0% found this document useful (0 votes)
499 views38 pagesAdvanced Techniques in LPC Analysis
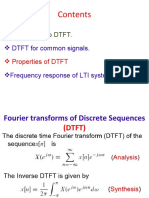
Linear Predictive Coding (LPC) is a technique for modeling audio signals using a linear combination of past samples and a source signal. By applying the Z-transform, this can be expressed as a transfer function. The goal of LPC is to minimize the error between the original and predicted signals. This is achieved by solving the Wiener-Hopf equations to find the prediction coefficients. LPC can be used for infinite memory prediction by applying a whitening process. The prediction coefficients are typically computed using the autocorrelation or covariance methods. LPC has applications in speech coding/synthesis, pitch prediction, computer music, and spectral envelope estimation.
Uploaded by
Han NguyenCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
499 views38 pagesAdvanced Techniques in LPC Analysis
Linear Predictive Coding (LPC) is a technique for modeling audio signals using a linear combination of past samples and a source signal. By applying the Z-transform, this can be expressed as a transfer function. The goal of LPC is to minimize the error between the original and predicted signals. This is achieved by solving the Wiener-Hopf equations to find the prediction coefficients. LPC can be used for infinite memory prediction by applying a whitening process. The prediction coefficients are typically computed using the autocorrelation or covariance methods. LPC has applications in speech coding/synthesis, pitch prediction, computer music, and spectral envelope estimation.
Uploaded by
Han NguyenCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd