Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F3-IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets
Uploaded by
Nadia AhmedOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F3-IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets
Uploaded by
Nadia AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
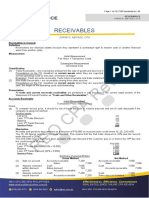
IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent assets
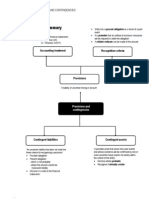
Provision: is a liability where there is uncertainty over its timing or the amount at which it will be settled. A provision should be recognised where: i.e. established past practice
An entity has a present obligation (legal or constructive) as a result of a past event; It is probable that there will be an outflow of resources in the form of cash or other assets; and A reliable estimate can be made of the amount A provision should not be recognised in respect of future operating losses since there is no present obligation arising from a past event.
Contingent liability: arises where a past event may lead to an entity having a liability in the future but the financial impact of the event will only be confirmed by the outcome of some future event not wholly within the entitys control. - A contingent liability should be disclosed in the financial statements unless the possible outflow of the resources is thought to be remote. Contingent asset: is a potential asset that arises from past events but where existence can only be confirmed by the outcome of future events not wholly within an entitys control. - A contingent asset should be disclosed in the financial statements only when the expected inflow of economic benefits is probable. - However, when the realisation of income is virtually certain, then the related asset is not a contingent asset and its recognition is appropriate (DR Asset: Receivable, CR Other income)
rahatdj@gmail.com
Page 1
You might also like
- Ias 37 Provisions Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets SummaryDocument5 pagesIas 37 Provisions Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets SummaryChristian Dela Pena67% (3)
- FAR 04 - ReceivablesDocument10 pagesFAR 04 - ReceivablesSheira Mae Sulit Napoles100% (1)
- Provision Contingent LiabilityDocument12 pagesProvision Contingent LiabilityGinamae CayangcangNo ratings yet
- Translation of Foreign FSDocument7 pagesTranslation of Foreign FSLloyd SonicaNo ratings yet
- Audit of LiabilitiesDocument12 pagesAudit of LiabilitiesAcier KozukiNo ratings yet
- AFAR-03 (Corporate Liquidation)Document6 pagesAFAR-03 (Corporate Liquidation)Maricris AlilinNo ratings yet
- AFAR 13 Derivatives and Hedge Accounting Under PFRS 9Document10 pagesAFAR 13 Derivatives and Hedge Accounting Under PFRS 9Louie RobitshekNo ratings yet
- Provisions and Contingencies SlidesDocument28 pagesProvisions and Contingencies SlidesAinnur Arifah100% (1)
- Module 1.6 - Joint Arrangements PDFDocument3 pagesModule 1.6 - Joint Arrangements PDFMila MercadoNo ratings yet
- Consolidation at Subsequent DateDocument7 pagesConsolidation at Subsequent DateJulie Mae Caling MalitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26Document8 pagesChapter 26Mae Ciarie YangcoNo ratings yet
- Module 17-Bonds-PayableDocument12 pagesModule 17-Bonds-PayableJehPoyNo ratings yet
- Buscom ReviewerDocument16 pagesBuscom ReviewereysiNo ratings yet
- Business TaxesDocument47 pagesBusiness TaxesJoyce MorganNo ratings yet
- CPAR Financial StatementsDocument5 pagesCPAR Financial StatementsAnjo EllisNo ratings yet
- Theories FAR - Special TopicsDocument17 pagesTheories FAR - Special TopicsLuiNo ratings yet
- JPIA EngagementDocument4 pagesJPIA EngagementcristinatubleNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Framework and RegulationDocument13 pagesModule 1 - Framework and RegulationLuiNo ratings yet
- Case 2Document4 pagesCase 2Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive Income: Irene Mae C. Guerra, CPA, CTTDocument21 pagesStatement of Comprehensive Income: Irene Mae C. Guerra, CPA, CTTRuaya AilynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 LiabilitiesDocument16 pagesChapter 1 LiabilitiesAlvin Dantes100% (1)
- Pfrs 16 LeasesDocument4 pagesPfrs 16 LeasesR.A.No ratings yet
- Toa PreboardDocument9 pagesToa PreboardLeisleiRagoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Business Combination Consolidated FS Subsequent To Aquisition DateDocument21 pagesModule 5 Business Combination Consolidated FS Subsequent To Aquisition DateJulliena BakersNo ratings yet
- Business Combination and ConsolidationDocument21 pagesBusiness Combination and ConsolidationCristel TannaganNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips - Effective Interest MethodDocument8 pagesSilo - Tips - Effective Interest MethodFuri Fatwa DiniNo ratings yet
- Government AccountingDocument10 pagesGovernment AccountingKristin Zoe Newtonxii PaezNo ratings yet
- Notes Payable and Debt RestructuringDocument14 pagesNotes Payable and Debt Restructuringglrosaaa cNo ratings yet
- Philippine Interpretations Committee (Pic) Questions and Answers (Q&As)Document6 pagesPhilippine Interpretations Committee (Pic) Questions and Answers (Q&As)verycooling100% (1)
- Investment in Securities (Notes)Document5 pagesInvestment in Securities (Notes)Karla BordonesNo ratings yet
- TOA 011 - Depreciation, Revaluation and Impairment With AnsDocument5 pagesTOA 011 - Depreciation, Revaluation and Impairment With AnsSyril SarientasNo ratings yet
- Foreign Currency TransactionsDocument24 pagesForeign Currency TransactionsCAPSNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Provisions - Contingent Liabilities and Contingent AssetsDocument23 pagesLecture 3 Provisions - Contingent Liabilities and Contingent AssetsBrenden KapoNo ratings yet
- Accounts Receivable - Demo TeachingDocument59 pagesAccounts Receivable - Demo TeachingNicole Flores100% (1)
- Accounting ChangesDocument5 pagesAccounting Changeskty yjmNo ratings yet
- PAS 34 Interim Financial Reporting: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesPAS 34 Interim Financial Reporting: Learning ObjectivesFhrince Carl CalaquianNo ratings yet
- Exercise No.4 Bus. Co.Document56 pagesExercise No.4 Bus. Co.Jeane Mae BooNo ratings yet
- CPAR Conceptual FrameworkDocument5 pagesCPAR Conceptual Frameworkrommel_007No ratings yet
- 01 Introduction and FormationDocument18 pages01 Introduction and Formationm_kobayashiNo ratings yet
- Toa - Preboard - May 2016Document11 pagesToa - Preboard - May 2016Kenneth Bryan Tegerero Tegio100% (1)
- Int. Acctg. 3 - Valix2019 - Chapter 3Document12 pagesInt. Acctg. 3 - Valix2019 - Chapter 3Toni Rose Hernandez Lualhati100% (1)
- Lecture Notes On Trade and Other ReceivablesDocument5 pagesLecture Notes On Trade and Other Receivablesjudel ArielNo ratings yet
- Interest Bearing: Chapter 5 - Notes ReceivableDocument4 pagesInterest Bearing: Chapter 5 - Notes ReceivableEUNICE NATASHA CABARABAN LIMNo ratings yet
- Property, Plant and EquipmentDocument6 pagesProperty, Plant and EquipmenthemantbaidNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Concepts and TechniquesDocument277 pagesManagement Accounting Concepts and TechniquesCalvince OumaNo ratings yet
- 09d Investment in Equity Securities Cost Equity Method PDFDocument76 pages09d Investment in Equity Securities Cost Equity Method PDFXNo ratings yet
- Audit of Receivable PDFDocument7 pagesAudit of Receivable PDFRyan Prado Andaya100% (1)
- Acctg 100C 08Document2 pagesAcctg 100C 08Maddie ManganoNo ratings yet
- Nfjpia Nmbe Far 2017 Ans-1Document10 pagesNfjpia Nmbe Far 2017 Ans-1Stephen ChuaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For DerivativesDocument8 pagesAccounting For DerivativesPrateek PatelNo ratings yet
- Financial Asset MILLANDocument6 pagesFinancial Asset MILLANAlelie Joy dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesQuiz 1 Solutionsgovt2No ratings yet
- Substantive Test of CashDocument16 pagesSubstantive Test of CashmanuelaristotleNo ratings yet
- Summary of Pas 36Document5 pagesSummary of Pas 36Elijah MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Events After The Reporting Period PDFDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Events After The Reporting Period PDFCaroline Bagsik100% (1)
- Misstatements in The Financial StatementsDocument56 pagesMisstatements in The Financial StatementsKimberly Pilapil MaragañasNo ratings yet
- Afar NotesDocument20 pagesAfar NotesChristian James Umali BrionesNo ratings yet
- IAS 37 - Provisons & ContingencyDocument2 pagesIAS 37 - Provisons & ContingencyJOEL VARGHESE CHACKO 2011216No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 LiabilitiesDocument5 pagesChapter 12 LiabilitiesAngelica Joy ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Chap - 1 IAS 37 Provisions and ContingenciesDocument12 pagesChap - 1 IAS 37 Provisions and ContingenciesSandyNo ratings yet
- Allowance For Doubtful DebtsDocument1 pageAllowance For Doubtful DebtsNadia AhmedNo ratings yet
- IAS 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument1 pageIAS 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodNadia AhmedNo ratings yet
- 14 Control AccountsDocument1 page14 Control AccountsNadia AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter Summary: 13: Provisions and ContingenciesDocument1 pageChapter Summary: 13: Provisions and ContingenciesNadia AhmedNo ratings yet
- 11 Accruals and PrepaymentsDocument1 page11 Accruals and PrepaymentsNadia AhmedNo ratings yet
- 10 Intangible Non-Current AssetsDocument1 page10 Intangible Non-Current AssetsNadia AhmedNo ratings yet
- Kaplan ACCA F3 (Int) Slides - Dec 2011Document58 pagesKaplan ACCA F3 (Int) Slides - Dec 2011Sohaib Khalid AccaNo ratings yet
- 9 Tangible Non-Current AssetsDocument1 page9 Tangible Non-Current AssetsNadia AhmedNo ratings yet
- 8 InventoryDocument1 page8 InventoryNadia AhmedNo ratings yet
- Trial Balance Errors & Rectification 1Document21 pagesTrial Balance Errors & Rectification 1Manju NathNo ratings yet