Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
Uploaded by
Anisah YusofOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Uploaded by
Anisah YusofCopyright:
Available Formats
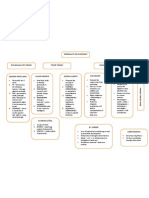
PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT PSYCHOANALYTIC THEORY BEHAVIOURAL THEORY HUMANISTIC THEORY TRAITS THEORY SIGMUND FREUD (1933) .
Personality has 3 parts; 1.ID Unconscious, Id will reduce tension through pleasure principle 2.EGO governed by reality principle, delay discharge of tension until appropriate object & environment are found. 3.SUPEREGO moral & standards of society, good & bad, right & wrong, moral principle. WILLIAM SHELDON .Used body build to identify personality & behaviour. 1.ENDOMORPH (round & soft friendly, happygo-lucky) 2.MESOMORPH (Strong & muscular active, energetic) 3.ECTOMORPH (slim & tall introvert, intelligent) GORDON ALLPORT .Proposed the concept of disposition 1.CARDINAL DISPOSITIONS an individual s entire lifestyle 2.CENTRAL DISPOSITIONS consistent tendencies (influence is limited) 3.SECONDARY DISPOSITIONS surface in specific situations RAYMOND CATTELL
.2 types of traits: 1.SOURCE underlying aspects of personality 2.SURFACE visible aspects of personality. CARL ROGERS .Stressed the critical role of the self-image .The way we see ourselves, our abilities and relationships. .Highly subjective depending on feelings. .Failure to integrate experiences will lead to maladjustments & abnormal behaviour. B.F. SKINNER .Laws of operational conditioning is used in personality development. .Humans learn through external factors. .Needs - ve & + ve reinforcement to strengthen a behaviour. .If reinforcer removed behaviour extincts. ABRAHAM MASLOW .Theory of Selfactualisation. .People always pursue the highest & most idealistic aims. .Human are driven by various motives. .Physiological needs > safety > belongingness > self-esteem > knowledge > aesthetic > selfactualisation. ALBERT BANDURA .Social Learning Theory .We learn something through observation.
You might also like
- Senarai Guru SK (Felda) Palong 5: Bil Nama CatatanDocument1 pageSenarai Guru SK (Felda) Palong 5: Bil Nama CatatanAnisah YusofNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Daily Lesson Plans: Skills Pedagogy (Strategy/Activity)Document6 pagesYear 5 Daily Lesson Plans: Skills Pedagogy (Strategy/Activity)Anisah YusofNo ratings yet
- RPH MTHDocument27 pagesRPH MTHAnisah YusofNo ratings yet
- Type of SentencesDocument1 pageType of SentencesAnisah YusofNo ratings yet
- Rekod Transit PBD Bi - Y6Document8 pagesRekod Transit PBD Bi - Y6Anisah YusofNo ratings yet
- RPH MTHDocument27 pagesRPH MTHAnisah YusofNo ratings yet
- Name: - ClassDocument7 pagesName: - ClassAnisah YusofNo ratings yet
- Year 1 (Revised) 2017 English TxbookDocument152 pagesYear 1 (Revised) 2017 English TxbookAnisah YusofNo ratings yet
- Picture Maze 1) Sail, Sail, Sail 2) Sweet, Nail, Nail 3) Green, Sweet, Sail 4) Nail, Green, Sweet 5) Sail, Nail, Sail 6) Sweet, Sail, NailDocument1 pagePicture Maze 1) Sail, Sail, Sail 2) Sweet, Nail, Nail 3) Green, Sweet, Sail 4) Nail, Green, Sweet 5) Sail, Nail, Sail 6) Sweet, Sail, NailAnisah YusofNo ratings yet
- Personality DevelopmentDocument1 pagePersonality DevelopmentAnisah YusofNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)