Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Name
Uploaded by
Michelle SedeñoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Name
Uploaded by
Michelle SedeñoCopyright:
Available Formats
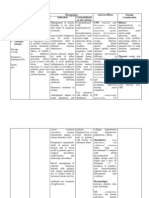
Drug name Generic name: Diazepam Brand name: Diaepam Intensol, Valium Classification: Sedative/hypnotic; skeletal muscle relaxant;
antiepileptic; anxiolytic; benzodiazepine Dosage: 10 mg IM
Therapeutic actions Exact mechanisms of action not understood; acts mainly at the limbic system and reticular formation; may act in spinal cord and at supra spinal sites to produce skeletal muscle relaxation; anxiolytic effects at does well below those necessary to cause sedation
Indications -management of anxiety disorders/for short term relief of symptoms of anxiety -muscle relaxant: adjunct for relief of reflex skeletal muscle spasm due to local pathology -antiepileptic: adjunct in status epilepticus and severe recurrent convulsive seizures
Contra-indications - Hypersensitivity - Cross-sensitivity with other benzodiazepines may occurs - Comatose patients - Pre-existing CNS depression - Uncontrolled severe painUse cautiously in: 1) Hepatic dysfunction 2) Severe renal impairment 3) History of suicide attempt or drug dependence
Adverse effects - CNS: 1) dizziness 2) drowsiness 3) lethargy 4) hangover 5) headache 6) depression - RESP: 1) respiratory depression - CV: 1) hypotension - GI: 1) constipation 2) diarrhea 3) nausea 4) vomiting
Generic name: Methylergometrine Brand name: Methergine
Acts directly on the smooth muscle of the uterus and increases the tone, rate and amplitude of rhythmic contractions through binding and the resultant antagonism
-post-partum hemorrhage and uterine atony, subinvolution -for routine management after delivery of placenta
-hypertension, toxemia, pregnancy
-hypo or hypertension, nausea, vomiting, chest pain, dyspnea, headache, hematuria, thrombophlebitis, water intoxication, hallucination, leg cramps, dizziness, tinnitus, nasal congestion, diarrhea, diaphoresis
Nursing considerations - Monitor BP, PR,RR prior to periodically throughout therapy and frequently during IV therapy. - Assess IV site frequently during administration, diazepam may cause phlebitis and venous thrombosis. - Caution patient to avoid taking alcohol or other CNS depressants concurrently with this medication. - Change from IV therapy to oral therapy as soon as possible. -evaluate patients medical history -assess patient condition -monitor BP and PR before administration -assess allergic reaction like GI disturbances -assess for toxicity -safety measures
You might also like
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsnurse_nurseNo ratings yet
- Diazepam (Valium) Drug StudyDocument1 pageDiazepam (Valium) Drug StudyEmika Dizon100% (7)
- Generic/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Classification Indication Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesGeneric/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Classification Indication Contraindication Side Effect Nursing Responsibilitieserika_banda_1No ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: ClassificationDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Classificationjeck_24No ratings yet
- Diazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexDocument6 pagesDiazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexRene John Francisco100% (1)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamFerdinand Sherwin MorataNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument5 pagesPhenobarbitalapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJJ SumayloNo ratings yet
- RisperdalDocument2 pagesRisperdalAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- DIazepamDocument1 pageDIazepamJonalin Magbanua100% (1)
- Notes 220728 202034Document9 pagesNotes 220728 202034mark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- CNS: Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia, Confusion, Paradoxic RageDocument4 pagesCNS: Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia, Confusion, Paradoxic RageYanna N. CuakiNo ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument50 pagesPsychopharmacologyIbrahim R. AyasrehNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document8 pagesDrug Study 2rey_tengNo ratings yet
- P-Mid Midterm ExamDocument10 pagesP-Mid Midterm ExamIan Mizzel A. DulfinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study No.1 Brand Name: Paracetamol Generic Name: Tempra Classification: Anti-Infectives Dosage: 100mg, 1ml Drops q4hrDocument7 pagesDrug Study No.1 Brand Name: Paracetamol Generic Name: Tempra Classification: Anti-Infectives Dosage: 100mg, 1ml Drops q4hrMary EnsomoNo ratings yet
- SeroquelDocument1 pageSeroquelE100% (1)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamStephanie PeNo ratings yet
- Anti Epileptic AgentsDocument64 pagesAnti Epileptic AgentsPrincess VanquirayNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY3DIAZEDocument1 pageDRUGSTUDY3DIAZEEryn_Casaclang_6640No ratings yet
- DIAZEPAMDocument2 pagesDIAZEPAMRassiel SandovalNo ratings yet
- Anti Epileptic AgentsDocument78 pagesAnti Epileptic AgentsPrincess VanquirayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ShenDocument12 pagesDrug Study ShenLass KazeNo ratings yet
- Problem 2Document9 pagesProblem 2Chan Myae NaingNo ratings yet
- 5 MG Iv BidDocument17 pages5 MG Iv BidhanzreinherNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyJibran Jones GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drug FeaturesDocument9 pagesDrug FeaturesLeah Claudia de OcampoNo ratings yet
- Re QuipDocument1 pageRe QuipKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- PropanolDocument8 pagesPropanolStacey CamilleNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Patient AssessmentDocument5 pagesPreoperative Patient Assessmenthonovezaann.a.campita.ctucvmNo ratings yet
- Drug Study..DokcyDocument7 pagesDrug Study..DokcyPeArl Peralta0% (1)
- ICU Pharmacology: Sean Forsythe M.D. Assistant Professor of MedicineDocument52 pagesICU Pharmacology: Sean Forsythe M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicinecoolboy1990No ratings yet
- PHARMA Practical Revesion CNSDocument26 pagesPHARMA Practical Revesion CNSAhmed samirNo ratings yet
- Muscle RelaxantsDocument20 pagesMuscle RelaxantsJearanell LabraNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic DrugsDocument5 pagesAnesthetic DrugsZuellen Mae Garapan BedañoNo ratings yet
- ICU Pharmacology: Sedatives Analgesics Paralytics PressorsDocument51 pagesICU Pharmacology: Sedatives Analgesics Paralytics Pressorsdevi trismiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Edited FinalDocument10 pagesDrug Study Edited FinalPureza Maye SalapangNo ratings yet
- RUSS Emergency DrugDocument6 pagesRUSS Emergency DrugKat BausaNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Medication: Information Leaflet PriorDocument4 pagesPrescribed Medication: Information Leaflet PriorHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Specific Drug Olanzapine (Classification IndicationDocument14 pagesSpecific Drug Olanzapine (Classification IndicationRIZZA JANE VELASCONo ratings yet
- Drug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsDocument57 pagesDrug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- TemazepamDocument1 pageTemazepamCris TanNo ratings yet
- DIAZEPAMDocument4 pagesDIAZEPAMCay SevillaNo ratings yet
- Brand NameDocument8 pagesBrand NameChristine Joy CamachoNo ratings yet
- Doctor's Order Levodopa +carbidopa 250mg/25mg 1 Tab BIDDocument25 pagesDoctor's Order Levodopa +carbidopa 250mg/25mg 1 Tab BIDspain michaelisNo ratings yet
- DiarryDocument10 pagesDiarryVan Ryan CondenoNo ratings yet
- Anti EpilepticsDocument23 pagesAnti EpilepticsSalman HabeebNo ratings yet
- Temazepam (Restoril)Document1 pageTemazepam (Restoril)E100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyDiolan Novero BagorioNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument5 pagesDiazepamapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesSummary of Product Characteristicsmayra chipanaNo ratings yet
- Drug PresentationDocument32 pagesDrug PresentationManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- I. Anxiolytic and Hypnotic AgentsDocument32 pagesI. Anxiolytic and Hypnotic AgentsDanica Abarquez100% (1)
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Syncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandSyncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hand Tremors, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hand Tremors, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Myasthenia Gravis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMyasthenia Gravis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet