Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
kret_26Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled
Uploaded by
kret_26Copyright:
Available Formats
Case facts Was founded by John C.
Lincoln in 1895 to manufacture electric motors and genera tors Headquartered in Euclid, Ohio, a suburb of Cleveland Lincoln Electric had been the worlds largest manufacturer of arc welding products for more than 30 years. Manufactured more than 40% of the arc welding equipment and supplies sold in US in 1974. Domestic net income was $17.5M on sales of $237M Approximately 48% of employees were shareholders in 1975 Problem statement How can the Lincolns philosophy and culture/norms implement the strategy of the c ompany successfully? Analysis
Strategy : 1) To build quality products at a lower cost 2) To concentrate on reducing costs and passing the savings through to the customer by continuously lowering prices 3) To give to the worker and the stockholders a higher return How do the companys philosophies implement this strategy? Philosophy, culture/norms Implementation Results Value in Individual 1)competition and adequate incentives enable every peopl e to develop to his or her fullest potential Compensation policies Wages based on piecework output A year-end bonus system Guaranteed employment for all workers Incentive management should be fair - Piecework price cannot be changed because the worker is making too much money. - System is open to challenge piecework price which is established by A Time Stu dy Department Increase of efficiency the labor cost per piece will be relative ly small and the overhead will be still less Guarantee of quality because employees were not paid for defective work Provides a tool to motivate all employees through bonuses that redistribute a lar ge portion of the corporation s yearly profits. There is a heightened sense of ownership in the company from top to bottom Open communication allows top management to get better acquainted with their empl oyees and to encourage cooperation and thus to maintain trust between employees and executives 2)Equality for every worker There are no privileged parking spaces, executive dining room, or fancy furnishings at company headquarters Organizational hierarchy was flat, with few levels between the bottom and the to p 3)Worker consultations and Open communication Maintained an open door to all employees Created an Advisory Board that has representatives of the workers who meet with executives twice a month A 12-member board of middle managers which met with executives once a month
Managements concern for the worker Sharing rewards employees, customers, shareholders Dividend payout policy h ad been to pay to the suppliers of capital a fair return each year for its use The customers get a proper share of the saving in lower price An employees earnings and promotion are in direct proportion to his individual co ntribution toward the companys success Management control system 1) Structure 2) Criteria 3) Measurement 4) Rewards and incentives
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- DirtyMobs' Ultimate Matchup GuideDocument5 pagesDirtyMobs' Ultimate Matchup GuideTempest JannaNo ratings yet
- Muhammad v. Hall, 10th Cir. (2017)Document12 pagesMuhammad v. Hall, 10th Cir. (2017)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Fuzzys CodesDocument39 pagesFuzzys CodesJak JakNo ratings yet
- The BrigadeDocument517 pagesThe Brigadele_chiffre4860100% (3)
- Handout of English For PsychologyDocument75 pagesHandout of English For PsychologyRivan Dwi AriantoNo ratings yet
- Leading a Community Through Integrity and CourageDocument2 pagesLeading a Community Through Integrity and CourageGretchen VenturaNo ratings yet
- The Ontological Argument.: A Basic IntroductionDocument12 pagesThe Ontological Argument.: A Basic IntroductionJas PalNo ratings yet
- Bombardier CityfloDocument14 pagesBombardier CityfloBiju KmNo ratings yet
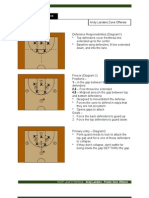
- Andy Landers - Freeze Zone OffenseDocument6 pagesAndy Landers - Freeze Zone OffenseWinston Brown100% (1)
- A Study On Inventory Management Towards Organizational Performance of Manufacturing Company in MelakaDocument12 pagesA Study On Inventory Management Towards Organizational Performance of Manufacturing Company in MelakaOsama MazharNo ratings yet
- ET's and Aliens: Problems of Exopolitics - Dec 2009Document8 pagesET's and Aliens: Problems of Exopolitics - Dec 2009Alex KochkinNo ratings yet
- Functional Appliances 2018Document45 pagesFunctional Appliances 2018tonhanrhmNo ratings yet
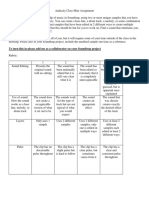
- Combined RubricsDocument3 pagesCombined Rubricsapi-446053878No ratings yet
- Autism AspergerDocument24 pagesAutism AspergerusavelNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court: Lichauco, Picazo and Agcaoili For Petitioner. Bengzon Villegas and Zarraga For Respondent R. CarrascosoDocument7 pagesSupreme Court: Lichauco, Picazo and Agcaoili For Petitioner. Bengzon Villegas and Zarraga For Respondent R. CarrascosoLOUISE ELIJAH GACUANNo ratings yet
- Ns5e rw3 SB Ak HyeDocument24 pagesNs5e rw3 SB Ak HyeKeys Shield JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Web Search - One People's Public Trust 1776 UCCDocument28 pagesWeb Search - One People's Public Trust 1776 UCCVincent J. CataldiNo ratings yet
- 4 Reasons To Walk With GodDocument2 pages4 Reasons To Walk With GodNoel Kerr CanedaNo ratings yet
- EY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseDocument2 pagesEY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseAayushi AroraNo ratings yet
- GWP - Unicef - Guidance Note Risk Assessments For Wash PDFDocument56 pagesGWP - Unicef - Guidance Note Risk Assessments For Wash PDFyomifNo ratings yet
- Physical Education For Class - 11thDocument19 pagesPhysical Education For Class - 11thdjjagu908No ratings yet
- The Other Side of Love AutosavedDocument17 pagesThe Other Side of Love AutosavedPatrick EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Code of Conduct GuidanceDocument17 pagesCode of Conduct GuidanceMuhammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- ViscosityDocument7 pagesViscositykiran2381No ratings yet
- Philosophical Perspectives Through the AgesDocument13 pagesPhilosophical Perspectives Through the Agesshashankmay18No ratings yet
- Why Narcissists Need You To Feel Bad About Yourself - Psychology TodayDocument51 pagesWhy Narcissists Need You To Feel Bad About Yourself - Psychology Todaytigerlo75No ratings yet
- SDLC - Agile ModelDocument3 pagesSDLC - Agile ModelMuhammad AkramNo ratings yet
- A Study On Consumer Behavior in Auro Food (True Biscuits) PVT LTDDocument52 pagesA Study On Consumer Behavior in Auro Food (True Biscuits) PVT LTDRoyal Projects100% (1)
- Umair Mazher ThesisDocument44 pagesUmair Mazher Thesisumair_mazherNo ratings yet
- Epithelial and connective tissue types in the human bodyDocument4 pagesEpithelial and connective tissue types in the human bodyrenee belle isturisNo ratings yet