Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LMMEC211
Uploaded by
Krishna Murari MauryaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LMMEC211
Uploaded by
Krishna Murari MauryaCopyright:
Available Formats
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
LABORATORY MANUAL
MEC211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
2010-2011
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Table of Contents
SL No Experiment 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 To conduct tensile test on mild steel and cast iron specimens. To conduct Impact test on mild steel and cast iron specimens. To conduct Torsion test on mild steel and cast iron specimens. To find out stiffness of spring and modulus of rigidity of spring wire material. To study tensile strength using strain gauge based cantilever beam apparatus To study torque pick up and torque Measurement using Strain gauges Comparison of measurements of test specimens using micrometer , vernier calliper & height gauge Measurement of surface roughness Measurement of gear profile Measurement of critical parameters of external threads. Measurement of eccentricity angle run out of a shaft To prepare a thermocouple and and its calibration
Page No 3 to 4 5 to 6 7 to8 9 10 to 11 12 to 13 14 to 15
8 9 10 11 12
16 17 18 19 20
2010-2011
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Experiment: 1 1.Experiment: To conduct tensile test on Mild steel and cast iron specimens Equipment to be used: Universal Testing Machine, Specimen of MS & CI, Scale, Vernier caliper 2.Learning Objective: To provides information related to the strength and ductility of metals under direct tension stress. 3.Procedure:Measure the original length and diameter of the specimen. The length may either be length of gauge section which is marked on the specimen with a preset punch or the local length of the specimen. Insert the specimen into test machine. Begin the load application and record load Vs elongation data. Measure elongation values with the
help of dividers and a ruler. Continue the test till fracture occurs. Measure the final length and diameter of specimen. 4.Scope of results to be reported: Parameters: A) Original dimensions: Length= ----------------------
Diameter= ---------------------Area= B) Final Dimensions: Length= --------------------------------------------
Diameter= ----------------------Area= Plots: Draw a graph: Stress Vs Strain and identify yeild point, ultimate tensile strength and E and % elongation and % reduction in area. . ------------------------
Result: 2010-2011 3
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I Average breaking Stress = 1. Ultimate Stress = 2.Average Percentage Elongation = 5.Cautions: If the strain measuring device is an extensometer it should be removed before necking begins. Measuring deflection on scale carefully and accurately.
2010-2011
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Experiment: 2
1.Experiment: To conduct impact test on mild steel and cast iron specimens. Equipment to be used: impact testing machine, Specimen of MS & CI, Steel. 2.Learning Objective: An impact test signifies toughness of material that is ability of material to absorb energy during plastic deformation. Static tension tests of un-notched specimens do not always reveal the susceptibility of a metal to brittle fracture. This important factor is determined by impact test. Toughness takes into account both the strength and ductility of the material. Several engineering materials have to withstand impact or suddenly applied loads while in service. 3.Procedure: A) Izod Test:
When the striking hammer (pendulum) in safe test position. Put the steel specimen notch face on impact testing machines anvil in such a way that the 75% inside and 25% above the top surface to its top most striking position
the hammer and is
of the slot .Bring the striking hammer
unless it is already there and lock it at that position. Bring indicator of the machine to zero. Release the hammer, It will fall due to and break the by the specimen through its momentum, the total energy is not gravity absorbed
specimen, the indicator stops moving, while the pendulum falls back. Again bring the hammer to its idle position and back.
B) Charpy Test:
With the striking hammer (pendulum) in safe test positions, put the Steel specimen on impact testing machine anvil in such a way that the notch faces opposite the hammer. 2010-2011 5
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I Bring the striking hammer to its top most striking position. Bring indicator of the machine to zero.Release the hammer. It will fall due to gravity and break the specimen through its momentum, the total energy is not absorbed by the specimen. Then it continues to swing. At its topmost height after breaking the specimen, the indicator stops moving, While the pendulum falls back. Note the indicator at that topmost final position.
4.Results Required
a. For Izod Test: Note the indicator at the topmost final position. Calculate energy. b. For Charpy Test: Note the indicator at the topmost final position. Calculate energy. 5.Caution: Measure the dimensions of the specimen carefully. Hold the specimen firmly. Take the readings carefully.
2010-2011
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Experiment: 3
1.Experiment: To conduct Torsion test on mild steel and cast iron specimen. Equipment to be Used: A Torsion testing Machine, Twist meter for measuring angle of twist, A steel rule and Vernier caliper or micrometer 2.Learning Objective: A torsion test is quite instrumental in determining the value of rigidity (ratio of shear stress to shear strain) of a metallic specimen. The value of modulus of rigidity can be found out through observations made during the experiment by using the torsion equation:
Where, T = Torque applied Ip = Polar moment of Inertia C = Modulus of rigidity I = Gauge length l = gauge length
In the torque equipment one end of the specimen is held by a fixed support and the other end to a pulley. The pulley provides the necessary torque to twist the rod by addition of weights (w). The twist meter attached to the rod gives the angle of twist. 3.Procedure: 1.Prepare the testing machine by fixing the two twist meters at some constant lengths from fixed support. 2.Measure the diameter of the pulley and the diameter of the rod and take the average. 2010-2011 7
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I 3.Set the maximum load pointer to zero. 4.Set the protector to zero for convenience and clamp it by means of knurled screw. 5.Carry out straining by rotating the hand-wheel in either direction. 6.Add weights in the hanger stepwise to get a notable angle of twist for T1 and T2. 7.Then load out to failure as to cause equal increments of strain reading. 4.Plot torque- twist (T- ) graph Read off co-ordinates of a convenient point from the straight line portion of the twist (T- ) graph and calculate the value of C by using above relation. torque
5.Scope of Result and Discussion : Gauge length of the specimen, l = Diameter of the specimen, Polar moment of inertia, d = Ip = .
Modulus of rigidity of the given specimen is _________ N/mm2 The graph between angle of twist and torque for the given specimen is plotted. Cautions: Measure the dimensions of the specimen carefully. Measure the Angle of twist accurately for the corresponding value of Torque.
2010-2011
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I Experiment no 4 1.Experiment: To determine the stiffness of the spring. Equipment to be Used: Spring testing machine, Spring specimen, Vernier Caliper, Micrometer. 2.Learning Objective: To determine the stiffness of the spring.
3.Procedure: 1.Measure the diameter of the wire of the spring by using the micrometer. 2.Measure the diameter of spring coils by using the venire caliper. Count the number of turns, 3.Insert the spring in the spring testing machine and load the spring by a suitable weight and note the corresponding axial deflection in tension or compression. 4.Increase the load and take the corresponding axial deflection. 4.Plot A curve between load and deflection. The shape of the curve gives the stiffness spring. 5.Scope of Results and Discussion : Least Count of Micrometer = Diameter of Spring wire, d= ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ of the
Least count of Vernier caliper = Diameter of the spring coil, D =
Mean coil diameter, Dm = D d = _______________ Number of turns, n = ___________________
The value of spring constant of Closed coiled helical spring is ___________ N/mm. Modulus of rigidity is ___________________________
6.Cautions: 1.Measure the dimensions of spring accurately. 2.Note the deflections accurately.
2010-2011
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I Experiment no 5 1.Experiment: To study tensile strength using strain gauge based cantilever beam apparatus. Equipment Required: Digital Voltmeter, Strain gage measurement kit, Standard Cantilever Beam apparatus. Material Requirement: Standard Weight Specimen. 2.Learning Objectives: 1) To learn the working principle of Wheatstone bridge. 2) Determination of strain and stress using strain gages. 3.Procedure 1) Connect the Voltmeter in Wheatstone bridge to calibrate the voltage change. 2) Adjust the resistor to obtain a zero output voltage when the cantilever beam is unloaded 3) Connect the strain gage wire to the strain gage measurement kit to complete the circuit. 4) Now apply the given standard load to the free end of beam. 5) Switch on gage measurement kit and set the current. 6) Note down the voltage for a given load. 7) Increase the load stepwise and note down the voltage respectively.
4.Scope of Expected Results: 1) Calculated result of strain (=(6*P*x)/E*b*t2) should be match with the experimental result (digital display). 2) Draw the Shear force and Bending moment diagram for respective load. 3) Hooke's Law states that for elastic behaviour that the strain is proportional to the load applied, does your graph verify Hooke's Law? 5.Parameters and Plot: 1) Note down the Voltage with respect to the load. 2) To calculate the change in resistance. 3) To calculate the tensile stress. 4) Plot the graph Load Vs Stress. 2010-2011 10
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I 5) Plot a graph of output voltage (in Volts) on the vertical axis versus beam loading (in kg) on the horizontal axis. 6.Cautions: 1) Put the load on span very carefully and slowly. 2) Check out the connection of voltmeter to Wheatstone bridge. 3) To maintain the constant power supply. 4)All the connection should be proper channel.
2010-2011
11
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I Experiment No 6 1.Experiment: To study torque pickup and torque Measurement using Strain gauges. Equipment required: Standard weights, multimeter, Torque measurement kit, and display or data gathering unit Material required: NIL 2.Learning objectives: To study the variation of torque with increase in weight, and measurement techniques for torque.
3.Outline of procedure: Place the torque measurement kit on the table free from any vibration Connect the kit to the display unit Now turn on the display unit Connect the multimeter to the Wheatstone bridge shown on the unit to the display unit Now gently put the weight on the on side in the vertical circular rod and measure the voltage Repeat the above step for different load and measure the voltage Convert the voltage data to torque using appropriate formulae Now compare that torque with the torque displayed on the display unit 4.Scope of the results expected: Student will learn the working of strain gauge and how torque varies with load 5.Parameter and plots: Plot the voltage vs. load.
Torque Measurement:
2010-2011
12
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Wheatstone bridge The output from the Wheatstone bridge can be expressed as:
T = Torque applied = Poisson ratio, E = Youngs Modulus = Strain, = Shear strain F= Gage factor, R= radius of shaft
6.Cautions: Make sure that multimeter is set in the proper range Do not put drop the weight, put is gently Do not exceed the limit of weight on the torque measurement unit High-quality transducers utilizing strain gages as the primary sensing element incorporate sophisticated techniques to minimize thermal effects, nonlinearities, hysteresis, and other sources of error. very accurate gage orientation and placement of all four gages is crucial for success.
2010-2011
13
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Experiment No 7
1.Experiment : Comparison of measurements of test specimens using micrometer and vernier caliper. Equipment & Tool Required: Vernier caliper 6 inch, Micrometer (0-25 mm), Micrometer (25-50mm ),test specimens . 2.Learning Objectives: To perform different operations of Measurement using micrometer and vernier caliper.
3.Out line of Procedure (Part -1) Select and collect instruments as per the specimen given to you .Find out the least count of all the instruments .Take two test specimens and measure all the dimensions (All Diameters as well as lengths,bore size ,bore depth ,thread diameter etc. )Draw the figure both of specimens on the copy and and show all the dimensions .
Procedure Part -II Take any one specimen and measure its dimensions ( length and diameter) using micrometer and vernier calipers and then find out its volume 2010-2011 14
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Procedure Part -III Take out your instrument (25-50 micrometer) and check its accuracy by using test piece provided in the box (check zero to zero alignment of datum line on barrel and zero of the thimble scale .Take a slip gauge piece of 25 mm and measure it with the given instrument .Take another piece of slip gauge of smaller size and wringer it with 25mm piece so that no air is present in between .then measure the two pieces considering them as one piece .If the reading matches with the size written on the slip gauge block then your instrument is correct . Observation : 1. Measurement using vernier caliper. 2. Measurement using micrometer. Error Analysis :1. Take any one dimension and measure it with both micrometer and vernier caliper,then do the error analysis . 2. Error =Measurement taken by micrometer(Actual size) Measurement taken by vernier caliper(measured size) 3. Relative error = (Actual size) (Measured Size) Actual size
% error = Relative Error x 100 4.Results required: : 1. Understand the principle and working of vernier caliper and micrometer. 2. Understand the difference in accuracy of measurement by vernier caliper and micrometer. 3. Select the instrument for the measurement of given work piece. 4. Calculate least count of the instrument and note down the readings. 5. Judge the required measuring pressure during measurement. 5.Caution : 1. There should not be any play between sliding jaw & the main scale. 2. Check the instruments for zero error. 3. Parallax or reading error must be avoided. 4. Do not apply undue pressure. 5. Handle instruments carefully as those are very sensitive esp. Taking care of not let them fall anywhere
2010-2011
15
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I Experiment No 8
1.Experiment 8: Measurement of surface roughness . Equipment & Tool Required: Portal Surface roughness tester, test specimen etc. 2.Learning Objectives: To study degree of roughness of various machining process. 3.Procedure: Take the measurement at various places and also in multiple directions. Some operations can produce direction dependent roughness .Make a drawing in first angle projection and mention all the dimensions and surface criterion. 4.Results Required:: 1. 2. process. 3. 5.Cautions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Understand the difference in all types of surface roughness factor. Understand and differentiate work pieces produced by different machining Understand the principle and working of surface roughness tester. Always wear shoes while performing the practical Always wear lab coat. Do not try to touch any machine without the permission of workshop in charge. Remove any oil and grease etc. from the surface. Place the probe gently on the measuring surface.
2010-2011
16
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Experiment No 9
1.Experiment 9: Measurement of gear profile Equipment & Tool Required: Vernier
1. 2. 3.
caliper : 0 150 mm Micrometer : 0 25 mm, 25 50 mm Sample gears(Spur ,bevel,Helical and Worm gears ) Profile projector study the elements of gear
2.Learning Objectives: To 3.Procedure: Take the
gear and clean It for removal of any dust or dirt.Take the vernier and measure its outer dia ,Thickness ,inner dia of hole .Place the gear on profile projector and measure all its dimensions like addendum, dedendum ,pitch circle diameter.Compare the measurements with the standard calculated data theoratically
4.Results Required:
1.Measurement using vernier caliper 2.Measurement using profile projector 5.Caution : 1. There should not be any play between sliding jaw & the main scale. 2. Check the instruments for zero error. 3. Parallax or reading error must be avoided. 4. Do not apply undue pressure. 5. Handle instruments carefully as those are very senstive esp. Taking care of not let them fall anywhere
2010-2011
17
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Experiment No 10
1.Experiment 10: Measurement of critical parameters of external threads. Equipment & Tool Required: Thread micrometer, Anvil set 2.Learning Objectives: To 3.Procedure: Take the
study the elements of gear
gear and clean It for removal of any dust or dirt. Take the vernier and measure its outer diameter, Thickness, inner diameter of hole .Place the gear on profile projector and measure all its dimensions like addendum, addendum, pitch circle diameter. Compare the measurements with the standard calculated data theoretically 4.Results Required:Measurement using vernier caliper Measurement using profile projector
Scope of the Result to be reported:
Understand the principle and working of profile projector. Understand the difference in measurements taken by profile projector and vernier calipers
5.Cautions:
1. There should not be any play between sliding jaw & the main scale. 2. Check the instruments for zero error. 3. Parallax or reading error must be avoided. 4. Do not apply undue pressure. 5. Handle instruments carefully as those are very sensitive esp. Taking care of not let them fall anywhere.
2010-2011
18
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Experiment No 11
1.Experiment 11: Measurement of egocentricity angle run out of a shaft Equipment & Tool Required:
DTI (Dial Test Indicator) with stand, surface plate, V- blocks, Bench center, Height Gauge Specimen work pieces 2.Learning objectives:-To learn how to measure the eccentricity
3.Procedure:
For measuring Straightness Measure the Diameter of given shaft with the help of a micrometer. Hold the parallel shaft in the centers of bench center .Set the height gauge at the center height with the centers of bench center .Mark a straight line on the piece .Rotate the piece by 360 degree. Mark another line on work piece .Both the lines should be parallel to each other. For measuring eccentricity :Hold the piece in between centers of a Bench center .Mount a dial gauge on the magnetic stand. Set the dial to zero degree with its plunger loaded on the job. Rotate the piece with hand and check and note any deflection in DTI. If No deflection, it means there is no eccentricity in the piece. Same operation can also be done carried out by holding the job on a V block and holding it with a clamp.
4.Results Required: Tabulate the difference in readings and find out deviation from basic size by plotting a graph. 5.Cautions: Always wear shoes while performing the practical. Do not wear bangles, bracelets, rings, chains, and even neck tie. Always wear Lab coat (white). Always wear safety goggles. Do not lean on to the machines. Follow the operative instructions given strictly
2010-2011
19
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I
Experiment No 12
1.Experiment 12-: To prepare a thermocouple and its calibration Equipment & Tool Required:- Mille voltmeter,PT-100 meter, J thermocouple meter, Connecting Wires Thermocouple wire,PT-100 Thermocouple, J type thermocouple, Thermometer, Heater, pan etc 2.Learning Objectives:- Preparation of thermocouple and its use for different range of temperature
3.Procedure:Take thermocouple wires and twist them with each other to for m a thermocouple Connect the other ends to the measuring meter .Connect all the parts as per circuit diagram .Start insert the heater and let the water to be heated up to 80-90 degree and then switch off the heater. the thermocouple and thermometer in the heated water; make sure that both thermometer and thermocouple are not touching the base of the container .Take 10 readings after every minute Compare the readings of thermometer and thermocouple .Plot the graph between time and Temperature for both the readings of thermometer and thermocouple. Take standard thermocouple instead of thermometer and repeat steps .Compare the two graphs
3. Result Required:
1 To know the working of a thermocouple 2 Compare readings of j type and PT -100 type thermocouple
4.Cautions
1 There should not be any play between sliding jaw & the main scale 2 Check the instruments for zero error 2010-2011 20
MEC 211 Unified Mechanical Engineering I 3 Parallax or reading err or must be avoided. 4 Do not apply undue pressure 5 Handle instruments carefully as those are very sensitive especially taking care of not to let them fall under any circumstance
2010-2011
21
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Radar Systems Range Equation PDFDocument6 pagesRadar Systems Range Equation PDFSanjid ElahiNo ratings yet
- Notes On Spur Gears: DefinitionsDocument6 pagesNotes On Spur Gears: DefinitionsKrishna Murari MauryaNo ratings yet
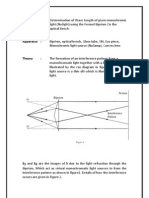
- Interference PatternsDocument8 pagesInterference PatternsAsa mathewNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesSoal Bahasa InggrisPelkeh Prianda25% (16)
- The Planets Comparative Superlative - 87358Document2 pagesThe Planets Comparative Superlative - 87358Maria AdamNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics.: Target-GateDocument5 pagesThermodynamics.: Target-GateKrishna Murari MauryaNo ratings yet
- PrefaceDocument11 pagesPrefaceKrishna Murari MauryaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document23 pagesPresentation 1Krishna Murari MauryaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Machining (ECM)Document17 pagesElectrochemical Machining (ECM)Krishna Murari MauryaNo ratings yet
- Information Folder LUCCON PDFDocument9 pagesInformation Folder LUCCON PDFASHOKKUMAR ENo ratings yet
- Filter Vessel Calculations Per As Me Viii 1Document40 pagesFilter Vessel Calculations Per As Me Viii 1Anonymous J1vjrU2No ratings yet
- Instructivo Luxometro Steren Her-410 PDFDocument12 pagesInstructivo Luxometro Steren Her-410 PDFLuis CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3.2 - Finale Internal Forced ConvectionDocument18 pagesChapter - 3.2 - Finale Internal Forced ConvectioneirinaNo ratings yet
- Curtain Wall System From Technal - Geode-BrochureDocument38 pagesCurtain Wall System From Technal - Geode-BrochurebatteekhNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel PropertiesDocument3 pagesStainless Steel Propertieskiwanis_lamNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Tablet Coating ProcessDocument17 pagesAnalysis of The Tablet Coating Processشروق سعد الدينNo ratings yet
- Anti Derivative Chain RuleDocument4 pagesAnti Derivative Chain Ruletutorciecle123No ratings yet
- Technical Notes On Duplex SSDocument22 pagesTechnical Notes On Duplex SSBhyrappaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Purification Methods ListDocument8 pagesChemical Purification Methods ListMd.Mehdi MasudNo ratings yet
- Judo Bio MechanicsDocument11 pagesJudo Bio MechanicsAttilio Sacripanti100% (6)
- Skema Chemistry Paper 3Document8 pagesSkema Chemistry Paper 3nurul atiqahNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics PDFDocument51 pagesElectrostatics PDFSaksham GuptaNo ratings yet
- SPE 122225 Gas Condensate Productivity Improvement by Chemical Wettability AlterationDocument12 pagesSPE 122225 Gas Condensate Productivity Improvement by Chemical Wettability AlterationGabriel EduardoNo ratings yet
- PEGN 419 / GPGN 419 Spring 2017: Manika Prasad Mansur Ermila Expert Resource: Robert LieberDocument30 pagesPEGN 419 / GPGN 419 Spring 2017: Manika Prasad Mansur Ermila Expert Resource: Robert LiebertahermohNo ratings yet
- Galloway 1989 Genetic Stratigraphic Sequence Basin Analysis IDocument18 pagesGalloway 1989 Genetic Stratigraphic Sequence Basin Analysis IMitreNo ratings yet
- Diketopiperazines RevDocument27 pagesDiketopiperazines RevIsaí MillánNo ratings yet
- Solving rectangular double-well potential problemDocument10 pagesSolving rectangular double-well potential problemMendoza JohnyNo ratings yet
- 08 Energy 03 Complementary Strain Energy PDFDocument2 pages08 Energy 03 Complementary Strain Energy PDFjack_hero_56No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Weak Electrolytes Including H3PO4Document10 pagesThermodynamics of Weak Electrolytes Including H3PO4buhalnitaNo ratings yet
- Cluster ExpansionDocument4 pagesCluster ExpansionflytrapsolNo ratings yet
- Engineering Failure Analysis: Ayad Subhy, Davide Lo Presti, Gordon AireyDocument11 pagesEngineering Failure Analysis: Ayad Subhy, Davide Lo Presti, Gordon AireyMohamed BoudabbousNo ratings yet
- Linear Differential Equations Standard Form and Operator FormDocument10 pagesLinear Differential Equations Standard Form and Operator FormJoSaNo ratings yet
- Heat and Temperature Unit3 - T4 - T6 PDFDocument28 pagesHeat and Temperature Unit3 - T4 - T6 PDFhiren_mistry55No ratings yet
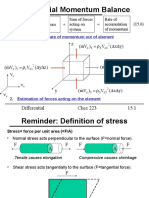
- Ch15 Differential Momentum BalanceDocument20 pagesCh15 Differential Momentum Balance89kkNo ratings yet