Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Primary Alcohol: Contains 2 Hydrogen's Connected To The Carbon Atom
Primary Alcohol: Contains 2 Hydrogen's Connected To The Carbon Atom
Uploaded by
Anum TauqirOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Primary Alcohol: Contains 2 Hydrogen's Connected To The Carbon Atom
Primary Alcohol: Contains 2 Hydrogen's Connected To The Carbon Atom
Uploaded by
Anum TauqirCopyright:
Available Formats
Alcohols: Contains a hydroxyl group C-OH 3 types of alcohols. Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary.
Primary Alcohol: Contains 2 Hydrogens connected to the carbon atom with the OH group on there.
Secondary Alcohol: Contains 1 Hydrogen connected to the carbon group with the OH group on there.
Tertiary Alcohol: No Hydrogens connected to the carbon with the OH group.
Polarities:
Alcohols are all polar molecules since carbon, oxygen and hydrogen all have different electronegativies.
Physical Properties:
High melting point and boiling point than alkanes of comparable molar mass. Soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding.
Summary of Alcohol Oxidations: Oxidising agent used is H2SO4(source of H+) and Potassium Dichromate(K2Cr2O7)
By heating and immediately distilling the product, oxidation can be stopped at aldehyde stage. By Refluxing with excess of the oxidising agent, further oxidation take place to form the carboxylic acid.
By heating with H+/Cr2O7 , a secondary alcohol can be oxidised to
form a keytone.
Reaction with Bromide Ions in acid
-Most reactions of alcohol require the presence of an acid.
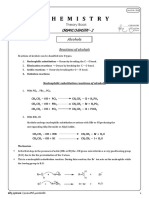
Dehydration of alcohols. When an alcohol is refluxed with a concentrated acid catalyst such as sulphuric acid H2SO4, or Phosphoric acid(H3PO4), and elimination reaction takes place: Water is eliminated of an alkenes. C2H5OHC2H4 + H20 Test for Alcohols: Alcohols react with Sodium releasing Hydrogen gas. The reaction involves the breaking of the O-H bond of the alcohol.
2C2H5OH + 2Na 2C2H5ONa
+ + H2
You might also like
- Alcohol: Boiling Points and Water SolubilitiesDocument4 pagesAlcohol: Boiling Points and Water SolubilitiesChelsea ManioNo ratings yet
- Definitions Topic 4.2.1 Alcohols OCR A Chemistry A LevelDocument2 pagesDefinitions Topic 4.2.1 Alcohols OCR A Chemistry A LevelCHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Notes On Alcohols, Haloalkanes and AnalysisDocument2 pagesNotes On Alcohols, Haloalkanes and Analysisfletcherberryheath2006No ratings yet
- Physical Properties of AlcoholDocument4 pagesPhysical Properties of AlcoholrhiNo ratings yet
- The Alchemy of Alcohols:: A Beginner's Guide in Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesThe Alchemy of Alcohols:: A Beginner's Guide in Organic ChemistrypentojochaunceyNo ratings yet
- Organic Presentation: Maam Sophia AwaisDocument30 pagesOrganic Presentation: Maam Sophia AwaisAMMAR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Hasan Sayginel: Edexcel A Level Organic ChemistryDocument41 pagesHasan Sayginel: Edexcel A Level Organic ChemistryDEEBANNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of AlcoholsDocument24 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of AlcoholsmeerasahibfarhanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 2Document15 pagesAlcohols 2Junaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Lectures 19-22 (LB) Alcohols-Phenols-EthersDocument61 pagesLectures 19-22 (LB) Alcohols-Phenols-Ethersvintu pvNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Ethers CHM457Document51 pagesAlcohols and Ethers CHM457AIMAN IMAN SHAIFUDDINNo ratings yet
- Hydroxy CompoundDocument37 pagesHydroxy CompoundZuhailimuna MudaNo ratings yet
- Organic Reactions PPT AlcoholsDocument43 pagesOrganic Reactions PPT Alcoholssmithsashay74No ratings yet
- Lab 3 AlcoholDocument11 pagesLab 3 AlcoholalihusseinNo ratings yet
- AlcoholDocument138 pagesAlcoholDidi LeraNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of AlcoholsDocument5 pagesOxidation of AlcoholsAna Sofia Guzman FernandezNo ratings yet
- Name - Shivpoojan Singh Course-B.Sc (Hon.) Maths ROLL NO - 202110203110008Document17 pagesName - Shivpoojan Singh Course-B.Sc (Hon.) Maths ROLL NO - 202110203110008Siddhant PatelNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 4 (Organic Chemistry II) Properties of Alcohols: Structure, Reactions and Identification of AlcoholsDocument11 pagesEXPERIMENT 4 (Organic Chemistry II) Properties of Alcohols: Structure, Reactions and Identification of AlcoholsNor Ashikin IsmailNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of The Alcohols Alcohols: Monohydric C H OHDocument23 pagesChemistry of The Alcohols Alcohols: Monohydric C H OHAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- Alcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction: Central Linking Role of Alcohols and CarbonylsDocument12 pagesAlcohols From Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction: Central Linking Role of Alcohols and CarbonylsAmihanNo ratings yet
- Hydroxy CompoundsDocument9 pagesHydroxy Compoundschong56No ratings yet
- UNIT - 11. Alcohols Phenols and Ethers - NotesDocument17 pagesUNIT - 11. Alcohols Phenols and Ethers - NotesAngelina DaisyNo ratings yet
- Alcohols ClassDocument29 pagesAlcohols ClassRyan JamesNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesDocument62 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesSubhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols Thiols and Ethers SimpleDocument58 pagesAlcohols Phenols Thiols and Ethers Simplevin ocangNo ratings yet
- 16 Hydroxyl compound-24-STDDocument38 pages16 Hydroxyl compound-24-STDManh Doan DucNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Phenol 2Document18 pagesAlcohol and Phenol 2Nayem Uddin ToukirNo ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument24 pagesHydrogensamuel kpamiosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes: © 2006 Thomson Higher EducationDocument70 pagesChapter 7 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes: © 2006 Thomson Higher EducationmacybnzNo ratings yet
- Alcoholes 3Document47 pagesAlcoholes 3Дана ЧилибаеваNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument74 pagesAlcoholsSmit PatelNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Ethers and PhenolsDocument45 pagesAlcohols, Ethers and Phenolsshivam08No ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDocument21 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and EtherAditya NandaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & EthersDocument27 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & Ethershgp9ms5gjcNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xii-Chem-11. Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument17 pagesHsslive-Xii-Chem-11. Alcohols Phenols and EthersHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- CHM 121 Lecture NoteDocument13 pagesCHM 121 Lecture NoteOyedotun TundeNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument36 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersHaiDer GrNo ratings yet
- AlcoholDocument78 pagesAlcoholMike EzioNo ratings yet
- Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7Document52 pagesStructure and Synthesis of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 7haha_le12100% (1)
- Xii CH-7 Synopsis Chemistry CCWSDocument10 pagesXii CH-7 Synopsis Chemistry CCWSTanmay RawatNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Alcohol PhenolDocument17 pagesCH 11 Alcohol Phenolsimran ranaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-10 SM Theory Book 2 EM For 2022GRDocument19 pagesUnit 7-10 SM Theory Book 2 EM For 2022GRThilanka LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Alchohols Phenols and EthersDocument5 pagesAlchohols Phenols and EthersPritika Yamini SaiNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Reaction Mechanism of AlcoholDocument26 pagesPreparation and Reaction Mechanism of AlcoholAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Shobhit NirwanDocument26 pagesHydrogen Shobhit NirwanANMOL SHREYAMNo ratings yet
- Senyawa KarbonilDocument61 pagesSenyawa KarbonilsalmaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 HCDocument22 pagesPart 1 HCGerald AquinoNo ratings yet
- ALKANOLSDocument25 pagesALKANOLSKoki KingNo ratings yet
- 07 - Hydroxy Compounds Tutor S PDFDocument35 pages07 - Hydroxy Compounds Tutor S PDFArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document45 pagesChapter 7Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- 202004032240234952abha Carbonyl Compounds PDFDocument14 pages202004032240234952abha Carbonyl Compounds PDFSrikeshav BNo ratings yet
- AldehydeDocument38 pagesAldehydeNischal AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Outline: Prepared by Andrea D. LeonardDocument53 pagesOutline: Prepared by Andrea D. LeonardCatherine Joy SalongaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Diols, TriolsDocument32 pagesAlcohols, Diols, TriolsShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Alkyl HalidesDocument27 pagesAlkyl HalidesCATHERINE BAGUIORONo ratings yet
- 241 Chem CH-1: AlcoholsDocument21 pages241 Chem CH-1: AlcoholsAlanoud AllaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenols and EthersDocument13 pagesAlcohol Phenols and EthersShivaanee SK100% (1)
- Alcohols 1Document13 pagesAlcohols 1Suresh VedpathakNo ratings yet
- Hydro CarbonsDocument3 pagesHydro CarbonsTomas BNo ratings yet