Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C Data Types
C Data Types
Uploaded by
ashi_vidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C Data Types
C Data Types
Uploaded by
ashi_vidCopyright:
Available Formats
DATA TYPES IN C Data types are the storage representation of the variables used in the program.
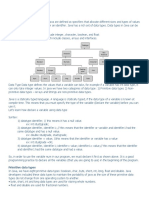
Use of data types specifies no. of bytes taken by any variable in the memory. In C there are 4 basic types of data types 1. 2. 3. 4. Primitive Data type Non-Primitive Data type User-Defined Data type Empty Data Type
Primitive Data Type It is also known as Primary data type. All C compilers support 4 fundamental data types namely; integer, character, floating point & double precision floating point. Integer types Integers are whole nos. with a range of value supported by a particular machine. Generally, integer occupies one word of storage. It takes 2 bytes. If we use 16-bit word length the size of integer value is limited to the range -32768 to 32767. Similarly, a 32-bit word length can store an integer ranging from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. Character types A single character can be defined as a character type data. Characters are usually stored in 8-bits of internal storage. Characters have values from -128 to 127 or from 0 to 255. Floating Point types Floating point numbers are stored in 4 bytes or 32-bits, with 6 digits of precisions. Floating point numbers are defined in C by the keyword float. A double data type number uses 64-bits giving a precision of 14-bits. Non Primitive Data Type These are also known as Derived data type. It consists of arrays, structures and unions. Arrays Array is actually a collection of similar data type and memory for an array is allocated on contiguous spaces. Structures Structure is a collection of fields in which the fields may be same or of different types.
User-Defined Data Types C support user-defined data types. Once a user-defined type has been established, then new variables, array, structures etc. can be declared in the terms of this new data type. In C language user-defined data types are: typedef & enum. typedef typedef is an abbreviation used for Type Definition. Its purpose is to redefine the name of an existing data type. This can be later used to declare variables. Its general form is: typedef standard-datatype userdefined-datatype. Ex: (i) typedef int age; int x; age p,q,r,s; Here, all the variables are holding integer value but age helps us to understand that these 4 variables will hold age. It helps users debugging the program. (ii) struct student { char name [30]; int roll_no; float percent; }; struct student s; Using typedef: struct student { char name [30]; int roll_no; float percent; }; typedef struct student STU; STU s1, s2; enum The enumerated data type gives us an opportunity to invent our own data type and define what values the variables of this data type can take. Its general form is: enum datatype-name {val1,val2,..,valn}; Ex:(i) enum weekdays {Sunday, Monday, Thursday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday}; weekdays x, y;
(ii) enum marks { gradeA=1, gradeB=2, gradeC=3 }; enum marks s1, s2; The values declared by enum are ordinal nos. Ordinal values starts from zero. Empty Data Type The keyword void can be used as a type specifier, when defining a function that does not return anything. The keyword void is the example of empty data type. Ex: void main ()
You might also like
- PERL - CompleteDocument302 pagesPERL - CompleteAngshusmita Baruah SegraNo ratings yet
- CMake Tutorial 8feb2012Document148 pagesCMake Tutorial 8feb2012kaosadNo ratings yet
- Programming in C by Kute T. B.Document116 pagesProgramming in C by Kute T. B.khan.sakeena83% (12)
- SWI Prolog 6.0.2Document439 pagesSWI Prolog 6.0.2daniel_guizaNo ratings yet
- SAPBW Technical Specification TemplateDocument30 pagesSAPBW Technical Specification TemplateAnilNo ratings yet
- Data Types in CDocument19 pagesData Types in CEr. Sunali Sharma100% (1)
- Different Data Types Used in C LanguageDocument6 pagesDifferent Data Types Used in C LanguagegunapalshettyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Data TypesDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Data TypesP.S. Mithul SouravNo ratings yet
- BIOMETRICS - A Seminar ReportDocument12 pagesBIOMETRICS - A Seminar ReportHemant MahajanNo ratings yet
- Data Types: in C ProgrammingDocument11 pagesData Types: in C ProgrammingHUB COLLECTIONNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Data TypesDocument6 pagesChapter 8 Data TypesVansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- C Notes 2-1Document28 pagesC Notes 2-1Rohit HegdeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Data Types: A Variable Is An Object or Element and It Is Allowed Change During The Execution of The ProgramDocument6 pagesChapter-8 Data Types: A Variable Is An Object or Element and It Is Allowed Change During The Execution of The ProgramYash WanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Data Types: IntroductionDocument6 pagesChapter-8 Data Types: IntroductionAdityaNo ratings yet
- Programming in CDocument27 pagesProgramming in Ccreative founderNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 Variable DatatypesDocument19 pagesLec 5 Variable DatatypesMD. ShamsuddohaNo ratings yet
- BCA C ProgrammingDocument103 pagesBCA C ProgrammingGiRiJi GamingNo ratings yet
- Data Classification PresentationDocument29 pagesData Classification PresentationmwanafalsafamNo ratings yet
- Data Types NotesDocument9 pagesData Types NotesSanthanaNo ratings yet
- Data Types in C++Document11 pagesData Types in C++Poonam PoonamNo ratings yet
- Data Types 20210513173436Document3 pagesData Types 20210513173436Fainox TesterNo ratings yet
- Different Data Types in C'Document20 pagesDifferent Data Types in C'Manish MaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument26 pagesChapter TwoAbenezer TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming With JavaDocument24 pagesObject Oriented Programming With JavarajamaheshNo ratings yet
- PPT5 - Data Types in C++Document26 pagesPPT5 - Data Types in C++Meena Preethi B100% (1)
- Data StructuresDocument59 pagesData StructuresbinalamitNo ratings yet
- Variables and DatatypesDocument30 pagesVariables and Datatypesskill courseNo ratings yet
- Principles of Programming Languages: UNIT II - Intro To Programming Concepts Lecture 7 - Data TypesDocument92 pagesPrinciples of Programming Languages: UNIT II - Intro To Programming Concepts Lecture 7 - Data TypesveningstonNo ratings yet
- JAVADocument51 pagesJAVAproject firstNo ratings yet
- CSE PresentationDocument13 pagesCSE PresentationTR SalmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Building Blocks of The LanguageDocument35 pagesChapter 2 Building Blocks of The Languagexitekol233No ratings yet
- C Language FundamentalsDocument16 pagesC Language FundamentalsSatNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER MIDTERMS NotesDocument10 pagesCOMPUTER MIDTERMS NotesLaarni De VeraNo ratings yet
- C DatatypesDocument21 pagesC Datatypesalfurquan90No ratings yet
- CSE 211: Data Structures Lecture Notes I: Ender Ozcan, Şebnem BaydereDocument11 pagesCSE 211: Data Structures Lecture Notes I: Ender Ozcan, Şebnem Baydereapi-3705606No ratings yet
- Data TypeDocument11 pagesData Typesingh.00vishwajeetNo ratings yet
- Header Files: #IncludeDocument15 pagesHeader Files: #Includeaikiplay01No ratings yet
- Module03 ClassNotesDocument26 pagesModule03 ClassNotesGeay PeterNo ratings yet
- ModifierDocument13 pagesModifierHARSH KHATRINo ratings yet
- COMS11500: Introduction To CDocument15 pagesCOMS11500: Introduction To CRodrigo SilvaNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To C++Document9 pages1.introduction To C++KAMBAULAYA NKANDANo ratings yet
- Variables of JavaDocument28 pagesVariables of JavaAxel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - CH 3. StructuresDocument17 pagesUnit 3 - CH 3. StructuresManjunatha H RNo ratings yet
- C++ BasicsDocument81 pagesC++ BasicsAjay PariharNo ratings yet
- Data TypeDocument14 pagesData TypejabbarbookeditorNo ratings yet
- Apply OOPL SkillsDocument72 pagesApply OOPL SkillsmetadelNo ratings yet
- Data Types in CDocument8 pagesData Types in CPriya VermaNo ratings yet
- DatA TypesDocument6 pagesDatA TypesMohd armanNo ratings yet
- Data Types in CDocument3 pagesData Types in CSwapnil SonarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Data Types Variables and ConstantsDocument23 pagesChapter 4 Data Types Variables and ConstantsAllyson AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Datatypes in PythonDocument6 pagesDatatypes in Pythonarvd examsectionNo ratings yet
- OPPS With C++Document125 pagesOPPS With C++Ranjithkumar Tamilselvam100% (1)
- C Session2Document29 pagesC Session2YogiNo ratings yet
- Algoritma & Pemrograman I: Kuliah Ke X Pokok Bahasan: Typedef, Enum, UnionDocument10 pagesAlgoritma & Pemrograman I: Kuliah Ke X Pokok Bahasan: Typedef, Enum, UnionsellyimandaNo ratings yet
- Programming Fundamentals: (PRACTICAL#02)Document18 pagesProgramming Fundamentals: (PRACTICAL#02)AliMuhammad LalaniNo ratings yet
- Week2 CM MDL CP1212Document13 pagesWeek2 CM MDL CP1212Kassandra GlorNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Engineering Faculty of Engineering Somali National University Course Name: Elementary Programing Concept Course Code: EPC 2309Document8 pagesElectromechanical Engineering Faculty of Engineering Somali National University Course Name: Elementary Programing Concept Course Code: EPC 2309kadar AhmedNo ratings yet
- DatatypesDocument17 pagesDatatypestomasinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C Program Assignment FsecDocument3 pagesIntroduction To C Program Assignment FsecAkiNo ratings yet
- C BookDocument9 pagesC BookTexansh DixitNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document28 pagesUnit 5dawnglianiNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument107 pagesUnit IIapi-3844028No ratings yet
- C BasicsDocument32 pagesC BasicsKunda Basetty ThrishaNo ratings yet
- String HandlingDocument70 pagesString Handlingsonu1070No ratings yet
- Shivani Varshney/RCET/Programming With CDocument62 pagesShivani Varshney/RCET/Programming With Csonu1070No ratings yet
- Conditional Constructs: Shivani Varshney/RCET/Programming With CDocument86 pagesConditional Constructs: Shivani Varshney/RCET/Programming With Csonu1070No ratings yet
- Structure of A C ProgramDocument2 pagesStructure of A C Programsonu1070No ratings yet
- STMT TypesDocument1 pageSTMT Typessonu1070No ratings yet
- Question Bank ModifiedDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank Modifiedsonu1070No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 01Document31 pagesExperiment No. 01sonu1070No ratings yet
- Data Files: Can Be Created, Updated, and Processed by C Programs Are Used For Permanent Storage of Large Amounts of DataDocument47 pagesData Files: Can Be Created, Updated, and Processed by C Programs Are Used For Permanent Storage of Large Amounts of Datasonu1070100% (1)
- Final C ManualDocument186 pagesFinal C Manualsonu1070100% (1)
- C OperatorsDocument4 pagesC Operatorssonu1070No ratings yet
- Computer Programming Using C & Numerical MethodsDocument1 pageComputer Programming Using C & Numerical MethodsSanjana XavierNo ratings yet
- QB - 2018 - EEM303 Soln (Updated 2.10.18) PDFDocument40 pagesQB - 2018 - EEM303 Soln (Updated 2.10.18) PDFMiNo ratings yet
- SQL Select CommandDocument24 pagesSQL Select CommandShraddha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Analysis and Design - Part2Document40 pagesObject Oriented Analysis and Design - Part2Kỉ Nguyên Hủy DiệtNo ratings yet
- Cns Course FileDocument14 pagesCns Course FilePhani Pitchika100% (1)
- CM304Document18 pagesCM304api-3849444No ratings yet
- VB Msgbox - MessageBox Function in Visual Basic 6Document3 pagesVB Msgbox - MessageBox Function in Visual Basic 6Gerald Toro DomenackNo ratings yet
- SDK InstructionDocument12 pagesSDK InstructionMohd Kamal0% (1)
- cs6001 C# Unit 2Document69 pagescs6001 C# Unit 2Mani DkmNo ratings yet
- CLAD Sample Exam-1Document20 pagesCLAD Sample Exam-1Jie Wei100% (1)
- DKMDocument4 pagesDKMDeepak MadheshiyaNo ratings yet
- R20 I B.Tech. CSE SyllabusDocument45 pagesR20 I B.Tech. CSE Syllabusvenkata sivaiahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers and Programming in CDocument1 pageIntroduction To Computers and Programming in CSanjay GomastaNo ratings yet
- Dac Eandc QB Question Bank PHP QuesDocument15 pagesDac Eandc QB Question Bank PHP Quesnisha sharmaNo ratings yet
- 200 Objective-Type Questions RameshDocument32 pages200 Objective-Type Questions RameshAnkurTyagiNo ratings yet
- Nikita Sagar, A.P (CSE Deptt.) Unit-3 Introduction Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument8 pagesNikita Sagar, A.P (CSE Deptt.) Unit-3 Introduction Object Oriented ProgrammingJagat RawatNo ratings yet
- 2.tutorial 1 - Implementation of A USB Based PIC-To-PC CommunicationDocument30 pages2.tutorial 1 - Implementation of A USB Based PIC-To-PC CommunicationMurat Şen100% (1)
- CSCI 2240 Program #1: Math QuizDocument3 pagesCSCI 2240 Program #1: Math Quizmueed6074No ratings yet
- SamDrawV3 3-User Manual PDFDocument414 pagesSamDrawV3 3-User Manual PDFMarcos Luiz AlvesNo ratings yet
- Syllabus-BCA Core Course-CC1-CC14Document30 pagesSyllabus-BCA Core Course-CC1-CC14Harsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Database Examples Installation Guide PDFDocument11 pagesDatabase Examples Installation Guide PDFHarish NaikNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computer and Programming in C: (CSE - 101 F)Document339 pagesFundamentals of Computer and Programming in C: (CSE - 101 F)Himanshu SukhejaNo ratings yet
- Standard C Iostreams and Locales Advanced Programmers Guide and ReferenceDocument19 pagesStandard C Iostreams and Locales Advanced Programmers Guide and ReferenceSourav Paul0% (2)
- KUKA AppendixDocument43 pagesKUKA AppendixAlexandru Ionut Toma100% (1)
- List of NOSQL DatabaseDocument23 pagesList of NOSQL DatabasePinkykaniNo ratings yet