Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Absorption Costing
Uploaded by
Burhan Ahmed CheemaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Absorption Costing
Uploaded by
Burhan Ahmed CheemaCopyright:
Available Formats
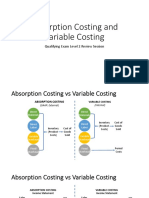
d. Marginal Costing leads to Contribution Margin (CM) then Net Profit.
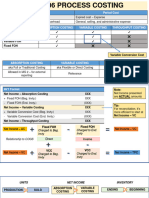
33. Absorption Costing
Sales XXXX Less Cost of Goods SoldOpening Stock XXXX
{Opening Stock x (Fixed FOH Rate/unit +Variable FOH Rate/unit)}
+ Production XXXX
{Units Produced x (Fixed FOH Rate/unit +Variable FOH Rate/unit)}
(-) Closing Stock (XXXX)
{Closing Stock x (Fixed FOH Rate/unit +Variable FOH Rate/unit)}
Cost of Goods Sold XXXX +Under / (-)Over Applied FOH XXXXCost of Goods Sold at Actual XXXX (XXXX) Gross Profit XXXX Less Marketing Expenses (if any)
Fixed Marketing Expenses XXXX+ Variable Marketing Expenses XXXXTotal Marketing Expenses XXXX (XXXX)
Net Profit by Absorption Costing XXXX
Notes to Absorption Costing:e. Over/Under Applied FOHBudgeted Production (Budgeted units x Fixed FOH Rate/unit) XXXX(-) Actual Production (Actual units x Fixed FOH Rate/unit) (XXXX)Over/Under Applied FOH XXXX If Actual Production > Budgeted Production ^ Over Applied FOH
If Actual Production < Budgeted Production
^ Under Applied FOHf. If Over Applied FOH ^ Minus from COGS at Actualg. If Under Applied FOH ^ Add in COGS at Actualh. Absorption Costing leads to Gross Profit (GP) then Net Profit . Confusing Terminologies of Cost Accounting 1. Inventory = Stock 2. Re-Order Period = Lead Time3. EOQ = Re-Order Quantity4. Standard = Budgeted5. Marginal Costing = Direct Costing6. Absorption Costing = Full Costing = Factory Cost = Production Cost7.
Total Production Cost = Manufacturing Cost...................................................................................... .......................................................... Best Regards, (DILAWAR ABBAS) B. Com (IT), MBA (Finance)digital_darwaish@hotmail.com
You might also like
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cost Accounting Formula'sDocument7 pagesCost Accounting Formula'sdigital_darwaish82% (38)
- Cost Accounting Imporatant FormulasDocument3 pagesCost Accounting Imporatant FormulassanthimbaNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costs (Extra Reading)Document15 pagesMarginal Costs (Extra Reading)Gabriel BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Financial Tools Week 2 Block BDocument15 pagesFinancial Tools Week 2 Block BBelen González BouzaNo ratings yet
- Absorption Marginal CostingDocument36 pagesAbsorption Marginal CostingsamiNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Variable CostingDocument12 pagesAbsorption and Variable CostingMatrika ThapaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Absorption Costing NotesDocument14 pagesDirect and Absorption Costing NotesAnru PienaarNo ratings yet
- Product CostingDocument34 pagesProduct CostingrhearomefranciscoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Accounting (Financial Statements) - 1-1Document8 pagesChapter 10 - Accounting (Financial Statements) - 1-1Sonali AnandNo ratings yet
- Absorption & Direct CostingDocument22 pagesAbsorption & Direct CostingMuhammad azeemNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingDocument28 pagesActivity Based CostingApril TorresNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Cost Concepts and Cost Behavior COGS Merchandising CompanyDocument6 pagesTopic 1: Cost Concepts and Cost Behavior COGS Merchandising CompanyKezNo ratings yet
- Absorption CostingDocument34 pagesAbsorption Costinggaurav pandeyNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting: Step 1: Determine The Highest and Lowest Activity and The Costs Associated ThereuntoDocument8 pagesCost Accounting: Step 1: Determine The Highest and Lowest Activity and The Costs Associated ThereuntoRinoah Mae OlorosoNo ratings yet
- Absorption MarginalDocument17 pagesAbsorption MarginalSHIVANSH BANSALNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 - FormulaDocument3 pagesCh. 1 - FormulaKen KensNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Income Measurement and ReportingDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Income Measurement and ReportingOmisha KhatiwadaNo ratings yet
- Persys Midterms FormulasDocument2 pagesPersys Midterms Formulaslingat airenceNo ratings yet
- A2 Accounting Revision Kit (1)Document135 pagesA2 Accounting Revision Kit (1)Waniya AmirNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost ManagementDocument6 pagesStrategic Cost ManagementMa. Elizabeth PaglicawanNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance Analysis BreakdownDocument26 pagesStandard Costing & Variance Analysis BreakdownAnuruddha RajasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Strat Cost Handout 02 CVP Analysis Updated 0212 - CompressDocument17 pagesStrat Cost Handout 02 CVP Analysis Updated 0212 - CompressAerwyna AfarinNo ratings yet
- Assignment: VarianceDocument3 pagesAssignment: VarianceFarhan MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Marginal Absorption Costing Week 6Document9 pagesMarginal Absorption Costing Week 6Susan MberiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Absorotion-Direct Costing Final-1Document30 pages1 Absorotion-Direct Costing Final-1moss roffattNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Absorption and Marginal CostingDocument31 pagesChapter 1 - Absorption and Marginal CostingTrinhNo ratings yet
- Cost-Formula: Separating Variable and Fixed Costs for Profit ModelingDocument3 pagesCost-Formula: Separating Variable and Fixed Costs for Profit ModelingStanley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Cost-Formula: Separating Variable and Fixed Costs for Profit ModelingDocument3 pagesCost-Formula: Separating Variable and Fixed Costs for Profit ModelingStanley AquinoNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Marginal CostingDocument19 pagesAbsorption and Marginal CostingsadikzeenatNo ratings yet
- CH - 3 Cost AccountingDocument23 pagesCH - 3 Cost AccountingKhushali OzaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3-4 CacDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 3-4 CacCARLA MEDRANONo ratings yet
- MS 06-06 Process CostingDocument6 pagesMS 06-06 Process CostingxernathanNo ratings yet
- Dr. (CA) Ankita Jain: Unit - IiiDocument11 pagesDr. (CA) Ankita Jain: Unit - IiiBHAVYA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing Reconciliation StatementDocument4 pagesAbsorption Costing Reconciliation Statementali_sattar15No ratings yet
- Five-Page Summary of Key Concepts:: Cost ClassificationsDocument16 pagesFive-Page Summary of Key Concepts:: Cost ClassificationsDar FayeNo ratings yet
- Marginal & Absorption Costing ST Academy With SolutionDocument14 pagesMarginal & Absorption Costing ST Academy With SolutionFaisal KhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Accounts NotesDocument9 pagesManufacturing Accounts NotesFegason FegyNo ratings yet
- Marginal vs Absorption Costing ComparisonDocument12 pagesMarginal vs Absorption Costing Comparisonhamza khanNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing: by - Jatin Pundhir I.I.L.M CmsDocument11 pagesMarginal Costing: by - Jatin Pundhir I.I.L.M CmsJatin PundhirNo ratings yet
- Chargeable ExpensesDocument33 pagesChargeable ExpensesMahmud MugdhoNo ratings yet
- Sba ComputationsDocument1 pageSba ComputationsAbdul Jamal NassirNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Variable Costing ReviewDocument13 pagesAbsorption and Variable Costing ReviewRodelLabor100% (1)
- Cost ManagementDocument23 pagesCost ManagementEswara ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cost Lectures DR - Mohiy SamyDocument12 pagesCost Lectures DR - Mohiy SamyEiad WaleedNo ratings yet
- Cost SheetDocument5 pagesCost Sheetgaurav gauravNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting PDFDocument22 pagesCost Accounting PDFLaiba Javed Javed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Accounting FormulaDocument4 pagesAccounting FormulaAndrea AbayaNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument79 pagesCVP AnalysisMRIDUL GOELNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis HandoutDocument24 pagesCVP Analysis HandoutAlexis RiveraNo ratings yet
- CA & CMA StatementsDocument2 pagesCA & CMA StatementsArsalan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Analisis Varians Dan Standar Products CostsDocument4 pagesAnalisis Varians Dan Standar Products CostsAhad KamisNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing vs Absorption CostingDocument23 pagesMarginal Costing vs Absorption CostingAfzal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Formula SummaryDocument4 pagesManagerial Accounting Formula Summaryمنیر ساداتNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument6 pagesCost AccountingMj PacunayenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Mixx MineNo ratings yet