Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1993paper I
1993paper I
Uploaded by
sliversniper0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pagesOriginal Title
1993Paper I
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pages1993paper I
1993paper I
Uploaded by
sliversniperCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
@
®
©
@
©
o
Useful Formulse in Physics
Relationships betwean initial velocity u, constant acceleration a, final
velocity v and displacement travelled 2 after time ¢:
Fem see
Paw o2ar
Poteatial energy pained by « body of mass m when raised through &
height hia mph.
Kinetic energy of body of mass m moving with speed ¥ is
1
ow.
z
Power = force x velocly
pile sie of eso Ry and Re:
inserter oR
tn praet =
Power = potential diference current
ACE PHY HI
93-CE
PHY
PAPER | HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AUTHORITY
HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 1993
PHYSICS PAPER |
8:30 am-10.00.am (14 hours)
‘This paper must be answered in English
1993
‘This paper consists of seven questions each carrying U8 marks
Answer any SIX questions.
‘Take g = 10ms?
“The last page of this question paper contains « list af physien
forenulie which you may find useful.
aa-cE-PHV nT
3
— 54 —
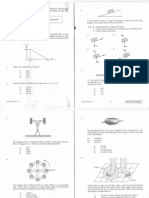
1. Ahelicopler of mass 1500 kg is initially at rest at a certain level above
the ground. 1 accelerates uniformly and vertically upwards for 75 m and
teaches a speed 15 ms". Assume the air resistance is negligible
@ Calculate
0
«iy
‘he acceleration of the helicopter,
the uplifting force acting on the helicopter.
5 marks)
(©) At this moment, an object is released from the helicopter. The
‘object reaches the ground after 6 s. Figure 1 shows the velocity:
time graph of the object, starting fom the instant the object is
released.
0
iy
win
w
99-CE-PHY 2
Write down the velocity of the object when it reaches
the ground.
‘State the physical meaning of the area of the shaded
‘gion in Pigare 1
Using Figure 1, or otherwise, find the height of the
object above the ground when iti released.
‘Comment on the following two statements:
Statement 1: Attime # = 1.5, the acceleration of the
‘object is zero,
‘Statement 2: If the object is replaced by a heavier one,
it would tke the same time to reach the
(20 marks)
93-ce-PaY Ia 35
93-CE-PHY 4
Figure 2
Figuee 2 shows horizontal eunway ABC consisting of wo parts,
smooth portion AB and a rough portion BC. A block P of mass 0.8 kg
undergoes the following motion :
Step (1): P is pressed against a spring at A and then released . Afier
(0.05 ¢, P loses contact with the spring and moves witha speed
‘Step 2): When P moves along AB, « lump of plasticine is dropped from
4 height slightly above P and slicks to it, The speed of
P is reduced to 1.6 ms.
‘Step (3): P enters the rough portion and stops at point D .
Calculate
(the average force acting on the block by the spring in
Step (),
Gi) the mass of the pl
ine,
i) the distance BD, given that the fictional force between,
P and the rough portion is 3 N.
7 marks)
(©) —_Deseribe the energy change in Step (1).
(2 mats)
(©) Is kinetic energy conserved in Step (2)? Explain briefly.
@ marks)
®
93-cE-PHY ES,
Figure 3
“The above process ix repeated with the cough portion BC
inclined at an angle 15° tothe horizontal. (Six Figure 3.) 1 the
{ictal force ix sill 3 N, what happens to P alter it reaches
the highest point’? Explain your answer
(4 marks)
”
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- CE Physics 2006 Paper2 (E)Document13 pagesCE Physics 2006 Paper2 (E)08150815whoimNo ratings yet
- 2005paper 2Document13 pages2005paper 2sliversniperNo ratings yet
- 2005paper 1Document16 pages2005paper 1sliversniperNo ratings yet
- 2004 Paper I Marking SchemeDocument12 pages2004 Paper I Marking SchemesliversniperNo ratings yet
- 2004paper IIDocument13 pages2004paper IIsliversniperNo ratings yet
- 2004paper IDocument10 pages2004paper IsliversniperNo ratings yet
- Physics 2003 Paper IIDocument14 pagesPhysics 2003 Paper IIapi-26423290No ratings yet
- 1 2 3cm 4cm 5cm 6cm CM CM: Multiple-Choice Questions 1986 Take G 10 m/s2Document16 pages1 2 3cm 4cm 5cm 6cm CM CM: Multiple-Choice Questions 1986 Take G 10 m/s2sliversniperNo ratings yet
- Physics 2002 Paper 1Document20 pagesPhysics 2002 Paper 1api-3739499100% (2)
- 2003paper IDocument8 pages2003paper IsliversniperNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Question 1985 Take G 10 m/s2.: Velocity/msDocument16 pagesMultiple-Choice Question 1985 Take G 10 m/s2.: Velocity/mssliversniperNo ratings yet
- 1985 Physics Paper1 Syl 2Document7 pages1985 Physics Paper1 Syl 2api-3736914100% (2)