Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Strengths and Weaknesses of HLL
Strengths and Weaknesses of HLL
Uploaded by
Pragun ThadaniCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Strengths and Weaknesses of HLL
Strengths and Weaknesses of HLL
Uploaded by
Pragun ThadaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Strengths and weaknesses of HLLs Distribution Model Strengths 1. Removes heterogeneity of the Indian market 2.
Vast Coverage- HUL virtually covers every geographical segment of the country. 3. Deeply Penetrated-HULs distribution system has enabled to penetrate into rural areas and small towns. 4. Covers all income groups-With Around a million retail points, HUL is able to cater to every income group.
Weaknesses 1. Huge Cost- Setting up of extensive distribution system with 7500 distributors and about million retail points requires huge cost, thus resulting in a hit on their bottomlines. 2. Time Involved-Setting up of extensive distribution network with million retail points involves great amount of time. 3. Extensive Hiring- large number of distributors. 4. Centralization Vs Decentralization.
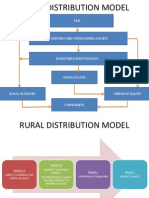
HLL DISTRIBUTION MODEL HUL caters to seven million distinct outlets across India (one for every 29 households) and 59% of these stores are in rural India. HUL directly services over one million stores and has network of over 7000 stockists and distributors. HUL's products are distributed through a network of 4,000 redistribution stockists, covering 6.3 million retail outlets reaching the entire urban population, and about 250 million rural consumers. There are 35 C&FAs in the country who feed these redistribution stockists regularly. The general trade comprises grocery stores, chemists, wholesale, kiosks and general stores. Hindustan Unilever provides tailor made services to each of its channel partners. It has developed customer management and supply chain capabilities for partnering emerging selfservice stores and supermarkets. Around 2,000 suppliers and associates serve HULs 40 manufacturing plants which are decentralized across 2 million square miles of territory. DISTRIBUTION MODEL- P& G 1. Reducing the number of price points. 2. Focus on class A and B towns. 3. Less presence in rural areas.
4. REDUCING NUMBER OF PRODUCT VARIANTS. DISTRIBUTION MODEL-NESTLE 1. IDENTIFICATION OF SELECTIVE MARKETS 2. WEEDING OUT LOW PROFITABILITY PRODUCTS.
You might also like
- HUL Distribution ModelDocument19 pagesHUL Distribution ModelArpan Mehra93% (70)
- The Secret Jewels of FMCG Retail distribution & Channel salesFrom EverandThe Secret Jewels of FMCG Retail distribution & Channel salesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- HUL, ITC & Godrej (Supply Chain Management Comparision)Document39 pagesHUL, ITC & Godrej (Supply Chain Management Comparision)Jeetesh Kumar92% (12)
- Hindustan Unilever Limited Geographical CoverageDocument3 pagesHindustan Unilever Limited Geographical CoverageHarish Chandra JoshiNo ratings yet
- HUL S&D ManagementDocument21 pagesHUL S&D ManagementKuldipak KheradiyaNo ratings yet
- Hul Distribution ModelDocument5 pagesHul Distribution ModelBhavik LodhaNo ratings yet
- The Long Tail (Review and Analysis of Anderson's Book)From EverandThe Long Tail (Review and Analysis of Anderson's Book)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- HulDocument13 pagesHulAmanBhatnagar75% (4)
- Hindustan Unilever Limited: Distribution System of HULDocument3 pagesHindustan Unilever Limited: Distribution System of HULRushabh JadavNo ratings yet
- HLL Case StudyDocument18 pagesHLL Case StudyjdwantsitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HUL-: Vision-Sales and Distribution of HUL - Evolution Over TimeDocument2 pagesIntroduction To HUL-: Vision-Sales and Distribution of HUL - Evolution Over TimeSaHil GuptaNo ratings yet
- HUL's Distribution ChannelDocument8 pagesHUL's Distribution ChannelNirmal Kumar100% (1)
- Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LTD NewDocument31 pagesDistribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LTD NewNachiket JaniNo ratings yet
- A Study On Distribution Strategies of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Rajnikant GharatDocument31 pagesA Study On Distribution Strategies of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Rajnikant GharatRajnikant GharatNo ratings yet
- Distribution Channel of HUL: Presented by Venkatesh Kumar A 36 Ranjit PS Pramodh Bhupathi A 43Document12 pagesDistribution Channel of HUL: Presented by Venkatesh Kumar A 36 Ranjit PS Pramodh Bhupathi A 43Srijit Jon ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- New Paradigm of Distribution For FMCG Companies: Presented By:-Group 5Document10 pagesNew Paradigm of Distribution For FMCG Companies: Presented By:-Group 5Shreya BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Distribution Strategy of Hul of Existing ProductsDocument4 pagesDistribution Strategy of Hul of Existing ProductsMahak Gupta Student, Jaipuria LucknowNo ratings yet
- A Study On Sale and Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LimitedDocument35 pagesA Study On Sale and Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LimitedJakir HussainNo ratings yet
- CF Project On Hul.Document20 pagesCF Project On Hul.Ankit Jaiswal0% (1)
- Analysis On Hindustan UnileverDocument9 pagesAnalysis On Hindustan Unileverkaran_mak100% (1)
- Rural Marketing: Challenges, Opportunities & Strategies: Wednesday, May 26, 2010Document14 pagesRural Marketing: Challenges, Opportunities & Strategies: Wednesday, May 26, 2010Yog MishraNo ratings yet
- A Study On Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Ashish AgarwalDocument32 pagesA Study On Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Ashish AgarwalAshish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- C CCC: CCCCCCCCCCC C C CC CDocument5 pagesC CCC: CCCCCCCCCCC C C CC CAshwin ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Planning and Management: New DelhiDocument33 pagesIndian Institute of Planning and Management: New DelhiDip RanjanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 RURAL MARKETING NotesDocument49 pagesUNIT 4 RURAL MARKETING NotesSufyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Introduction of HulDocument3 pagesIntroduction of HulSujataJoshiNo ratings yet
- Retail ManagementDocument40 pagesRetail ManagementAditya GowriNo ratings yet
- MM CASE ASSIGNMENT On Unilever in India Hindustan Levers Project Shakti by PGP - 26 - 112 Sourav AnandDocument4 pagesMM CASE ASSIGNMENT On Unilever in India Hindustan Levers Project Shakti by PGP - 26 - 112 Sourav AnandSOURAV ANANDNo ratings yet
- Rural Retailing and Its ChallengesDocument26 pagesRural Retailing and Its Challengesvenkateshkanumilli100% (9)
- Section B - Group 9 - ReportDocument13 pagesSection B - Group 9 - ReportShruthi chatlaNo ratings yet
- Rural Retail Channel MGMTDocument8 pagesRural Retail Channel MGMTAnuja BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Distribution Channels HULDocument12 pagesDistribution Channels HULnavdeep98480% (10)
- Rural Marketing Research PaperDocument8 pagesRural Marketing Research PaperShazia JamalNo ratings yet
- Cases RSMDocument8 pagesCases RSMPrateek MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Rural MarketDocument3 pagesRural MarketAbid91No ratings yet
- FMCG Industry AnalysisDocument23 pagesFMCG Industry AnalysisAditi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- SCM Synopsis HulDocument17 pagesSCM Synopsis HulSanjib BiswasNo ratings yet
- Rural MarketingDocument9 pagesRural MarketingPrashant GurjarNo ratings yet
- Sales and Distribution Manaagement in HULDocument18 pagesSales and Distribution Manaagement in HUL'Gitesh ⎝⏠⏝⏠⎠ Patil'No ratings yet
- Cornered - But Not TrouncedDocument11 pagesCornered - But Not TrouncedSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- M C CC C CC C CDocument6 pagesM C CC C CC C CAmulya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Rural DistributionDocument17 pagesChallenges in Rural DistributionAnkit KushwahNo ratings yet
- HUL (Supply Chain)Document19 pagesHUL (Supply Chain)rohan_jangid8100% (4)
- Unit 4 - DistributionDocument33 pagesUnit 4 - DistributionVidurNo ratings yet
- Rural MarketingDocument8 pagesRural Marketingsalim1321No ratings yet
- Distribution Strategy in Rural MarketingDocument82 pagesDistribution Strategy in Rural Marketingm_dattaias100% (10)
- Distribution Strategy in Rural MarketingDocument82 pagesDistribution Strategy in Rural MarketingRajat OberoiNo ratings yet
- Distribution Strategy in Rural MarketingDocument89 pagesDistribution Strategy in Rural Marketingm_dattaias100% (6)
- Rural Marketing - Challenges, Opportunities & StrategiesDocument5 pagesRural Marketing - Challenges, Opportunities & Strategiesapi-3740973100% (2)
- Rural Marketing FinalDocument14 pagesRural Marketing FinalSailesh NagariNo ratings yet
- Business Valuation Project: Valuation of FMCG Sector - Hindustan Unilever LimitedDocument4 pagesBusiness Valuation Project: Valuation of FMCG Sector - Hindustan Unilever LimitedAkshatAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Innovation and Creativity in Rural Retail Marketing in India 1 4Document10 pagesInnovation and Creativity in Rural Retail Marketing in India 1 4samuelNo ratings yet
- "Integrated Marketing Communication" of LUXDocument42 pages"Integrated Marketing Communication" of LUXLalit Kothari75% (8)
- Gilles Lipovetsky: Selected Summaries: SELECTED SUMMARIESFrom EverandGilles Lipovetsky: Selected Summaries: SELECTED SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Paradoxical Happiness" By Gilles Lipovetsky: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Paradoxical Happiness" By Gilles Lipovetsky: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Model Answer: Launch of a laundry liquid detergent in Sri LankaFrom EverandModel Answer: Launch of a laundry liquid detergent in Sri LankaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Marketing - Principles of Wholesale and Retail DistributionFrom EverandIntroduction to Marketing - Principles of Wholesale and Retail DistributionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)