings yet
- Stack Compiled NoteDocument9 pagesStack Compiled NotesyabseeshoesNo ratings yet
- 05 Stacks and Its ImplementationDocument36 pages05 Stacks and Its ImplementationHaseeb MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document32 pagesLecture 4NodirNo ratings yet
- DS Unit 2Document34 pagesDS Unit 2aaNo ratings yet
- Stack (Data Structure) : "Pushdown" Redirects Here. For The Strength Training Exercise, SeeDocument15 pagesStack (Data Structure) : "Pushdown" Redirects Here. For The Strength Training Exercise, Seegurpreetkr55No ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument67 pagesUnit 3 NotesRiya SuryavenshiNo ratings yet
- Stacks and QueuesDocument34 pagesStacks and QueuesgdskumarNo ratings yet
- StackDocument18 pagesStacknurulalomadorNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - StackDocument22 pagesUnit 3 - StackSarwesh MaharzanNo ratings yet
- Queues and StacksDocument20 pagesQueues and Stacksindu_singh_9No ratings yet
- Stacks Explained NewNotesDocument5 pagesStacks Explained NewNotesdfgfdfsdfNo ratings yet
- Stacks Data StructuresDocument42 pagesStacks Data StructuresAnand PanchalNo ratings yet
- DSA 10 QuestionDocument23 pagesDSA 10 Questionlandgesantosh240No ratings yet
- DSA Lecture - 2Document16 pagesDSA Lecture - 2pooja0letscrackitNo ratings yet
- Stack and Queue Presentation NewDocument48 pagesStack and Queue Presentation NewzelalemNo ratings yet
- 4505 StackDocument30 pages4505 Stackanejaajay1461No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Stack DataStructure in C++Document40 pagesLecture 6 Stack DataStructure in C++Simple lyrics100% (1)
- Chapter 4&5 Stack and QueueDocument18 pagesChapter 4&5 Stack and QueueZo ZoNo ratings yet
- Oop 13Document24 pagesOop 13usainbolt297No ratings yet
- Introduction of DdsuDocument29 pagesIntroduction of Ddsusatya kambleNo ratings yet
- CSC 382 Computer Lab 3Document2 pagesCSC 382 Computer Lab 3Class wrapperNo ratings yet
- Module 2 NotesDocument35 pagesModule 2 NotesHimanshu RanjanNo ratings yet
- DS Notes FinalDocument146 pagesDS Notes FinaltopmotivezzNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document23 pagesLec 2EshaalKhanNo ratings yet
- Chap4 Dsa (2017)Document30 pagesChap4 Dsa (2017)YOHANIS YADETANo ratings yet
- Unit 2 StackDocument73 pagesUnit 2 StackNone OtherNo ratings yet
- Stack and QueueDocument39 pagesStack and QueueHenschell CorolloNo ratings yet
- CH Datastructure StackDocument2 pagesCH Datastructure StackUma TNANo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document10 pagesLecture 4Ahmed SaadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 StacksDocument23 pagesUnit 2 Stackstestingupon1No ratings yet
- StackDocument54 pagesStackishwaryanambirajan7No ratings yet
- 05 StacksDocument23 pages05 StacksDann LaurteNo ratings yet
- StacksDocument27 pagesStacksRitesh JanaNo ratings yet
- Primitive Data Structures: 2. Types of Data Structure?Document8 pagesPrimitive Data Structures: 2. Types of Data Structure?Gautham SajuNo ratings yet
- StackDocument13 pagesStackKeywan MohammadNo ratings yet
- Datastructures 20-21 Fall L8Document25 pagesDatastructures 20-21 Fall L8hazha yosufNo ratings yet
- 005 - DS StackDocument65 pages005 - DS StackSSUET Course ModeratorNo ratings yet
- DSA - M03 - C01 - SLM - StacksDocument40 pagesDSA - M03 - C01 - SLM - StacksZaisha RomaniaNo ratings yet
- FINALS CC4 ReviewerDocument15 pagesFINALS CC4 ReviewerMarc Joel JunioNo ratings yet
- UNIT III Data Structures OUDocument34 pagesUNIT III Data Structures OUjason.orchard.5341No ratings yet
- Chinmoy Dinda - 50Document7 pagesChinmoy Dinda - 50Chinmoy DindaNo ratings yet
- Arrays: - ArrayDocument157 pagesArrays: - ArrayVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Programming in C++ - Module 05Document12 pagesProgramming in C++ - Module 05Pandu PatilNo ratings yet
- CTSD Home Assignment-6: NAME: S Adarsh ID-NO: 2100010062Document19 pagesCTSD Home Assignment-6: NAME: S Adarsh ID-NO: 2100010062praveen tummalacharlaNo ratings yet
- M251 Meeting 5Document60 pagesM251 Meeting 5ray hajjarNo ratings yet
- C++ STL: CSCI 3110Document30 pagesC++ STL: CSCI 3110Suganya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- C Gate QuestionsDocument12 pagesC Gate QuestionsSherril VincentNo ratings yet
- Class XI (As Per CBSE Board) : Computer ScienceDocument18 pagesClass XI (As Per CBSE Board) : Computer ScienceRajkumariNo ratings yet
- 3 CDocument143 pages3 CNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- CPP Template Generic A3Document9 pagesCPP Template Generic A3semabayNo ratings yet
- Repliconlog (Sync Issue)Document91 pagesRepliconlog (Sync Issue)yuvaraj91No ratings yet
- What Is A Stack?: Some Key Points Related To StackDocument23 pagesWhat Is A Stack?: Some Key Points Related To StackKamran RaziNo ratings yet
- Akmal Maulana - X3B - PSD - TUGAS BAB 1Document24 pagesAkmal Maulana - X3B - PSD - TUGAS BAB 1Ichwan MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Rhel7 - JsonDocument18 pagesRhel7 - JsonRanjit Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Java MCQDocument13 pagesJava MCQAlan Joe100% (1)
- Pointers in C PresentationDocument105 pagesPointers in C PresentationManish Gurjar100% (1)
- Java Inheritance. Possible Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesJava Inheritance. Possible Questions and AnswersKartheeban KamatchiNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Topic: QueueDocument34 pagesData Structures Topic: QueueRahna RwpcNo ratings yet
- Generic Programming in JavaDocument15 pagesGeneric Programming in JavaNavin sNo ratings yet
- Python Programming ExamplesDocument23 pagesPython Programming ExamplesAbu Al SaidNo ratings yet
- Generics in JavaDocument12 pagesGenerics in JavaVincentNo ratings yet
- Enum and ConstantsDocument6 pagesEnum and ConstantsJobin SebastianNo ratings yet
- Algorithms and Data Structures in C++ PDFDocument36 pagesAlgorithms and Data Structures in C++ PDFshervlad100% (1)
- Applications of Stack:: Storing Function CallsDocument5 pagesApplications of Stack:: Storing Function CallsAzeez OluwafemiNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum StackDocument3 pagesLaporan Praktikum StackAnis Nurul HanifahNo ratings yet
- Coding Test 1 1: Array GameDocument39 pagesCoding Test 1 1: Array GameGauravNo ratings yet
- Stacks and QueuesDocument18 pagesStacks and QueuesAbdullah TahirNo ratings yet
- Week 2 C++ Linked Lists, Stacks and Queues PDFDocument36 pagesWeek 2 C++ Linked Lists, Stacks and Queues PDFJendaeNo ratings yet
- DS Through JAVA Lab Manual-BSCDocument31 pagesDS Through JAVA Lab Manual-BSCBeta12 SinghNo ratings yet
- 2.2.1 Introduction To QueuesDocument12 pages2.2.1 Introduction To QueuesSomesh RamanNo ratings yet
- The Punjab College of Commerce and Computer Sciences HaroonabadDocument2 pagesThe Punjab College of Commerce and Computer Sciences HaroonabadShahid JamalNo ratings yet