Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coding
Uploaded by
Sharavana KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Coding
Uploaded by
Sharavana KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Coding: using using using using System; System.Collections.Generic; System.Linq; System.
Text;
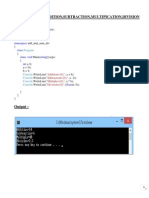
namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class branch { static void Main(string[] args) { int a,b; Console .WriteLine ("Enter the values of a"); a=int.Parse (Console.ReadLine()); int[] n = new int[a]; Console.WriteLine("Enter the values"); for (b = 0; b < a; b++) { n[b] = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); } for (b = 0; b < a; b++) { if(n[b]%2==0) { Console.WriteLine(n[b]+"is EventArgs number"); } else{ Console.WriteLine(n[b]+"is odd no"); } Console.ReadLine(); } } } }
output
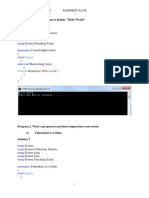
namespace dowhile { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int m1=0, m2=0, m3=0, m4=0, m5=0; float avg; int i, n=0, total=0, ch; Console.WriteLine("Student merit list"); Console.WriteLine("Enter the no of student"); n = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); Console.WriteLine("Enter the marks m1,m2,m3,m4,m5"); for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) { m1 = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); m2 = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); m3 = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); m4 = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); m5 = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); } for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { Console.WriteLine(m1); Console.WriteLine(m2); Console.WriteLine(m3); Console.WriteLine(m4); Console.WriteLine(m5); } Console.WriteLine("Enter the choice:"); Console.WriteLine("\t1.Total\n\t2.Average\n\t3.Exit"); ch = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); do { switch (ch) { case 1: total = m1 + m2 + m3 + m4 + m5; Console.WriteLine(total); break; case 2: avg = total / 5; break; default: Console.WriteLine("press 3 to exit"); break; } } while (ch != 3); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
using using using using
System; System.Collections.Generic; System.Linq; System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int n; n = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); Console.WriteLine(n); foreach (int i in n) { Console.WriteLine(i); if (n < 20) {
Console.WriteLine(" " + n); continue; } if (n == 30) { Console.WriteLine(); n = n + 10; continue; } if (n > 50) { break; Console.WriteLine(" " + n); n = n + 10; } Console.ReadLine(); } } } }
METHOD: using using using using System; System.Collections.Generic; System.Linq; System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication2 { class Passing { static void change(int m) { m = m + 20; } static void swap(ref int x, ref int y) { int temp = x; x = y; y = temp; } static void output(out int p) { p = 1000; } static void Main(string[] args) { int l = 100; change(l); Console.WriteLine("l=" + l); int a = 100, b = 200; Console.WriteLine("BEFORE SWAPPING"); Console.WriteLine("a=" + a); Console.WriteLine("b=" + b); swap(ref a, ref b); Console.WriteLine("AFTER SWAPPING"); Console.WriteLine("a=" + a); Console.WriteLine("b=" + b); int c; output(out c); } } }
You might also like
- Muhammad Hashim Roll - No - 052 - ITDocument17 pagesMuhammad Hashim Roll - No - 052 - ITArslan AzharNo ratings yet
- Awp New CompiledDocument50 pagesAwp New CompiledYogesh PatilNo ratings yet
- C Sharp-1 New eDocument32 pagesC Sharp-1 New emarshmallow12211221No ratings yet
- C# Program To Demonstrate Multilevel InheritanceDocument5 pagesC# Program To Demonstrate Multilevel Inheritancepiyushi gulatiNo ratings yet
- Nested Loop and Conditional Looping ProgramsDocument13 pagesNested Loop and Conditional Looping ProgramsRidhatur RohmatNo ratings yet
- 1-Program To Addition, Subtraction, Multipication, Division: OutputDocument28 pages1-Program To Addition, Subtraction, Multipication, Division: OutputDiveshDuttNo ratings yet
- Lab3 BC00108 KyPLTDocument6 pagesLab3 BC00108 KyPLTkypltbc00108No ratings yet
- Wa0003Document30 pagesWa0003Randy OrtonNo ratings yet
- C# Program to Calculate Quadratic Equation RootsDocument11 pagesC# Program to Calculate Quadratic Equation RootsGhouse cyber cafeNo ratings yet
- Using Using Using Using Using Namespace Class Static Void StringDocument8 pagesUsing Using Using Using Using Namespace Class Static Void StringAlamgir HossainNo ratings yet
- Obtains Four Int Values From The User and Displays The ProductDocument15 pagesObtains Four Int Values From The User and Displays The ProductAnonymous R0vXI894TNo ratings yet
- C# Programming ExamplesDocument77 pagesC# Programming ExamplesDeep SainiNo ratings yet
- Journal CDocument24 pagesJournal CSanikaNo ratings yet
- Using System Class Name (Public Static Void Main (Console - Writeline ("My Name Is Sujit") ) )Document26 pagesUsing System Class Name (Public Static Void Main (Console - Writeline ("My Name Is Sujit") ) )Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Dot Net ProgramsDocument44 pagesDot Net ProgramsAman PadhyNo ratings yet
- C# Code Examples for Tables and SwappingDocument3 pagesC# Code Examples for Tables and SwappingFasih DawoodNo ratings yet
- Practical Assignment No 1 To 9Document46 pagesPractical Assignment No 1 To 9Nishant Sonavane100% (2)
- Lab File: Jamia Hamdard UniversityDocument15 pagesLab File: Jamia Hamdard UniversitymushfiqNo ratings yet
- NET Framework OverviewDocument52 pagesNET Framework Overviewmudhangula jyothsnaNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Programmin 3Document4 pagesBài Tập Programmin 3Le Thanh Nhat Hung (FGW DN)No ratings yet
- Q1. Write A Program To Compute The Area of A TriangleDocument18 pagesQ1. Write A Program To Compute The Area of A TriangleNishant KumariaNo ratings yet
- 19IT470 3IT42 PracticalFileDocument55 pages19IT470 3IT42 PracticalFileAmol TiwariNo ratings yet
- First Assignment C#Document29 pagesFirst Assignment C#jamshed90No ratings yet
- TASK 01:: Name: Syed Tanzeel Ur Rehman ROLL NO: 2020-BSCS-037 Sec: ADocument8 pagesTASK 01:: Name: Syed Tanzeel Ur Rehman ROLL NO: 2020-BSCS-037 Sec: ASahil JagdeshNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Programming 1Document8 pagesBài Tập Programming 1Le Thanh Nhat Hung (FGW DN)No ratings yet
- IndexDocument84 pagesIndexSaeel ShindeNo ratings yet
- C# Lab Programs for Palindrome, Command Line Arguments, Quadratic EquationDocument12 pagesC# Lab Programs for Palindrome, Command Line Arguments, Quadratic EquationSunkadahalli Govindaiah Bhanu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Progarmming 4Document3 pagesBài Tập Progarmming 4Le Thanh Nhat Hung (FGW DN)No ratings yet
- Final AwpDocument62 pagesFinal AwpLucky Lucky100% (1)
- C#.Net Lab Record ProgramsDocument50 pagesC#.Net Lab Record Programsakshay sasiNo ratings yet
- Dot Net LAb Manual - 5th Sem BCADocument18 pagesDot Net LAb Manual - 5th Sem BCAPriyamNo ratings yet
- Lab #3Document7 pagesLab #3Zubair SonijaNo ratings yet
- AwppracticalmanishaDocument70 pagesAwppracticalmanishaAnu stephie NadarNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledКатја ШимуновNo ratings yet
- Write A Program For Error Detecting Code Using CRC-CCITT (16bit)Document43 pagesWrite A Program For Error Detecting Code Using CRC-CCITT (16bit)raspreetNo ratings yet
- C# LabDocument35 pagesC# LabNavee NaveenNo ratings yet
- C# programs demonstrating command line arguments, boxing unboxing, operator overloading, arrays, exceptionsDocument75 pagesC# programs demonstrating command line arguments, boxing unboxing, operator overloading, arrays, exceptionsChandan PandaNo ratings yet
- Practical File Dot Net (Nishu)Document6 pagesPractical File Dot Net (Nishu)PagLi NisHaNo ratings yet
- 6.perform Matrix Operations Using Object: System System - Collections.Generic System - Linq System - TextDocument5 pages6.perform Matrix Operations Using Object: System System - Collections.Generic System - Linq System - Textmarshmallow12211221No ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument29 pagesNew Text DocumentRohan TandekarNo ratings yet
- Awp Real PracDocument90 pagesAwp Real PracSweety RonishaNo ratings yet
- C# Console App CalculationsDocument7 pagesC# Console App Calculationsminh tuan taNo ratings yet
- Using Using Using Using Namespace Class Static Void String Int Int Do Int If IfDocument4 pagesUsing Using Using Using Namespace Class Static Void String Int Int Do Int If IfHerrera IsaccNo ratings yet
- Probleme Rezolvate Subiectul 1 Atestat A 2011Document28 pagesProbleme Rezolvate Subiectul 1 Atestat A 2011Răducu AlbuNo ratings yet
- Nama: Ismia Iwandini NPM: 197006416003 KLS: K.02 Soal: GanjilDocument8 pagesNama: Ismia Iwandini NPM: 197006416003 KLS: K.02 Soal: GanjilismiaiwandiniNo ratings yet
- C# AnswersDocument104 pagesC# Answersshangavi prithivirajNo ratings yet
- NeetikaDocument27 pagesNeetika40 poojaNo ratings yet
- C# programs for arithmetic, series, prime numbersDocument11 pagesC# programs for arithmetic, series, prime numbersDiveshDuttNo ratings yet
- C# Onwords11Document76 pagesC# Onwords11pradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- C# RECORD UpdatedDocument70 pagesC# RECORD UpdatedrlmahanthiNo ratings yet
- VB Programming AssignmentsDocument15 pagesVB Programming AssignmentsRushna AttariaNo ratings yet
- ShaktimanDocument46 pagesShaktimanZoom CommunicationNo ratings yet
- AWT Assignment 1Document11 pagesAWT Assignment 1jaldhi sonagaraNo ratings yet
- C# Program Examples: Palindrome Checker, Command Line Arguments, Matrix MultiplicationDocument20 pagesC# Program Examples: Palindrome Checker, Command Line Arguments, Matrix Multiplicationpankhi_20077474100% (3)
- Jiwaji University Gwalior: (2021-2023) Mba E-Com 2 SEMDocument27 pagesJiwaji University Gwalior: (2021-2023) Mba E-Com 2 SEMAnshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- C#.NET Lab Manual PDFDocument41 pagesC#.NET Lab Manual PDFlibranhitesh7889100% (1)
- algoritams programing 3Document6 pagesalgoritams programing 3Предраг КлепићNo ratings yet
- C# Programs for Temperature Conversion, Area Calculations, and Matrix OperationsDocument47 pagesC# Programs for Temperature Conversion, Area Calculations, and Matrix OperationsDirector Ishu ChawlaNo ratings yet