Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cumene A
Cumene A
Uploaded by
Gary Kiel Palacios EspinozaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cumene A
Cumene A
Uploaded by
Gary Kiel Palacios EspinozaCopyright:
Available Formats
Material Balances Design Problem Cumene Production
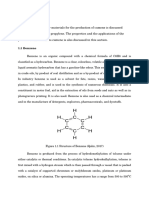
Background Cumene (isopropyl benzene) is produced by reacting propylene and benzene over an acid catalyst. Cumene may be used to increase the octane in gasoline, but its primary use is as a feedstock for manufacturing phenol and acetone. The plant where you are employed has been buying cumene to produce phenol. Management is considering manufacturing cumene rather than purchasing it to increase profits. Someone has made a preliminary sketch for such a process and has submitted to the engineering department for consideration. Your group is assigned the problem of evaluating the sketch and recommending improvements in the preliminary design. Cumene Production Reactions The reactions for cumene production from benzene and propylene are as follows: C3H6 + propylene C6H6 benzene C6H5-C3H7 cumene
C3H6 + propylene
C6H5-C3H7 cumene
C3H7-C6H4-C3H7 diisopropyl benzene (DIPB)
The best technology for cumene production is a catalytic process that is optimized at 350C and 25 atm. pressure. The benzene is kept in excess to limit the amount of DIPB product. Process Description The reactants are fed as liquids from their respective storage tanks. After being pumped up to the required pressure dictated by catalyst operating conditions, the reactants are mixed, vaporized and heated up to the reactor operating temperature. The catalyst converts the reactants to the desired and undesired products according to the reactions listed above. The molar feed ratio is 2:1 benzene to propylene; propylene conversion is 99%; the product molar selectivity ratio is 31:1 cumene to DIPB. The product gases are cooled to 40C at 25 atm. pressure to condense essentially all of the cumene, DIPB, and unreacted benzene to a liquid. The unreacted propylene and a propane impurity are separated from the liquid and are used as fuel gas. The liquid stream is sent to two distillation towers. The first distillation tower separates benzene from cumene and DIPB. The benzene purity level is 98.1 mole%. We have no chemical market for this stream and plan to sell it as unleaded gasoline. The second distillation tower separates cumene from DIPB. The cumene is 99.9 mole% pure. The DIPB stream will be sold as fuel oil. A sketch of the process is attached. The reaction units and process streams are described in the tables.
Table 1. Description of Process Units Symbol Name Comments V-201 R-201 Vaporizer Reactor Liquid feeds are vaporized and heated for reactor Vapors are reacted over catalyst; temperature 350C; pressure 25 atm.; 99% propylene conversion per pass; 31/1 cumene/DIPB molar selectivity Vapor is cooled to 40C at 25 atm. pressure, separating essentially all of the benzene, cumene and DIPB as a liquid from propylene and propane gases Overhead stream contains 98.1 mole% benzene, balance cumene; bottoms stream contains cumene and DIPB Overhead stream contains 99.9 mole% cumene; bottoms stream contains pure DIPB
S-201
Separator
T-201 T-202
Distillation Tower No. 1 Distillation Tower No. 2
Table 2. Description of Process Streams Stream Number Comments 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 benzene>99.9 mole% pure; liquid feed 95 mole% propylene; 5 mole% propane; liquid feed 2/1 benzene/propylene molar feed ratio 99% propylene conversion; 31/1 cumene/DIPB molar selectivity propylene + propane only 0 mole% propylene + propane 98.1 mole% benzene purity, balance cumene, sold as gasoline 0 mole% benzene 99.9 mole% cumene, balance DIPB; 100,000 tons/year production 100 mole% DIPB; sold as fuel oil
Problem Your group needs to optimize the cumene manufacturing process to make maximum profit. Your plant currently purchases 100,000 tons of cumene per year to make phenol. Calculate material balances for the process in the sketch. Compute the value of the products and the cost for raw materials. Feedstock costs and product values are listed in Table 3. The difference between the product value and raw material costs is gross profit. We do not yet know how to calculate operating expenses for different process configurations so that operating expense will be ignored in these calculations.
3 Table 3. Prices for Feedstocks and Process Streams Chemical or Fuel benzene feed, >99.9% propylene feed, 95 mole% propylene, 5 mole% propane cumene, >99.8 mole% fuel gas gasoline fuel oil
Price $0.90/gallon $0.095/lb $0.21/lb $0.080/lb $0.60/gallon $0.50/gallon
Your assignment is to propose process modifications that increase gross profit. constrained to operating the same catalyst with the same selectivity. Design Groups
You are
This is a group activity that will produce a group grade. You are to form your own 3 or 4 person group. Larger or smaller groups are not acceptable. Individuals who do not form groups will be assigned to one. Past experience suggests that students are happier in student-formed groups than in instructor-assigned groups. Design Report Design groups are to submit a single report signed by each participating member . Groups should follow department guidelines for design reports, which are distributed separately. Material balance calculations should be made by hand and be attached as an appendix to the typed report. Repetitive calculations made by computer (spreadsheet or programming) should be accompanied by one representative hand calculation. Report Grading Grading will be based on both content (2/3) and writing style (1/3). Everyone who signs the report as an author will receive the same grade. Individuals who do not contribute to the project should not be included as authors. Date Due Design reports are due at 3:00pm on December 6, 1995.
E.L. Kugler November 12, 1995
You might also like
- Acetylene, the Principles of Its Generation and Use A Practical Handbook on the Production, Purification, and Subsequent Treatment of Acetylene for the Development of Light, Heat, and PowerFrom EverandAcetylene, the Principles of Its Generation and Use A Practical Handbook on the Production, Purification, and Subsequent Treatment of Acetylene for the Development of Light, Heat, and PowerNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument55 pagesFluidsdanena88No ratings yet
- Latest Edited 1 PDFDocument95 pagesLatest Edited 1 PDFDiv SavaliyaNo ratings yet
- ButadineDocument68 pagesButadineraihonaNo ratings yet
- Presentation CumeneDocument39 pagesPresentation Cumeneممدوح الرويليNo ratings yet
- Improve Contaminant Control in Ethylene Production: Hpimpact TechnologyDocument6 pagesImprove Contaminant Control in Ethylene Production: Hpimpact TechnologyVenkatesan DevendranNo ratings yet
- Ethylbenzene ProductionDocument30 pagesEthylbenzene ProductionUum LukmanNo ratings yet
- Cumene ProductionDocument9 pagesCumene ProductionDrVedprakash MishraNo ratings yet
- Methyl Methacrylate Plant CostDocument3 pagesMethyl Methacrylate Plant CostIntratec Solutions50% (2)
- Feasibility Study of Cumene ProductionDocument4 pagesFeasibility Study of Cumene ProductionIntratec SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Project Group 9 CC01 PDFDocument24 pagesProject Group 9 CC01 PDFHuy NinhNo ratings yet
- Cumene Energy 2520balanceDocument13 pagesCumene Energy 2520balanceismailchoughule50% (2)
- AIChEJournalVolume57issue32011doi10 1002 - Aic 12289WilliamL Luyben - Designandcontroloftheethylbenzeneprocess1 PDFDocument16 pagesAIChEJournalVolume57issue32011doi10 1002 - Aic 12289WilliamL Luyben - Designandcontroloftheethylbenzeneprocess1 PDFTobias De SomerNo ratings yet
- Cumene ProductionDocument26 pagesCumene ProductionAMOGH JHANWARNo ratings yet
- Aceton PlantDocument25 pagesAceton PlantMaryam AlqasimyNo ratings yet
- Final Interim Report Myza 25034Document18 pagesFinal Interim Report Myza 25034hasnizaNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Ethylbenzene To StyreneDocument5 pagesKinetics of Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Ethylbenzene To Styreneibrahim3318No ratings yet
- Final Project2Document135 pagesFinal Project2Mr NU KHANNo ratings yet
- Presentation CumeneDocument39 pagesPresentation CumeneBis ChemNo ratings yet
- Phenol PlantDocument33 pagesPhenol PlantrakeshNo ratings yet
- Advances in Biofuels Production, Optimization and ApplicationsFrom EverandAdvances in Biofuels Production, Optimization and ApplicationsMejdi JeguirimNo ratings yet
- International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State: Propylene (Propene)From EverandInternational Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid State: Propylene (Propene)No ratings yet
- Toluene Toluene Toluene Hydrogen Chromium PlatinumDocument6 pagesToluene Toluene Toluene Hydrogen Chromium PlatinumBerry101No ratings yet
- CumeneDocument21 pagesCumeneDiv SavaliyaNo ratings yet
- Cumene Production Robert SchmidtDocument14 pagesCumene Production Robert SchmidtVatsalNo ratings yet
- Project 2 CumeneDocument9 pagesProject 2 CumeneUmar Alijandro50% (2)
- CDtech CumeneDocument2 pagesCDtech CumeneAnusha RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- Ethylbenzene MSDS PDFDocument6 pagesEthylbenzene MSDS PDFyuanitaNo ratings yet
- Hydrodealkylation SimulationDocument8 pagesHydrodealkylation SimulationSchaieraNo ratings yet
- Cumene Methods 2520of ProductionDocument4 pagesCumene Methods 2520of ProductionYunardi YusufNo ratings yet
- Cumene Process, Prod - CBIDocument2 pagesCumene Process, Prod - CBIChris LindseyNo ratings yet
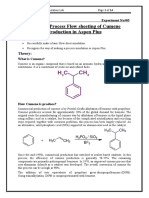
- Task: 01 Process Flow Sheeting of Cumene Production in Aspen PlusDocument14 pagesTask: 01 Process Flow Sheeting of Cumene Production in Aspen PlusAsma ChNo ratings yet
- Integrate Ethyl Benzene Production With An Olefins Plant, HC Processing, 1999, Pg77-88Document8 pagesIntegrate Ethyl Benzene Production With An Olefins Plant, HC Processing, 1999, Pg77-88ypzoNo ratings yet
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument4 pagesKing Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Department of Chemical EngineeringRosmery AruquipaNo ratings yet
- CumeneDocument5 pagesCumeneNasmiyeth Rodriguez VittaNo ratings yet
- Cumene Production Process DescriptionDocument1 pageCumene Production Process DescriptionAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Cumene Property ValueDocument4 pagesPhysical Properties of Cumene Property ValueC.Çağrı Yekeler50% (2)
- Side ReactionsDocument22 pagesSide ReactionsAna Mariel VenturaNo ratings yet
- Cumene Production PlantDocument6 pagesCumene Production PlantMertcan AslanNo ratings yet
- Cumene212 PDFDocument10 pagesCumene212 PDFtiaradyepiNo ratings yet
- It1.Introduction & History:-: 1.1 Introduction To Cumene:-StructureDocument12 pagesIt1.Introduction & History:-: 1.1 Introduction To Cumene:-StructureJaymin GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Designandcontrolofthecumeneprocess PDFDocument24 pagesDesignandcontrolofthecumeneprocess PDFTobias De Somer100% (1)
- Cumene PhenolDocument4 pagesCumene PhenolSushant SinhaNo ratings yet
- MEK in School SecondDocument13 pagesMEK in School Secondifiok100% (1)
- Viewcontent11 PDFDocument54 pagesViewcontent11 PDFEr Mayur PatilNo ratings yet
- Butene-1: Trans-2-Butene, Isobutylene, and ButadieneDocument1 pageButene-1: Trans-2-Butene, Isobutylene, and ButadieneYESIKBMARTIN100% (1)
- Cumene Process DesignDocument16 pagesCumene Process Designendang dian lestariNo ratings yet
- Styrene From Ethane and BenzeneDocument6 pagesStyrene From Ethane and BenzeneAmy Puah100% (2)
- تعديلات المشروعDocument114 pagesتعديلات المشروعSadam FirasNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Report CompletedDocument28 pagesPreliminary Report CompletedJacky100% (1)
- Production of Isopropyl BenzeneDocument15 pagesProduction of Isopropyl BenzeneMehdi SirajNo ratings yet
- 0910 4 AbsDocument9 pages0910 4 AbsEngr Muhammad AqibNo ratings yet
- Manfacture OF: Cyclo HexaneDocument91 pagesManfacture OF: Cyclo HexaneNikhil Kumar Chennuri100% (4)
- CHE655 - Plant Design Project #5 Summer 2010 Design of An Ehtyl Benzene Production ProcessDocument13 pagesCHE655 - Plant Design Project #5 Summer 2010 Design of An Ehtyl Benzene Production ProcessAyşe ÖztürkNo ratings yet
- Ethyl Benzene Production ReactionsDocument2 pagesEthyl Benzene Production ReactionsMohd Hakimie0% (1)
- Production of Methyl Ethyl KetoneDocument89 pagesProduction of Methyl Ethyl KetonePablo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in the Science and Technology of Zeolites and Related Materials: Proceedings of the 14th International Zeolite Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 25-30th April 2004From EverandRecent Advances in the Science and Technology of Zeolites and Related Materials: Proceedings of the 14th International Zeolite Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 25-30th April 2004No ratings yet
- Main Project Part IDocument7 pagesMain Project Part IBigNo ratings yet
- Cumene Manufacturing ProcessDocument41 pagesCumene Manufacturing Processdhanagopal saiNo ratings yet
- What Does It Mean To Be A Domain ExpertDocument2 pagesWhat Does It Mean To Be A Domain Expertdanena88No ratings yet
- Codes UsedDocument9 pagesCodes Useddanena88No ratings yet
- GWA Calculator by FilipiKnowDocument17 pagesGWA Calculator by FilipiKnowdanena88No ratings yet
- CheatSheet DW 25082023Document2 pagesCheatSheet DW 25082023danena88No ratings yet
- Acid Base TitrationDocument117 pagesAcid Base TitrationAboahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas Law PracticeDocument2 pagesCombined Gas Law Practicedanena88No ratings yet
- Beginner Cheat Sheet KNIME 5.1Document2 pagesBeginner Cheat Sheet KNIME 5.1danena88No ratings yet
- Ch08 Part4 Lewis Structures of CompoundsDocument19 pagesCh08 Part4 Lewis Structures of Compoundsdanena88No ratings yet
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction PrinciplesDocument34 pagesLiquid-Liquid Extraction PrinciplescocoayisaNo ratings yet
- EvaporationDocument2 pagesEvaporationdanena88100% (1)
- Gas Stoichiometry PracticeDocument2 pagesGas Stoichiometry Practicedanena88No ratings yet
- THERMOCHEMISTRYDocument80 pagesTHERMOCHEMISTRYdanena8850% (2)
- Fluid DynamicsDocument30 pagesFluid DynamicsvarshiniNo ratings yet
- Charles's Law: For Chemistry Help, Visit © 2003 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesCharles's Law: For Chemistry Help, Visit © 2003 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights Reserveddanena88No ratings yet
- Fatty AcidsDocument31 pagesFatty Acidsdanena88No ratings yet
- 1.4x33 Rotary KilnDocument5 pages1.4x33 Rotary Kilndanena88No ratings yet
- Tertiary Treatment:: Nutrient Removal, Solids Removal, and DisinfectionDocument31 pagesTertiary Treatment:: Nutrient Removal, Solids Removal, and Disinfectiondanena88No ratings yet