Professional Documents
Culture Documents
sm3 004
Uploaded by
Sadie HnatowOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
sm3 004
Uploaded by
Sadie HnatowCopyright:
Available Formats
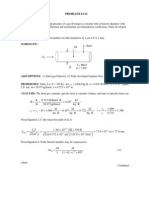
PROBLEM 3.
4
KNOWN: Desired inner surface temperature of rear window with prescribed inside and outside air conditions. FIND: (a) Heater power per unit area required to maintain the desired temperature, and (b) Compute and plot the electrical power requirement as a function of T,o for the range -30 T,o 0C with ho of 2, 20, 65 and 100 W/m2K. Comment on heater operation needs for low ho. If h ~ Vn, where V is the vehicle speed and n is a positive exponent, how does the vehicle speed affect the need for heater operation? SCHEMATIC:
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Steady-state conditions, (2) One-dimensional heat transfer, (3) Uniform heater flux, q , (4) Constant properties, (5) Negligible radiation effects, (6) Negligible film resistance. h PROPERTIES: Table A-3, Glass (300 K): k = 1.4 W/mK. ANALYSIS: (a) From an energy balance at the inner surface and the thermal circuit, it follows that for a unit surface area,
T ,i Ts,i 1 hi
q = h
+ q = h
o
Ts,i T ,o L k + 1 ho
and that q = h
o o
Ts,i T ,o L k + 1 ho
T ,i Ts,i 1 hi
2 2
15 C 10 C 0.004 m 1.4 W m K +
1
2
25 C-15 C 1
2
= (1370 100 ) W m = 1270 W m
<
65 W m K 10 W m K
(b) The heater electrical power requirement as a function of the exterior air temperature for different exterior convection coefficients is shown in the plot. When ho = 2 W/m2K, the heater is unecessary, since the glass is maintained at 15C by the interior air. If h ~ Vn, we conclude that, with higher vehicle speeds, the exterior convection will increase, requiring increased heat power to maintain the 15C condition.
3500 3000 Heater power (W/m^2) 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 -30 -20 -10 0
Exterior air temperature, Tinfo (C) h = 20 W/m^2.K h = 65 W/m^2.K h = 100 W/m^2.K
COMMENTS: With q = 0, the inner surface temperature with T,o = -10C would be given by h
T ,i Ts,i T ,i T ,o = 1 hi 0.10 = = 0.846, 1 h i + L k + 1 h o 0.118
or
Ts,i = 25 C 0.846 35 C = 4.6 C .
( )
o
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- CH 14Document82 pagesCH 14Sadie Hnatow75% (4)
- sm9 010Document1 pagesm9 010Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document82 pagesCH 14Sadie Hnatow75% (4)
- sm8 126Document1 pagesm8 126Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 001Document1 pagesm9 001Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 008Document1 pagesm9 008Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm9 004Document1 pagesm9 004Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 119Document1 pagesm8 119Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 125Document1 pagesm8 125Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 120Document1 pagesm8 120Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 116Document2 pagessm8 116Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 123Document1 pagesm8 123Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 117Document3 pagessm8 117Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 114Document2 pagessm8 114Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 089Document2 pagessm5 089Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 093Document1 pagesm5 093Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 087Document2 pagessm5 087Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm8 113Document1 pagesm8 113Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- sm5 084Document3 pagessm5 084Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet