Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands?
Uploaded by
durga411Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands?
Uploaded by
durga411Copyright:
Available Formats
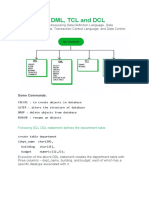
1. What are the difference between DDL, DML and DCL commands? DDL is Data Definition Language statements.
Some examples: CREATE - to create objects in the database ALTER - alters the structure of the database DROP - delete objects from the database TRUNCATE - remove all records from a table, including all spaces allocated for the records are removed COMMENT - add comments to the data dictionary GRANT - gives user's access privileges to database REVOKE - withdraw access privileges given with the GRANT command DML is Data Manipulation Language statements. Some examples: SELECT - retrieve data from the a database INSERT - insert data into a table UPDATE - updates existing data within a table DELETE - deletes all records from a table, the space for the records remain CALL - call a PL/SQL or Java subprogram EXPLAIN PLAN - explain access path to data LOCK TABLE - control concurrency DCL is Data Control Language statements. Some examples: COMMIT - save work done SAVEPOINT - identify a point in a transaction to which you can later roll back ROLLBACK - restore database to original since the last COMMIT SET TRANSACTION - Change transaction options like what rollback segment to use
You might also like
- Ejercicio (3) Junio15 PDFDocument3 pagesEjercicio (3) Junio15 PDFCesar IsazaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands?Document1 pageWhat Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands?azizNo ratings yet
- MySQL What Is DDL, DML and DCLDocument6 pagesMySQL What Is DDL, DML and DCLyashada baneNo ratings yet
- What Are The Difference Between SQLDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Difference Between SQLMuralyNo ratings yet
- What Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands - Oracle FAQDocument1 pageWhat Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands - Oracle FAQRohan JainNo ratings yet
- SQL (Structured Query Language) : DatabaseDocument6 pagesSQL (Structured Query Language) : DatabaseDaniel EssienNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument1 pageDBMScompu_xNo ratings yet
- DML (Data Manipulation Language) :: SQL Commands Are Divided Into Four Categories As BelowDocument2 pagesDML (Data Manipulation Language) :: SQL Commands Are Divided Into Four Categories As BelowKarthick SagaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands - Oracle FAQDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands - Oracle FAQSajid UmarNo ratings yet
- 4-Simple SQL QueriesDocument2 pages4-Simple SQL QueriesSanNo ratings yet
- DDL DML DCLDocument3 pagesDDL DML DCLSaravana Kumar NarendranNo ratings yet
- SQL - DDL, DQL, DML, DCL and TCL Commands: - Transaction Control Language. So We Will See in Detail About TCL As WellDocument2 pagesSQL - DDL, DQL, DML, DCL and TCL Commands: - Transaction Control Language. So We Will See in Detail About TCL As WellDevinder KaurNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument2 pagesDBMSvr0046No ratings yet
- Definition of Components of SQLDocument4 pagesDefinition of Components of SQLvaishali sulkhlanNo ratings yet
- DBM S ObjectiveDocument1 pageDBM S ObjectiveRajesh VhadlureNo ratings yet
- Aim: To Implement Various DDL, DML Commands and Constraints TheoryDocument2 pagesAim: To Implement Various DDL, DML Commands and Constraints TheorySushant WaghNo ratings yet
- Database LanguagesDocument3 pagesDatabase LanguagesHumera Gull100% (1)
- SQL - DDL, DML, TCL and DCLDocument3 pagesSQL - DDL, DML, TCL and DCLShobha Kumari ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- What Is DDL in Mysql?: - S.ManojDocument8 pagesWhat Is DDL in Mysql?: - S.ManojManoj SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems (It 311) : Department of Information and TechnologyDocument60 pagesDatabase Management Systems (It 311) : Department of Information and TechnologyShahid afridi saikiaNo ratings yet
- Practical Examination Assignment OF SQL Sublanguages and FunctionsDocument6 pagesPractical Examination Assignment OF SQL Sublanguages and FunctionsSajjad QureshiNo ratings yet
- SQL Commant A1Document13 pagesSQL Commant A1stan31878No ratings yet
- Introduction To SQLDocument17 pagesIntroduction To SQLPatrick JacintoNo ratings yet
- SQL Data Definition Language PDFDocument6 pagesSQL Data Definition Language PDFRohini AI&DSNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-3 NotesDocument19 pagesDBMS Unit-3 NotesDvrao ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Reading Material Experiment 1.1Document5 pagesReading Material Experiment 1.1AkhilNo ratings yet
- SQL QueriesDocument62 pagesSQL Queriesmugeshmsd5No ratings yet
- SQL Short Notes PDFDocument9 pagesSQL Short Notes PDFCare CureNo ratings yet
- What Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands - Oracle FAQDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands - Oracle FAQatulsinha12No ratings yet
- Introduction To SQLDocument3 pagesIntroduction To SQLspiharsh100% (10)
- Unit1pptx 2020 07 08 20 04 48Document63 pagesUnit1pptx 2020 07 08 20 04 487094 HEMEET VAKHARIANo ratings yet
- SQL (Structured Query Language)Document9 pagesSQL (Structured Query Language)AnuNo ratings yet
- What Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands - Oracle FAQDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Difference Between DDL, DML and DCL Commands - Oracle FAQAnonymous 293DQYNo ratings yet
- SQL (Structured Query LanguDocument16 pagesSQL (Structured Query Languadarsh sarafNo ratings yet
- Oracle Apps Technical DayDocument4 pagesOracle Apps Technical DaySekharBynaNo ratings yet
- D C S & E CSP 249 Dbms LAB File: Epartment of Omputer Cience NgineeringDocument15 pagesD C S & E CSP 249 Dbms LAB File: Epartment of Omputer Cience NgineeringLokesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Structured Query Language 2021 FinalDocument20 pagesGroup 6 Structured Query Language 2021 FinalMarian NyamukondaNo ratings yet
- SQL CommandsDocument18 pagesSQL CommandsShajirNo ratings yet
- SQL Commands - DML, DDL, DCL, TCL, DQL With Query ExampleDocument9 pagesSQL Commands - DML, DDL, DCL, TCL, DQL With Query ExampletitobesaleelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Structured Query Language (SQL)Document1 pageIntroduction To Structured Query Language (SQL)ashwani5667No ratings yet
- Database ProjectDocument10 pagesDatabase ProjectAbdulazeez RaboNo ratings yet
- Imp SQL CommandsDocument9 pagesImp SQL CommandsAmisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sld-7-Modeling LanguagesDocument7 pagesSld-7-Modeling LanguagesMd SoyalNo ratings yet
- Data Definition Language: CREATE StatementsDocument2 pagesData Definition Language: CREATE StatementsAkhil MadavanNo ratings yet
- 2k19-SWE-16 AmaanullahDocument11 pages2k19-SWE-16 AmaanullahAmaan LaghariNo ratings yet
- SQL ContinuedDocument13 pagesSQL Continuedradika thapaNo ratings yet
- The Relational ModelDocument84 pagesThe Relational ModelMani Chandra TejaNo ratings yet
- SQL - DDL, DQL, DML, DCL and TCL Commands - GeeksforGeeksDocument3 pagesSQL - DDL, DQL, DML, DCL and TCL Commands - GeeksforGeeksisc_fjmvNo ratings yet
- Commands:: A Complete GuideDocument9 pagesCommands:: A Complete GuideJ. Karthick Myilvahanan CSBSNo ratings yet
- SQL CommandsDocument18 pagesSQL CommandsSiri Yadav 18-521No ratings yet
- Sql/MysqlDocument15 pagesSql/MysqlSandeep BhardwajNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument9 pagesDBMSOperation ResearchNo ratings yet
- DMS CH2 2020-21Document28 pagesDMS CH2 2020-21Sanskruti ladNo ratings yet
- MySQL Background Theory 12Document1 pageMySQL Background Theory 12Hi HloNo ratings yet
- Structured Query LanguageDocument2 pagesStructured Query LanguageRositaNo ratings yet
- (Unit 3) Introduction To SQL: SQL (Structured Query Language)Document30 pages(Unit 3) Introduction To SQL: SQL (Structured Query Language)devdattaghorpade1No ratings yet
- Document SQLDocument3 pagesDocument SQLbarunakumariNo ratings yet
- Experiment Title-1: Introduction To DBMS, RDBMS, ORACLE, Basic SQL CommandsDocument7 pagesExperiment Title-1: Introduction To DBMS, RDBMS, ORACLE, Basic SQL CommandsShreyansh RajNo ratings yet
- DB2 9 for z/OS Database Administration: Certification Study GuideFrom EverandDB2 9 for z/OS Database Administration: Certification Study GuideNo ratings yet