100% found this document useful (1 vote)
786 views3 pagesEmbedded Application Design with PIC
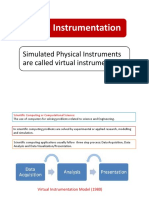
The document discusses designing an embedded application using a PIC microcontroller to create a temperature indicator. It includes the circuit design in Proteus, the C program code, and an explanation of the program. Students learn simulation software, embedded C programming, and how to build systems using microcontrollers by completing this project.
Uploaded by
Rahul PolCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
786 views3 pagesEmbedded Application Design with PIC
The document discusses designing an embedded application using a PIC microcontroller to create a temperature indicator. It includes the circuit design in Proteus, the C program code, and an explanation of the program. Students learn simulation software, embedded C programming, and how to build systems using microcontrollers by completing this project.
Uploaded by
Rahul PolCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd