Professional Documents
Culture Documents
انجليزي ثاني متوسط ف1
Uploaded by
rosefawazCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
انجليزي ثاني متوسط ف1
Uploaded by
rosefawazCopyright:
Available Formats
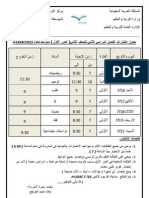
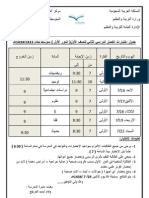
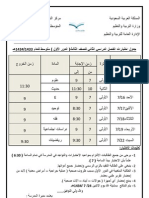
. .
. .
. .
.
.
. .
.
1431 1430
2010 2009
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Ministry of Education
www.sscbrisbane.com
,_, _ ,:-_ .,, .| = ,, ,
,-| _=, , =-|
,-| _=, , _-
==,
.=,| _- , ,.-
,=| ,-|=,-
2012
There are many different ways of teaching
English. Some courses teach through grammar;
others through topics, a third kind teaches through lan guage functions.
In courses which are based on topics or functions, grammar is used as
required.
In this course students use English to commu ni cate from day one. The
course is based upon lan guage functions in which grammar is carefully
con trolled. Students see sentences in diagrams and tables where they are
in tro duced to parts of speech.
Unlike other courses, this course provides enough time to students to
mas ter and acquire lexi con and structures taught.
The skills of listening, speaking, reading and writing are developed
gradually. Dont expect your students to acquire these skills from the frst
time. Moreover, revision and recycling are integrated into the course to
fa cili tate learning.
There are six units. Each unit is divided into four forty-fve- minute
lessons. Enough time is set aside for review.
Teachers :
a
m
e
s
s
a
g
e
t
o
t
h
e
t
e
a
c
h
e
r
A
. 400
660
.
.
.
:
1
.
3
.
.
4
.
5
.
7
.
8
.
.
9
:
10
.
.
.
2 1
3 4
6
5
7
C
/
.
...
.
1
.
3
.
4
.
/
5
.
D
- - ...
...
. .
-
1
.
/ /
2
.
.
3
/
) (
:
.
/
.
/
E
.
- -
.
.
. ...
.
.
.
.
.
)Word Bank(
. )grammar(
5
.
...
6
F
-
) Say it in English (
)Language Functions(
.)Communicative Purpose(
:
: 2
/ .
.
: 3
...
: 4
/
.
- /
: 5
/
- -
/ .
.
: 6
.
: 7
. ...
/ /
)Punctuation & Capitalization(
.)four lined notebook(
)Phonics( : 9
)Consonant(
.
.
)Vowels(
H
( )Spelling(
10
/ .)
.
: 11
/
.)
: 12
.
.
I
P
l
a
n
s
o
f
S
t
u
d
e
n
t
s
B
o
o
k
U
n
i
t
T
o
p
i
c
s
F
u
n
c
t
i
o
n
s
G
r
a
m
m
a
r
L
i
s
t
e
n
i
n
g
P
h
o
n
i
c
s
R
e
a
d
i
n
g
/
W
r
i
t
i
n
g
H
o
b
b
i
e
s
T
i
m
e
a
r
o
u
n
d
t
h
e
w
o
r
l
d
W
e
e
k
e
n
d
s
T
a
l
k
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
a
b
i
l
i
t
i
e
s
.
T
a
l
k
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
h
o
b
b
i
e
s
.
A
s
k
i
n
g
f
o
r
a
n
d
g
i
v
i
n
g
i
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
.
T
a
l
k
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
p
a
s
t
a
c
t
i
o
n
s
,
p
l
a
c
e
s
a
n
d
l
e
i
s
u
r
e
t
i
m
e
.
C
a
n
f
o
r
a
b
i
l
i
t
y
.
L
i
k
e
+
i
n
g
(
a
f
f
r
m
a
t
i
v
e
,
n
e
g
a
t
i
v
e
a
n
d
i
n
t
e
r
r
o
g
a
t
i
v
e
)
.
Y
e
s
/
n
o
q
u
e
s
t
i
o
n
s
i
n
t
h
e
p
r
e
s
e
n
t
c
o
n
t
i
n
u
o
u
s
t
e
n
s
e
.
P
a
s
t
t
e
n
s
e
o
f
r
e
g
u
l
a
r
a
n
d
i
r
r
e
g
u
l
a
r
v
e
r
b
s
.
D
i
d
i
n
Y
e
s
/
N
o
q
u
e
s
t
i
o
n
s
w
i
t
h
p
a
s
t
t
e
n
s
e
v
e
r
b
s
.
W
h
q
u
e
s
t
i
o
n
s
w
i
t
h
p
a
s
t
t
e
n
s
e
v
e
r
b
s
.
L
i
s
t
e
n
i
n
g
t
o
a
n
i
n
t
e
r
v
i
e
w
f
o
r
p
e
r
s
o
n
a
l
i
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
.
L
o
n
g
s
o
u
n
d
/
u
:
/
L
i
s
t
e
n
i
n
g
t
o
a
c
o
n
v
e
r
s
a
t
i
o
n
f
o
r
t
i
m
e
.
b
l
e
n
d
s
L
i
s
t
e
n
i
n
g
f
o
r
w
e
e
k
e
n
d
a
c
t
i
v
i
t
i
e
s
.
b
l
e
n
d
s
R
e
a
d
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
h
o
b
b
i
e
s
.
(
r
e
a
d
i
n
g
a
c
t
i
v
e
l
y
)
W
r
i
t
i
n
g
a
d
e
s
c
r
i
p
t
i
v
e
p
a
r
a
g
r
a
p
h
a
b
o
u
t
o
n
e
s
e
l
f
.
R
e
a
d
i
n
g
a
s
t
o
r
y
:
A
r
o
u
n
d
t
h
e
W
o
r
l
d
i
n
8
0
D
a
y
s
.
(
s
c
a
n
n
i
n
g
u
s
i
n
g
i
n
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
s
k
i
l
l
s
)
W
r
i
t
i
n
g
a
d
e
s
c
r
i
p
t
i
v
e
p
a
r
a
g
r
a
p
h
u
s
i
n
g
p
i
c
t
u
r
e
s
.
R
e
a
d
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
a
s
p
e
c
i
a
l
e
x
p
e
r
i
e
n
c
e
.
(
s
k
i
m
m
i
n
g
)
W
r
i
t
i
n
g
a
d
e
s
c
r
i
p
t
i
v
e
p
a
r
a
g
r
a
p
h
a
b
o
u
t
w
e
e
k
e
n
d
a
c
t
i
v
i
t
i
e
s
.
1 2 3 4
R
e
v
i
e
w
U
n
i
t
T
o
p
i
c
s
F
u
n
c
t
i
o
n
s
G
r
a
m
m
a
r
L
i
s
t
e
n
i
n
g
P
h
o
n
i
c
s
5 6 7 8
R
e
v
i
e
w
R
e
a
d
i
n
g
/
W
r
i
t
i
n
g
P
e
o
p
l
e
G
r
e
e
t
i
n
g
s
D
a
i
l
y
L
i
f
e
T
a
l
k
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
t
h
e
l
i
f
e
o
f
a
f
a
m
o
u
s
p
e
r
s
o
n
I
n
t
r
o
d
u
c
i
n
g
s
o
m
e
o
n
e
E
x
c
h
a
n
g
i
n
g
p
e
r
s
o
n
a
l
i
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
.
T
a
l
k
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
d
a
i
l
y
a
c
t
i
v
i
t
i
e
s
T
a
l
k
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
w
o
r
k
a
n
d
s
c
h
o
o
l
P
a
s
t
t
e
n
s
e
o
f
B
e
(
a
f
f
r
m
a
t
i
v
e
a
n
d
n
e
g
a
t
i
v
e
)
.
Y
e
s
/
N
o
q
u
e
s
t
i
o
n
s
w
i
t
h
B
e
i
n
t
h
e
s
i
m
p
l
e
p
a
s
t
.
W
h
-
Q
u
e
s
t
i
o
n
s
w
i
t
h
B
e
i
n
t
h
e
s
i
m
p
l
e
p
a
s
t
.
W
h
q
u
e
s
t
i
o
n
s
a
n
d
s
t
a
t
e
m
e
n
t
s
w
i
t
h
B
e
Y
e
s
/
N
o
q
u
e
s
t
i
o
n
s
a
n
d
s
h
o
r
t
a
n
s
w
e
r
s
w
i
t
h
B
e
S
u
b
j
e
c
t
p
r
o
n
o
u
n
s
P
o
s
s
e
s
s
i
v
e
a
d
j
e
c
t
i
v
e
s
A
d
v
e
r
b
s
o
f
f
r
e
q
u
e
n
c
y
T
i
m
e
e
x
p
r
e
s
s
i
o
n
s
P
r
e
s
e
n
t
t
e
n
s
e
L
i
s
t
e
n
i
n
g
f
o
r
f
a
c
t
s
a
b
o
u
t
t
h
e
l
i
f
e
o
f
a
f
a
m
o
u
s
p
e
r
s
o
n
.
C
o
n
s
o
n
a
n
t
b
l
e
n
d
s
:
b
l
e
n
d
s
L
i
s
t
e
n
i
n
g
f
o
r
g
r
e
e
t
i
n
g
s
S
h
o
r
t
a
a
n
d
s
h
o
r
t
e
L
i
s
t
e
n
i
n
g
t
o
p
e
o
p
l
e
t
a
l
k
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
d
i
f
f
e
r
e
n
t
a
c
t
i
v
i
t
i
e
s
S
h
o
r
t
i
a
n
d
s
h
o
r
t
e
R
e
a
d
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
t
h
e
l
i
f
e
o
f
P
r
o
p
h
e
t
M
u
h
a
m
m
a
d
(
p
e
a
c
e
b
e
u
p
o
n
h
i
m
)
.
I
n
f
e
r
r
i
n
g
v
o
c
a
b
u
l
a
r
y
W
r
i
t
i
n
g
a
p
a
r
a
g
r
a
p
h
a
b
o
u
t
t
h
e
l
i
f
e
o
f
a
f
a
m
o
u
s
p
e
r
s
o
n
.
R
e
a
d
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
g
r
e
e
t
i
n
g
s
a
r
o
u
n
d
t
h
e
w
o
r
l
d
(
S
c
a
n
n
i
n
g
f
o
r
f
a
c
t
s
)
W
r
i
t
i
n
g
,
e
d
i
t
i
n
g
,
r
e
v
i
s
i
n
g
a
n
d
p
r
o
o
f
r
e
a
d
i
n
g
a
p
a
r
a
g
r
a
p
h
R
e
a
d
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
a
d
a
y
i
n
t
h
e
l
i
f
e
o
f
a
t
o
u
r
g
u
i
d
e
(
S
c
a
n
n
i
n
g
f
o
r
m
a
i
n
i
d
e
a
,
f
a
c
t
s
a
n
d
k
e
y
w
o
r
d
s
)
W
r
i
t
i
n
g
a
p
a
r
a
g
r
a
p
h
a
b
o
u
t
a
j
o
b
Content
Units Topic Page number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Hobbies
Time Around the World
Weekends
Review
People
Greetings
Daily Life
Review
1
11
21
31
40
50
62
73
Hobbies
Hobbies
Unit 1
In this unit, you are going to:
l name different hobbies.
l talk about abilities.
l talk about things you like.
l write a para graph about yourself.
1
2
A. Listen and practise.
U
n
i
t
1
Lesson 1
- What are the people in the pictures doing?
- What do you do in your free time?
- What is your favourite hobby?
Johara :
Amna :
Johara :
Amna :
Johara :
Amna :
Johara :
I go for drawing classes every Tuesday.
Why?
I love to draw but I cant.
Oh, I can draw, but I cant sew. Does the centre give
sewing classes, as well?
I dont think so. But you can get self-teaching video
tapes and CDs at the book store.
I cant use the computer, either. Could you ask if the
centre gives computer courses, as well?
I think so.
Hobbies
B. In pairs : Talk about yourself. What can you do? What cant you do?
free time
favourite
hobby
Conversation
drawing using a computer reading
cooking writing sewing
3
Hobbies 1
Grammar
A. Use the drawings to complete the sentences.
B. Use the sentences above to talk about your abilities.
In pairs : Ask your partner questions about what he/she can do and cant do.
I ____ read
En glish.
She ___ sew!
I _______
write stories.
He ___ draw.
I _____ work on
the computer.
Can you count
to 100?
Yes, I can.
Can you swim? No, I cant.
Speaking
stand on your hands.
spell your name backwards.
sew.
write with your left hand.
speak Spanish.
cook Italian food.
Can for ability
He can draw.
They cant draw.
Can he draw?
Can they draw?
Yes, he can.
No, they cant.
They __ cook!
4
U
n
i
t
1
Lesson 2
A. Match the pictures to the hobbies.
swimming
bowling
collecting stamps
playing bas ket ball
fshing
1
2
3 4
5
B. In pairs : Tell your partner about your abilities. What can you do ?
A. Listen and practise.
Nawaf :
Fahad :
Nawaf :
Fahad :
Nawaf :
Fahad :
Nawaf :
Fahad :
Nawaf :
Fahad :
You have lots of books, Fahad.
Yes, I like reading; its my hobby.
How many books do you read in a week?
One a week.
Are these books yours, too?
No, these are my brothers computer books.
I dont like reading about com puters.
l like computers. Can I borrow one of the books?
Im not sure. But!
Oh, no! I know I cant take it without his per mission.
Here he is. Lets ask him.
B. Listen to the rest of the conversation. Does Nawaf ask Fahads brother for the book?
C. Is it right to take something from a friend without asking for permission?
I can _____
Vocabulary
Conversation
3
Hobbies 2
Grammar
A. Choose.
(Do - Does) you like cooking? Yes, its my hobby. I always try out new recipes. I also like
(buy - buying) cooking books. Every week, my friend Loulou comes to my house. She
(doesnt - dont) like (cook - cooking), but she likes (eat - eating) the food I make.
B. What do you like doing after school?
A. Read, then mark the statements with True or False.
- You can give vegetables as a gift. ( ) - Rock painting is expensive. ( )
- Exercising is good for your body. ( )
- There are only three good hobbies. ( )
B. In pairs : Discuss these questions.
- Which of the above hobbies would you like to try?
- Why do you think exercising is a must?
Reading
Like + ing
Affrmative
I like reading.
She likes painting.
Negative Interrogative
I dont like swimming.
She doesnt like swimming.
Do you like swimming?
Does she like painting?
Do you ever stay home with nothing to do? Are you eager to do something new?
Here are some ideas for hobbies you can enjoy in your free time.
Gardening is both fun and useful. You can easily grow fresh vegetables which
you can enjoy with your family and friends. You can also send some as a gift
to your relatives or share with those in need.
Rock painting is an interesting craft that does not cost much. You can use any
type of colour to decorate different shapes of rocks. You can draw houses, fowers,
cars or almost anything on the rocks to start your own collection.
Exercising is a must for every part of your body and your brain. People who
exercise regularly stay active throughout their lives.
Ways to Spend Your Free Time
6
B. Read Faridas paragraph about the student. Correct the mistakes.
C. In pairs : Interview a friend and complete the table.
Fawzia Abdulkarim is fourteen years old. Her favourite colour
is pink. She likes cooking but doesnt like reading.
A. Faridah is interviewing a student at another school. Listen to the interview and
complete the table.
Listening
Name
Age
Favourite colour
Hobby
Dislikes
Name
Age
Favourite colour
Hobby
Dislikes
U
n
i
t
1
Lesson 3
7
B. Use the information in the web to write a paragraph about yourself.
A. Complete the web about yourself.
My name is
dislikes
name
age
Me
abilities
hobbies
favourite
school
sub jects
colours
Hobbies 3
Writing
8
Phonics
B. Listen to the words. Repeat them chorally. Tick the ones that have the long u sound.
Rule
A vowel usually has the long sound
when a consonant and e come after it.
The e is silent. You can hear the long u
sound in mute and cute.
Rule
When two vowels are together,
the frst vowel usually has the long
sound. The second vowel is silent. You
can hear the long u sound in fuel.
1. bug
2. clue
3. fuse
4. unique
5. june
6. duck
7. dune
8. jug
9. fue
10. rule
A. Listen and circle the letters to show where you hear the long u sound.
U U U U U U U U U U U U
U U U U U U U U U U U U
U
n
i
t
1
Lesson 4
Long u sounds like the sound in uniform and glue.
Long u sound
9
Hobbies 4
A. In pairs : Use the chart below to ask and answer questions about abilities in English.
Complete the sentences by choosing the correct words.
a. Can they ( play - playing ) tennis?
b. We dont like ( read - reading ).
c. I can ( swimming - swim ).
d. Samia and Muna dont like ( watch - watching ) TV.
e. Mariam doesnt like ( cooking - cook ).
Grammar Summary
Student 1 : Can you ....?
Student 2 : Yes, I can. / No, I cant.
Speaking
* Singular and Plural.
I
You*
We
They
He
She
It
like
dont like
likes
doesnt like
swimming.
running.
playing.
sewing.
cooking.
Like + ing
Can
I
he / she / It
you* / we / they
swim?
run?
sew?
cook?
Can for ability
can
cant
I
He / She / It
You / We / They
swim.
run.
sew.
cook.
count
read
write
greet
introduce
to twenty
to a hundred
a menu
a newspaper
someone
someone
a paragraph
a letter
10
Hobbies 4
What do you like / dislike doing on these days?
B. Write Yes / No questions with can. Then under your re sponse, check Yes or No to
give your opinion about each question.
C. Now in groups of ten : Do a survey by asking each student in your group his / her
opinion about the questions. Write the total number of Yes and No answers in each
column. Com pare your opinion to your classmates. Give reasons for your an swers.
Your response
1. woman / be police offcer
_________________________________________________________ ?
Total
Yes No Yes No
2. woman / be engineer
_________________________________________________________ ?
3. woman / be good nurse
_________________________________________________________ ?
4. man / be good cook
_________________________________________________________ ?
5. women / work as shopkeepers
_________________________________________________________ ?
6. man / be tailor
_________________________________________________________ ?
Like ____________________________________________________________________________________
Dislike ____________________________________________________________________________________
Like ____________________________________________________________________________________
Dislike ____________________________________________________________________________________
Like ____________________________________________________________________________________
Dislike ____________________________________________________________________________________
Eid Al - Fitr
Eid Al - Adha
Rainy Days
Writing
1
Time Around the World
Time Around the World
Unit 2
In this unit, you are going to:
l
ask for and tell the time.
l
describe what people are doing.
l
write a paragraph about things you and your family do.
11
12
A. Listen and practise.
Time Around the World
- What time is it in Riyadh?
- What time is it in Tokyo?
- How many hours is Tokyo ahead of Riyadh?
B. - What time is it in Malaysia now?
- Why do you think its important to help others?
U
n
i
t
2
Lesson 1
ahead
air port
be hind
fight
Conversation
Saeed :
Rashed :
Saeed :
Rashed :
Saeed :
Rashed :
Saeed :
Rashed :
Hello, Rashed.
Is it you Saeed? Are you calling from the airport?
Yes, I am. The fight to Malaysia has been
delayed. Could you do me a favour?
Sure. What can I do for you?
Can you remind my mom to water my plants
and feed my fsh.
No problem. Make sure you call when you
reach Malaysia.
But you may be sleeping then. Malaysia is four hours ahead.
Well arrive at about 2:30 after midnight.
Well then, e-mail us. Have a nice time.
Tokyo
Mexico
city
Riyadh
London
Behind Ahead
13
Grammar
In pairs : Look at the map on page 82, ask and answer about the time in the cities.
B. In pairs : Read your card and mime the verb written on it. Your partner guesses the verb.
Student A : Are you smiling?
Student B : Yes, I am. / No, I m not.
A. Look at the picture. Complete the questions and answers.
1. _______ the fight attendant __________ (serve) food?
No, _______________ . She _____________ (serve) drinks.
2. ____ the old man ________ (look) out of the window? Yes, __________________ .
3. _________ the lady ___________ (talk) to her daughter?
No, ___________________ . She is ___________ (feed) her.
4. ________ the boys _____________ (watch) the movies? ___________________ .
5. __________ the young man ___________ (sleep)?
________________________________________________ .
Student 1: Its 7:45 in Saudi Arabia. What time is it in Tokyo?
Student 2: Tokyo is 6 hours ahead, so it is 1:45 in Tokyo.
Time Around the World 1
Speaking
Yes / No questions - present continuous
Yes, he is.
Are you travelling now?
Is he calling from the airport?
No, Im not.
No, he isnt.
Yes, I am.
14
B. Complete the table with your fathers timings.
A. What time is it?
B. Look at the clocks. Say the times.
C. In pairs : Ask your partner about the things she / he does at these times.
U
n
i
t
2
Lesson 2
A. Listen to the conversation. Complete the table with the times.
Vocabulary
It is fve past three.
It is three-oh-fve.
It is ten past fve.
It is fve-ten.
a. b.
It is twenty past seven.
It is seven twenty.
It is twenty-fve to ten.
It is nine-thirty fve.
It is twenty to eleven.
It is ten forty.
It is ten to twelve.
It is eleven ffty.
f. e. d.
c.
Listening
goes to work has lunch
Ahmad
Amina
Your father
15
Time Around the World 2
Read the story. Then, an swer the questions below.
Around the World in Eighty Days
This is an adventure story about an Englishman called Phileas
Fogg. Fogg takes on a challenge to travel around the world in
eighty days. To make such a journey in 1872 was thought of
as a crazy idea. There were no planes, and trains were a new
invention. No one believed anyone could circle the world in
eighty days. In the story however, Fogg plans his journey and
studies the schedules for the trains and boats that leave the
cities he is to pass through.
He starts his journey on Wednesday, 2
nd
October at 8:45 p.m.
He sails from London to Suez with no problems. Then, he goes through the four con ti nents
where he meets many new people. In India, China and America, he has many ad ven tures and
faces lots of diff culties.
Fogg reaches London thinking that he has taken eighty-one days to fnish the jour ney.
However, he fnds out that traveling from east to west has saved him twenty-four hours. Phileas
Fogg has done what other people thought impossible.
Reading
Look at Mr. Foggs record, then answer the questions.
Wednesday, October
2
nd
, 8:45 p.m.
Paris
London
Thursday, October 3
rd
,
7:20 a.m.
Wednesday, December 3
rd
,
7:00 a.m.
City Arrives
Paris
Thursday, October 3
rd
,
8:40 a.m.
Wednesday, October 9
th
,
11:00 a.m.
Wednesday, October 9
th
,
5:00 p.m.
Sunday, October 20
th
,
12:00 noon.
Sunday, October 20
th
,
8:00 p.m.
Hong Kong
Tuesday, November 6
th
,
6:00 a.m.
Thursday, November 8
th
,
5:00 p.m.
Suez
Suez Bombay
Bombay
Hong Kong San Francisco
Leaves City
1. When does Fogg reach these cities?
a. Suez
b. Hong Kong
c. San Francisco
2. What lesson do you learn from this story?
16
Saeed and his family are in Pakistan now. Look at the pictures. Describe what they
are doing and at what time.
U
n
i
t
2
Lesson 3
Writing
Saeed and his family are leaving for Malaysia via Pakistan. Their fight is at 7 oclock
in the morning. It takes four hours to reach Pakistan. After staying for fve hours in
Pa ki stan, the plane will fy to Malaysia. It takes only two hours to reach Malaysia from
Pa ki stan. (use the map on page 83)
In pairs : Find out :
1. the Saudi time they arrive in Pakistan.
2. the local time in Pakistan.
3. the Saudi time they arrive in Malaysia.
4. the local time in Malaysia.
Speaking
1.
2.
3.
4.
Saeed and his family are in Pakistan now. It is one oclock in the afternoon.
They are performing their Dhuhrr prayer.
17
Look at the pictures of Saeeds family in Malaysia. What are they doing?
Write a paragraph.
Time Around the World 3
18
Phonics
Rule
A consonant blend is two or more
consonants that are together. The
sounds blend together. Each sound
is heard.
You can hear an l blend at the
be ginning of clay and plant.
A. Listen to the words. Repeat them chorally.
B. 1. Write each blend once to make a new word. Say the new word.
gloves fowers block plane slide
2. Can you think of more words that start with l blends?
C. Circle the consonant blend you hear.
1. bl cl gl pl sl
2. bl cl gl pl sl
3. bl cl gl pl sl
4. bl cl gl pl sl
5. bl cl gl pl sl
__ __ ace
__ __ ue
__ __ ag
__ __ imb
__ __ eep
cl
bl
f
sl
pl
L blends
L blends are the l sound with another
consonant like in
fag clay and plant .
U
n
i
t
2
Lesson 4
19
Time around the world 4
A. In groups of three : The teacher gives two cards to each student in the group.
- Take turns to read the cards to the others.
- Listen to the information and mark the clock faces accordingly.
B. Take turns to tell the other members what people in the cities are doing at that time.
Student A : What time is it in London?
Student B : Its Friday 3 a.m. in London.
Student A : Are the people sleeping?
Student B : Yes, they are. / No, theyre not.
Sydney
1 p.m. Fri day
Vancouver
p.m. Thurs day
New York
p.m. Thurs day
Brazilia
p.m Thurs day
Riyadh
a.m. Fri day
London
3 a.m. Fri day
Delhi
a.m. Fri day
Tokyo
a.m. Fri day
Singapore
a.m. Friday
Grammar Summary
Speaking
Yes,
I am.
he
she
it
is.
you
we
they
are.
No, not.
I am
he
she
it
you
we
they
are
is
Yes / No questions-present continuous
working?
Am
Is
Are
I
he
she
it
you
we
they
20
In groups : Match the paragraphs to the pictures.
Time around the world 4
Reading
A. It is seven oclock in the morning.
At the moment, people are getting
up, getting dressed and having
break fast or driving to work.
B. It is fve twenty now. People are going
home from work. Some are walking to
bus stops. Others are waiting for the
underground. A few are walking to the
cafs to have some thing to eat.
C. Its ten-thirty at night. At the
moment, some people are having
dinner in restaurants. Many
families are at home. Theyre
watching tele vision, reading the
newspaper or playing games.
D. It is twelve forty-fve in the af ter noon.
Many people are on their lunch break.
Some of them are having a quick lunch.
Others are seeing their friends or
shopping.
Weekends
Weekends
Unit 3
In this unit, you are going to:
l
name weekend activities.
l
say the past tense of regular and irregular verbs.
l
ask and answer questions about time and activities.
21
22
Discussion
- What do you do on your weekends?
B. There are 48 hours in a weekend. How well do you plan and use them?
U
n
i
t
3
Lesson 1
Noura :
Sara :
Noura :
Sara :
Noura :
Sara :
Noura :
Sara :
Noura :
beach
last week
yesterday
take part
collect shells
go sailing
Conversation
Guess what we did last week, Sara?
What?
We rented a beach house and stayed there for the
weekend.
Great! What did you do?
Well, I walked on the beach, watched the sunset and went
sailing. Oh, and I collected many nice shells, as well.
How nice!
Yes, and my brother took part in a jet ski race.
So, you really had fun?
Yes, I did. What about you? Im sure you had a good time
last weekend, as well.
A. Listen and practise.
23
Grammar
1. On Thursday morning, Nahla _________________ a book. She____________ TV.
2. In the afternoon, her family __________________________ on the beach but they
_________________ any shells.
3. At night, she _________________ a cake, but she _________________ it.
C. In groups : Take turns, telling your group three things you did last weekend.
A. Write the past tense of these verbs.
B. Look at the pictures and write what Nahla and her family did / did not on the week end.
1. do
2. have
3. see
4. carry
5. stop
6. study
Weekends 1
Morning
Night
Afternoon
Past simple - regular / irregu lar verbs
We didnt rent a boat.
I didnt collect any stones.
I didnt see my grandfather.
We rented a house last month.
I collected some shells on the beach.
I saw my grandmother yesterday.
smile - smiled
rent - rented
collect - collected
stop - stopped
study - studied
drive - drove
go - went
see - saw
24
Ali :
Talal :
Ali :
Talal :
Ali :
Talal :
Ali :
Talal :
Ali :
Grammar
A. Write the simple present tense of these irregular verbs.
drove bought ate made
1. ___________ 2. ___________ 3. ___________ 4. ___________
Conversation
B. Did you enjoy your weekend? Why?
Did you go to Taif last month?
Yes, we spent a weekend there.
Did you fy there?
No, we didnt.
Tell me about your trip?
Well, frst we drove to Al-Shafa. The weather there
was nice and cool.
Great!
Then, we met my uncle and his family at King Fahad
Park. We had a barbecue. We were lucky to fnish
before it rained.
It mustve been fun!
A. Listen and practise.
brought drank had did
5. ___________ 6. ___________ 7. ___________ 8. ___________
Present past
go - went
drive - drove
fy - few
meet - met
Did in Yes / No questions with Past Tense Verbs
Yes, I did. I went there on Thurs day.
No, he didnt. He drove to Taif.
Yes, we did. We had a lot of fun.
Did you go to Taif?
Did he fy to Taif?
Did you have fun?
U
n
i
t
3
Lesson 2
25
Weekends 2
B. Match the questions with the answers.
C. In pairs : Ask the above questions and give your own answers.
This passage is about a schoolgirl called Afnan who spent her weekends helping others.
Read about what she did and how.
Answer the following questions.
1. Who is the passage about? ________________________________________
2. Who did she help? _______________________________________________
3. What did she do at the centre? ______________________________________
4. Why did she work at the centre? ____________________________________
5. Do you think she was paid for her work? Why? Why not?
________________________________________________________________
Reading
1. Did Ali sleep early on the weekend? a. No, he didnt. He visited his family.
2. Did he visit any friends? b. Yes, he did. He helped him wash the car.
3. Did he help his father? c. No, he didnt. He slept late.
4. Did he watch the news? d. Yes, he did his homework.
5. Did he do his homework? e. No, he didnt. He watched the match.
6. Did he exercise? f. Yes, he did. He played basketball.
Today, I would like to tell you about an experience that made me feel proud of myself. For
the past year, I have spent every Thursday morning at the Special Children Cen tre with
25 handicapped children. I wanted to help these children live a normal life. I started teaching
some of them to recite the Holy Quran. I had another group
knit and sew. Some children worked on Islamic art projects.
At frst, we had few problems but soon things got easier.
By the end of the year the children had put up their work for
an exhibition. Everyone loved it. I am so glad that I used my
weekends to help others and please Allah.
26
U
n
i
t
3
Lesson 3
B. What did you do last night?
C. What do you think about staying up late at night?
Grammar
A. Write questions to these answers.
B. In pairs : Ask each other the questions in exercise A and give answers for yourself.
Conversation
A. Listen and practise.
Where did you go last night?
I went to the football match.
Why didnt you call me? I wouldve liked to go, too.
I called you, but no one answered.
What time did you call?
Around three in the afternoon.
I was asleep. Who did you go with?
I went with my new neighbour, Jihad.
I wish youd called me earlier. I really wanted to go.
Rayan :
Jameel :
Rayan :
Jameel :
Rayan :
Jameel :
Rayan :
Jameel :
Rayan :
Wh-Questions with past tense verbs
Where did you go yesterday?
When did he visit his friend?
What time did she arrive in Jeddah last week?
Who did we meet yesterday morning?
Why didnt they come last night?
I went to the foot ball match.
He visited his friend last week.
She arrived at 12 midnight.
We met our friends.
Because they were sick.
1. A : _________________________________________________
B : I went to the supermarket yesterday.
2. A : _________________________________________________
B : I bought some fruit and bread last night.
3. A : _________________________________________________
B : Last time, I went with my mother.
4. A : _________________________________________________
B : I went to the bookstore yesterday morning because I wanted to buy a book.
27
Weekends 3
A. Read Fatimas notes about the things she did last weekend.
B. Read her paragraph.
Listening
Listen to these people talking about what they did last weekend. Number the pictures
as you hear the conversations.
Writing
C. Write notes, then use them to write a paragraph about your activities last week end.
Bake a cake
Visit uncle
Picnic in the desert
Last weekend, I wanted to surprise my cousins. I woke up early and baked a chocolate
cake for them. I took it with me to my uncles house. In the afternoon, we went on a
picnic to the desert. We barbecued meat and chicken. The weather was very nice and
we really enjoyed ourselves. We returned home very late at night.
28
Phonics
Rule
Remember that in a consonant
blend, two or more consonants are
together.The sounds blend together.
Each sound is heard. You can hear an r
blend at the beginning of brown and
crab.
A. Listen to the words, and repeat them chorally.
B. Listen, and circle the blends that begin each word.
train bread crown drum frog
C. Listen, and complete the words with the correct blends.
dr cr tr gr fr pr
br tr
gr cr
pr gr
dr fr
tr dr
br cr
fr tr
pr dr
___ ___ apes ___ ___ ess ___ ___ ab
___ ___ ee ___ ___ ayer ___ ___ uit
1.
2. 3.
4.
5. 6.
U
n
i
t
3
Lesson 4
R blends
R blends are the r sound with another
consonant like in crab and dress .
29
Weekends 4
Complete the conversation.
Rami : I really __________ (enjoy) the game. _________ you _________ (like) it, too?
Saleh : It was okay. But they _________ (play) much better last week . Dont you think so?
Rami : I ___________ (not, watch) the last game. I ___________ (miss) it. By the time
I ___________ (get) home, it was over.
Saleh : Yes, I remember. It _____________ (start) early that day.
Grammar Summary
Past simple tense / affr mative
I
You
We
They
He
She
It
Negative
walked
(regular)
went
(irregular)
home last night.
I
You
We
They
He
She
It
did not
didnt
walk.
go home.
Did in Yes / No questions
did.
didnt.
I
You
He
She
It
They
We
walk
go
home?
I
You
He
She
It
They
We
Yes,
No,
Did
Wh - questions with past tense verbs I
You
He
She
It
They
We
went
home.
I
you
he
she
It
they
go? did
Where
When
What time
Why
yesterday.
at six oclock.
to study.
30
A. What did you do last weekend? Complete the table.
B. In pairs : Guess what your partner did last weekend. Find out how many guesses
were right.
Write a paragraph describing your partners weekend activities in your workbook page 14.
Weekends 4
Listen to four girls talking about their weekends. What did they do on Thursday morning?
Write the names under the correct pictures.
Listening
Speaking
Writing
1. 2. 3. 4.
My last weekend / Where did I go? __________________________ .
I went with _______________________
I went by _______________________
I stayed in a ______________________
I stayed there for __________________
I saw _______________________________
I ate _______________________________
In the mornings, I _____________________
In the evenings, I _____________________
My partners last weekend.
Where did she / he go? __________ .
She / He went with ______________
She / He went by _______________
She / He stayed in a _____________
She / He stayed there for _________
She / He saw _________________
She / He ate _________________
In the mornings, she / he ________
In the evenings, she / he ________
= I was right.
= I was wrong.
Review
Review
Unit 4
32
Vocabulary
A. Write an action verb under each picture.
B. Make sentences using the past tense of the verbs in activity A. Underline the verbs.
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
U
n
i
t
4
Lesson 1
33
Lesson 1
In groups : Play, Win, Lose or Draw. The teacher will give you a set of sentences.
A student in each group draws the frst sentence. The other students guess the
sen tence. Take turns to draw and guess.
A. Listen to these people telling the time in their cities. Write the times.
Speaking
Listening
B. Refer to the map on page 82. Calculate the time in Saudi Arabia and fll in the table.
C. Write how many hours Saudi Arabia is ahead or behind the given cities.
What time is it in ......?
1. Tunis
2. Paris
3. New York
4. Tokyo
5. Karachi
Time in Saudi Arabia Ahead Behind
34
Vocabulary
Match the categories in A to the words in B. Then, give a few more words for each
category.
clothes, stores, nationalities, jobs, hobbies, months, colours, cities,
prepositions, adjectives
A.
In groups : Find a job. The teacher will give you cards. Read your card. If you have a
wanted card, look for someone in your group who can do the job. The game fn ishes
when everyone has a job.
__________ 1. On, in, _______________ , ________________ , ________________ .
__________ 2. April, June, May, _____________ , _____________ , _____________ .
__________ 3. Blue, white, black, _____________ , ____________ , _____________ .
__________ 4. Reading, drawing, _____________ , ____________ , _____________ .
__________ 5. Writer, teacher, _____________ , ______________ , _____________ .
__________ 6. Chinese, Japanese _____________ , ____________ , ____________ .
__________ 7. Sweater, shirt, _____________ , ______________ , _____________ .
__________ 8. Tokyo, Jeddah, _____________ , ______________ , _____________ .
__________ 9. Quiet, friendly, pretty, ____________ , ____________ , ___________ .
__________ 10. Bookshops, grocers, ____________ , ____________ , ___________ .
B.
Im looking for a me chanic.
Can you drive?
Yes, I can.
No, I cant.
Speaking
U
n
i
t
4
Lesson 2
35
A. In groups : Make a group survey. Ask your group members about the activities they
like. Complete the questionnaire.
B. Fill in the blanks, using the information from your survey. Then, complete the
para graph.
In my group, there are ____________ students. ___________ students like
___________ and ___________ dont ( doesnt ).
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
(number)
(ac tivity) (number)
(number)
Lesson 2
Writing
Activities
Name
Cooking
Yes
Collecting Stamps
No
Reading Drawing
Yes No Yes No Yes No
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Total
36
Who did it?
In groups : Use the school plan below to play the game.
Students
Basheer
Saud
Rashid
Ibrahim
Ahmad
Sameer
Khalid
Fawaz
Saf
Yousuf
Abdullah
Saleh
Speaking
U
n
i
t
4
Lesson 3
37
Vocabulary
A. Circle the word that doesnt belong to the group.
B. Write why each word doesnt belong to the group.
1. They are all dates. 2:30 is time.
2. _____________________________________
3. _____________________________________
4. _____________________________________
C. Start from the centre. Use one word or expression from each section to make a question.
1. ________________________________
2. ________________________________
3. ________________________________
4. ________________________________
5. ________________________________
6. ________________________________
7. ________________________________
8. ________________________________
9. ________________________________
10. ________________________________
Grammar
Lesson 3
1. 1925, 1616, 2001, 2:30 p.m.
2. is, am, was, are.
3. drawing, white, cooking, writing.
4. Makkah, Tokyo, Hong Kong, Chinese.
38
In groups of three: Look at the picture story and guess what is happening.
Speaking
U
n
i
t
4
Lesson 4
39
Lesson 4
Reading
Read the passage.
o you ever get bored at home? Would you like to have some fun?
Start your own MINI GREEN HOUSE. You will need a plastic bottle, some soil and
seeds of your choice (tomatoes, corn, lentils, beans etc.). Take the bottle. Remove
the label and cap. Pinch a few holes around the top to keep the inside cool. Place
some soil at the bottom of the bottle. Throw the seeds and sprinkle them with water.
In a few days, the seeds will start to vine. Water regularly. When your plants reach
the top, cut the bottom of the bottle and transfer them into a pot or to the garden.
D
a. Complete the sentence.
A green house is a place where ___________________________________________
b. Choose the correct words.
- Place means a. put b. buy c. cook
- a cap means a. a pot b. a cover c. a bottle
- vine means a. die b. grow c. fnd
- mini means a. very small b. very big c. very tall
c. Answer the questions.
- What do you need to make a mini green house?
_____________________________________________________________________
- Why do you make holes in the bottle?
_____________________________________________________________________
- When do you put the plant in a pot or the garden?
_____________________________________________________________________
People
People
Unit 5
In this unit, you are going to:
l
talk about things that happened in the past.
l
ask and answer questions about past events.
l
write about the life of a famous person.
l
read a passage about Prophet Mohammad
(peace be upon him).
40
41
Discussion
U
n
i
t
5
Lesson 1
- Do you know any of the people in the pictures?
- Which of these people would you like to know more about?
Listen to two friends, Ali and Fayez, talking about the life
of a famous person.
A. Listen and practise.
B. Practise the conversation, talking about someone else.
C. Setting goals is a must for a successful future. Why?
founder
born
famous
die
invent
scholar
King Abdulaziz
Founder of Saudi Ara bia
born : 1293 H
died : 1373 H
Ahmad Zuwail
Arab American
scientist
born : 1946
Abdulaziz Bin Baz
Saudi
Mufti
born 1330 H
died : 1420 H
Conversation
Fayez :
Ali :
Fayez :
Ali :
Fayez :
Ali :
Fayez :
Ali :
Fayez :
Did you choose a person to write about?
Yes, I chose Abdulaziz Bin Baz.
Who was he?
He was a very famous Muslim scholar. Al though he
was blind, he wrote many books.
Thats amazing.
He was a teacher and a Mufti.
When and where did he live?
He was born in 1330 H, and he lived in Saudi Arabia.
Id really like to read more about him.
Mohammad Hussain
Zaidan
Saudi
writer
born : 1325 H
died : 1414 H
42
Grammar
People 1
A. Match the questions with the answers.
B. In pairs : Ask each other the questions in A.
C. Complete the sentences, using the correct form of Be.
1. Today, _______________________ . Yesterday, ____________________________ .
2. This month, ___________________ . Last month, __________________________ .
3. This year, _____________________ . Last year, ___________________________ .
1. When were you born?
2. Were you born in Dammam?
3. Were your parents born in Taif?
4. Who was your best friend in school?
5. Who was your favourite teacher?
Yes / No questions
Was she born in Madinah?
Was it a black pen?
Were you in the room?
Were they friends?
Yes, she was.
Yes, it was.
Yes, I was.
Yes, we were.
Yes, they were.
No, she wasnt.
No, it wasnt.
No, I wasnt.
No, we werent.
No, they werent.
Past Tense of Be
I was a teacher last year.
He was in Makkah yes ter day.
It was a short story.
You were born in 1984.
We were at school last week.
They were Saudis.
( Was / were) / Affrmative Negative
I wasnt a teacher.
He wasnt in Makkah yesterday.
It wasnt a short story.
You werent born in 1984.
We werent at school last week.
They werent Saudis.
Wasnt = was not.
Werent = were not.
Wh - questions
How old was he?
When was she born?
Where were you yesterday?
Who were your friends at school?
What was the lesson like?
He was 60 years old.
She was born in 1882.
I was in Makkah.
Salma and Amal were my friends.
It was easy.
a. My best friend was Shaker / Maha.
b. No, they werent. They were born in Tabouk.
c. I was born in 1992.
d. No, I was born in Jeddah.
e. My favourite teacher was Mr. / Mrs. Rami.
43
Vocabulary
A. Listen and practise.
B. Write the jobs under each picture.
C. In groups : Choose a job. Name a fa mous person and say something about him / her.
Listen to Sami asking about a famous person. Choose the right answers.
a. _____________ b. _____________ c. _____________ d. _____________
e. _____________ f. _____________ g. _____________
U
n
i
t
5
Lesson 2
1. name
2. prizes won
3. job
a. Nelson Mandela
a. Nobel prize
a. artist
b. Hadi Sawan
b. Silver medal
b. peace activist
c. Van Gogh
c. World cup
c. P.E. teacher
Listening
pilot , writer , cook , scientist , teacher , shepherd , artist.
44
- Where was Prophet Mohammad peace be upon him born?
- What was he like?
A. Read. Guess from the sentences what these words mean.
1) An orphan is a child who doesn t have ___________________
a) a brother b) an uncle c) a father
2) A shepherd is a person who ___________________
a) teaches children b) looks after sheep c) sells clothes
3) Truthful means a person who always ___________________
a) says the truth. b) talks a lot. c) keeps quiet.
B. Write the opposite of the underlined words.
1. The Prophets mother died when he was a child. ___________
2. His uncle was poor and didnt have much money. __________
C. Tick () or (). Then correct the false statements
1. The Prophet worked as a shepherd because he was rich. ( )
2. He got married at the age of twenty-fve. ( )
- Why do you love
the Prophet?
- How do you
show your love for
the Prophet?
Reading
Prophet Mohammad (peace be upon him) was born in Makkah in 571 AD. He was
an or phan. His father, Abdullah, died before he was born. His mother, Amena, died
when he was a child of six. He lived with his grandfather, Abdul Muttaleb, and then
with his loving uncle , Abu Taleb.
Mohammad (peace be upon him) was poor and he worked as a shepherd to help
his uncle. Later, he looked after his uncles trade. He was always honest and people
called him The Truthful: Al Sadiq Al Ameen. When he was twenty-fve years old,
he got married to a rich widow, Khadija bint Khuwailed.
When Prophet Mohammad (peace be upon him) was forty, he became the
messen ger of Allah. He started spreading the message of Islam in Makkah. The frst
few years were very diffcult for the Prophet. In 622 AD, Allah ordered him to move to
Al Madina. He lived in Al Madina for eleven years. The people of Al Madina supported
him a lot. He died on the 12
th
of Rabei Al Awal, 11 Hijra (633 AD) in Madina.
The Last Prophet Mohammad (PBUH)
People 2
45
U
n
i
t
5
Lesson 3
Vocabulary
A. Write the years in words.
1995
1622
1840
2002
1912
2014
B. In pairs : Ask each other when you were born / started to walk / started school?
In pairs : Ask and answer about these people.
King Khalid Al Saud
Born : 1331 H.
Died : 1402 H.
Ibn Khaldoon
Born : 732 H.
Died : 808 H.
Al-Ghazali
Born : 1335 H.
Died : 1416 H.
Mohammad Ali Jinnah
Born : 1876.
Died : 1948.
When was ____ born?
When did he die?
He was born in _____.
He died in _________.
Speaking
46
A. Look at the information Ali collected about Shaikh Abdulaziz Bin Baz. He wrote this
in for mation on a time line.
B. Use the time line to write a paragraph about Shaikh Abdulaziz Bin Baz.
1330 H 1346 H 1390 H 1414 H 1420 H
born in
Saudi Arabia
become blind become the
President of the
Islamic University
become
The General
Mufti
die
Writing
People 3
47
Phonics
A. Listen to the words. Repeat them chorally.
B. Look at the picture. Listen to the picture name. Circle the beginning blend. Write
the blend on the blanks. Say the word.
C. Circle the blend you hear.
1. 2. 3.
6. 5. 4.
7. 8. 9.
skirt smell snow spoon
square star swing
____uirrel ____ail ____amp
____ile
____ot ____op
____ide ____ip
____im
1. sk sm sn sp sq st sw
2. sk sm sn sp sq st sw
3. sk sm sn sp sq st sw
4. sk sm sn sp sq st sw
5. sk sm sn sp sq st sw
6. sk sm sn sp sq st sw
7. sk sm sn sp sq st sw
sq sl sl sn sm st
sk str st sl st sm
sw sl sl st sp st
Rule
Remember that in a consonant
blend, two or more consonants
are to gether. The sounds blend
to gether. Each sound is heard.
You can hear an s blend at the
be ginning of snow and skate.
S blends
S blends are the s sound with another
consonant like:
sk - sm - sn - sp - sq - st - sw
U
n
i
t
5
Lesson 4
48
Look at the Be family tree. Complete it with the right subject pronouns.
Grammar Summary
Be
Past Present
is am
are
was were
they
I
Past Tense of Be (Affrmative and Negative)
I
He
She
It
was
wasnt
were
werent
at home last night.
You
We
They
Yes / No Questions with Be in the Simple Past
I
he
she
it
was
were
in Riyadh in 1999?
you
we
they
I
he
she
it
you
we
they
was.
were.
Yes,
I
he
she
it
you
we
they
wasnt.
werent.
No,
I
They
He
She
It
was in 1992.
in Dhahran.
were
was
born
Mr. Tahir.
kind to us.
very fat.
Wh - Question with Be in the Simple Past
you
they
your frst teacher?
she like?
your cat?
were
When
Where
Who
What
How fat
was
born?
People 4
49
People 4
Read the text and make notes in the table. Then, ask your partner about her / his
fa mous traveller, and complete the table in the same way.
Student A turn to page 84.
Student B turn to page 85.
A. Look at the timeline. It shows information about King Faisal.
B. Write a paragraph about King Faisals life, using the dates on the timeline.
Speaking
Writing
1324 1364 1384 1395
born take the King dom into the
United Nations
become king die
50
Greetings
Greetings
Unit 6
In this unit, you are going to:
l
Introduce people.
l
exchange personal information.
l
read about greetings around the world.
l
listen to people talking about greeting customs.
l
write a paragraph about yourself.
50
51
Discussion
U
n
i
t
6
Lesson 1
- Do you name a country for each picture?
- Which greeting is the most common? Unusual?
- Remember a Muslim never bows when he greets others.
A. Listen and practise.
B. If youre with a group of friends, do you always introduce newcomers to them? Why?
Conversation
Teacher :
Misfer :
Teacher :
Raj :
Teacher :
Raj :
Teacher :
Raj :
Teacher :
Hello, Misfer. I see youre with a new friend today.
Yes, Mr. Yehya. This is Raj Anand.
Nice to meet you, Raj.
Pleased to meet you, Mr. Yehya.
This is the frst time someone greets me with a press
of his palms.
It is called The Namaste.
Where are you from?
Im from India and Im here on vacation.
Enjoy your holiday.
shake hands hug bow
pat the back press palms
together
52
Grammar
Greetings 1
A. Complete this conversation with verb Be, subject pronouns or possessive ad jectives.
Check your answers with your partner..
B. In pairs : Make three wh-questions about your friends using the verb Be then
take turns asking and answering your questions.
C. In groups : Take turns introducing a partner to others.
Student 1 : Saleh / Elham, this is ___________
Hes / Shes from __________
Student 2 : Hello, __________. Nice to meet you.
Student 3 : Hi, pleased to meet you, too.
Hana :
Sahar :
Noha and Layla :
Hana :
Noha :
Hana :
Layla :
Hana :
I see your cousins _______________ here at last!
Girls, this is ________________ best friend Hana.
Oh, so you ____________ Hana! Were so happy to meet _______.
Good to meet you, too.
I _____ Noha and _______ from Jordan.
This is ________ cousin Layla, __________ from Lebanon.
Which city ___________ you from?
__________ from Beirut.
_________ hope you have fun during ___________ stay.
Wh - questions with Be
Whats your name?
Where are you from?
Where is she from?
Who are they?
My name is Raj.
Im from India.
Shes from Britain.
Theyre her friends.
my
your
his
her
its
our
your
their
Subject
Pronouns
Possessive
Adjectives
I
you
he
she
it
we
you
they
53
Vocabulary
Reading
Which of the following are international and which are traditional? complete the table.
thobe and ghotra - hand shake - English language -
hamburger - Arabian coffee - Kabsa
A. - Why is it important to know about greeting customs?
- How are international schools different from local schools?
International Traditional
At Dahran International School, I learnt that greeting customs differ from one
country to another. Normally, students greet each other saying hi, hello or good morning.
However, on special occasions, each practices his traditional way of greeting.
My Japanese friends occasionally like to use their famous ojigi to greet each other.
They bow to say good morning, hello or goodbye. Dilip and I use the Indian namaste
to greet each other. We press the palms of our hands to gether and lift them up to our
chins. Then, we say namaste. Filipino students shake hands, but close friends pat
each other on the back and say Kamusta. John, Jack and Patrick from Britain greet
each other with a hug. If they meet some one for the frst time, they shake hands.
Our friends from the Emirates, Saleh and Hamad, shake hands with all of us every
morning.
Going to an international school helped me learn about different greeting customs.
U
n
i
t
6
Lesson 2
54
Greetings 2
B. Fill in a country for each greeting custom. Check if the greeting is formal or in for mal.
If you can not tell, write dont know.
C. Do you know of any other greeting customs? Tell your friend about them.
D. Role play: In pairs, act out the custom of the country named by the teacher.
Listening
Listen to different greeting customs. Tick the box for each country.
bow to each other.
shake hands.
a pat on the back.
a hug.
press palms and lift to chin.
Country Form of greeting Formal Informal
bend knees bow press noses
1. Japan
2. Zambia
3. New Zealand
Greeting
Country
55
Conversation
A. Listen and practise.
Yasser :
Tarik :
Yasser :
Tarik :
Yasser :
Saleh :
Yasser :
Saleh :
Hi, Tariq! How are things with you?
Great! What about you?
Im fne, thanks.
Yasser, Id like you to meet Saleh.
Hes from Jordan.
Hi, Saleh. Are you on the team with us?
No, Im not. Im a mem ber of this youth club.
Are you and Tariq playing in the match next week?
No, we arent.
B. - Listen to the rest of the conversation.
- Where is Yasser from?
C. Are you a member of any youth club?
Grammar
A. Complete the conversation and practise with a partner.
Student 1 :
Student 2 :
Student 1 :
Student 2 :
Student 1 :
Hello _____________ you on the basketball team?
Yes, _______ __________.
_______________ you new?
No, ____________. But Ive been ill for a long time.
_______________ our coach here?
Yes, he __________ in the next room.
Yes / No Questions and short answers with Be
Am I on the team?
Are you a member of this club?
Is basketball diffcult?
Are you and Tariq on the same team?
Are the players Egyptian?
Yes, you are.
Yes, I am.
Yes, it is.
Yes, we are.
Yes, they are.
No, youre not.
No, Im not.
No, it isnt.
No, were not.
No, theyre not.
Affrmative Negative
U
n
i
t
6
Lesson 3
56
Greetings 3
B. Go around the class and fnd the in for mation. Compare your answers with the group.
1. How many students have the same frst name? ________________
( Ask: Whats your frst name? )
2. Are there any students who have the same last name? ________________
( Ask: Whats your last name? )
3. How many students come from another coun try? ________________
( Ask: Are you Saudi? )
4. How many students come from another city? ________________
( Ask: Are you from this city? )
Writing
A. 1. What is a paragraph?
- A paragraph is a group of sentences about one main idea. This main idea is called
the topic.
2. What does a paragraph look like?
- An English paragraph has a special form. Look at the para graph be low. It is written in
the correct form.
A. 1. Do you remember the rules of writing a paragraph?
Rules of paragraph writing:
1. Begin each sentence with a capital letter.
2. End each sentence with a full stop.
3. Do not start each sentence on a new line.
My name is Glenn Tolo. I am 32 years old. I am from
Ma nila, Philippines. My native language is Tagalog. I
am an art worker.
57
Greetings 3
2. What is wrong with this paragraph?
The following paragraph is not written in the correct form. Look at the para graph
with a partner and discuss what is wrong with its form.
my name is Maria Andro
i am 30 years old
i am from Italy
my native language is Italian
i am a hairdresser
3. Rewrite the corrected paragraph.
4. Turn to page 26 in your workbook. Write a paragraph about yourself.
58
Phonics
Short a as in
man
Short e as in
men
A. Listen and repeat.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
man
pan
sat
pat
bat
mat
men
pen
set
pet
bet
met
B.
Short e sound is also written as ea
Weather , feather , bread , spread ,
head , dead , heavy.
C. Tick the word you recognize from the box above in each sen tence you hear.
D. Read the sentences. Put the underlined words in the right col umn.
- It rained heavily yesterday.
- I took my old leather bag and held my um brella over my head.
- I went to the shop and asked the salesman to give me a bread pan.
- I went back home and baked some bread in it.
Short a Short e
Lesson 4
U
n
i
t
6
59
Subject pronoun + Be
I
He
She
It
We
They
You
Be contractions
am
is
are
Im
Hes
Shes
Its
Were
Theyre
Youre
Greetings 4
Grammar Summary
Possessive adjectives
This
my
your
his
her
our
their
its
is friend.
Wh-Questions with Be
What
is
your
his / her
Where
Who
are
is
are
is
are
their
my
their
my
your
his / her
our
name(s)?
school(s)?
teacher(s)?
Yes / No Questions with Be
Is
Are
Is
English
they
she
easy?
from Italy?
Chinese?
Yes / No Questions with Be
Yes, it is.
No, it isnt.
Yes, they are.
No, they arent.
Yes, she is.
No, she isnt.
60
Greetings 4
Speaking
In groups of three or four:
- Make a conversation with group members. Ask about his/her age, family, school,
last name, nationality, ....etc.
- Write down the information. Find what you have in common. e.g. same age, same
number of sisters / brothers ...etc.
Reading
A. Read about four people. Complete the chart below.
Lee is a student in an English lan guage
centre. He comes from Seoul, South
Korea. He can speak two languages Korean and
Chinese. In addition, he wants to learn English
so that he can become a doctor. He likes swim-
ming very much, but he has no time nowadays.
Eduardo is from Mindanao, Philippines.
His mother tongue is Tagalog, but he also
speaks English fuently. He is a secretary in a big
offce in Saudi Arabia. One day, he wants to own
a business. His hobby is playing foot ball.
61
Lesson 4
Who is
he / she?
Where is he / she
from?
What does he / she
want to be?
What languages does
he / she speak?
1
2
3
4
B. Imagine that you are one of these people. Talk about your self.
e.g. My name is Ameera / Lee. Im from Egypt / Korea, ...........etc.
Listen to three conversations and complete the in for mation about each person.
Listening
Family name First name Studying Country
1.
2.
3.
Bilal Germany
computer science
Khalid
Ameera is a librarian in Egypt. She
was born in Cairo, but her family moved
to Alexandria recently. She can speak
and write En glish very well. She wants to im prove
her spelling be cause she would like to be a
journalist someday. She also reads a lot.
Su Chen is a Chinese nurse. She is from
Taipei, Taiwan. Mandarin Chinese is her
frst language. She can read and write
English well, but she needs to im prove her
spoken lan guage. She wants to do her doctorate
in nursing. In her free time, she likes to cook.
Daily Life Daily Life
Unit 7
In this unit, you are going to:
l
talk about daily activities.
l
talk about work and school.
l
listen to someone talk about his daily activities.
l
read about a day in the life of a tourist guide.
l
write a paragraph describing a job.
62
63
Discussion
A. Listen and practise.
B. What activities do you enjoy doing after school?
Conversation
Saif :
Yasser :
Saif :
Yasser :
Saif :
Yasser :
Saif :
Yasser :
Saif :
Yasser :
What do you do, Yasser?
I work for the Ministry of Health.
Do you have a long working day?
I usually work from 10:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m.
So you wake up late in the morning.
No, I always get up early so that I can perform Fjar
prayer at the mosque, read the Holy Quran, ex er cise
and read the newspaper.
Do you usually have lunch at work?
No, I usually have lunch with my family, but some times
I eat out with my friends.
How about having lunch with me next week?
Oh! Id love that.
- How often do you _______________?
meet friends watch sports look after chil dren
visit relatives study do housework
eat out
spend time with family
U
n
i
t
7
Lesson 1
64
Grammar
Daily life 1
A. Complete the sentences with suitable words or expressions.
1. My family _______________ has breakfast at exactly _________ every weekend.
2. I _________ go to school on Thursdays, so I have time to clean my closet _______.
3. My mother __________ cooks on ___________ because we usually have lunch at
my grandmothers.
4. We ___________ go to the funfair at around ______________.
5. My family __________ goes to the beach on weekends because it is overcrowded.
A. Take turns asking and answering about some activities you do on weekends. Use
suitable adverbs of frequency.
I usually meet them on
Thurs days.
How often do you
meet friends?
Adverbs of Frequency
Al ways
100%
Usually
99-90%
Often
90-75%
Never
0%
Rarely
10-1%
Seldom
25-10%
Some times
75-25%
Adverbs of frequency
I always get up
He often goes to bed
I usually have dinner
We never stay
She is always the best in class.
at 7:30
early
at around quarter to nine
at exactly half past seven
before / after four
in the morning.
at night.
in the evening.
in the afternoon.
Time ex pressions
65
Vocabulary
A. Look at the pictures.
Match the pictures to the jobs in the box. Say what each person does.
Abdulaziz is describing his working day to Ahmad. When can he do each activity?
Listen and tick.
B. Imagine you are a ____________. Talk about your daily activities.
(job)
Listening
Day shift Activity Night shift
watch sports
spend time with family
eat out
visit friends
shop
exercise
Journalist
writes for
newspapers
waiter
serves in a
res tau rant
secretary
writes letters
(types)
announcer
presents
(news)
policeman
controls
traffc
____________ ____________ __________ ____________ ________
U
n
i
t
7
Lesson 2
66
Lesson 2
A. Read this article about Ali Habeeb who works as a tour guide in Cairo, Egypt.
Reading
B. Read the article, then circle the better answer.
The article talks about
- Alis daily routine.
- A tour around Cairo.
C. Answer the questions.
1. Name two places Ali takes the tourists to.
____________________________________________________________________
2. How many hours does Ali work everyday?
____________________________________________________________________
D. Find a word from the article that means:
- Old = _____________________ - People who travel for fun = _______________
- To like doing = ______________
E. How often does Ali do these things?
F. Would you like being a tour guide? Why? Why not?
Sometimes people ask me, Do you like your job? I say,
I love it. I always meet in ter esting people from different countries.
Everyday, I start work very early. By nine-thirty, I meet my group
of tourists at the hotel. Then, we start our trip around the city.
I always take them to historical places, such as ancient mosques
and museums. For lunch, I usually take the tourists to typical
Egyptian restaurants. In the evenings, we often visit other places
such as the Pyramids of Al Giza where tourists greatly enjoy the
Sightand Sound Show. They also enjoy visiting traditional market places, es pe cially
Khan Al-Khaleeli. I often help them shop around be cause they dont speak Ara bic.
My work keeps me away from home for long hours. I usually return home at 5.30 p.m.
Sometimes, I stay away for days when I take tourists to Aswan or Hurghada, but I enjoy it.
My wife and kids dont like my job. I seldom go out with them on holidays because I am
busy showing other people around.
Take tourists to ancient places.
Enjoy holidays with family.
See people of many nationalities.
Make shopping easy for tourists.
Not see family 2-3 days.
Always Usually Often Some times Sel dom
67
Conversation
A. Listen and practise.
Noura :
Sara :
Noura :
Sara :
Noura :
Sara :
Noura :
Sara :
Noura :
Sara :
Which school do you go to, Sara?
I go to the Little Womens School.
Oh, I see. My sister Alia works there.
What does she do?
She teaches geography.
What about you, where do you work?
In a hospital. Im a nurse. I look after patients.
It must be hard work.
Yes, it is. What about you, do you like school?
I love it even though some subjects are diffcult.
B. What would you like to be when you grow up? Why?
Grammar
Wh-questions with Do
What do you do?
Which school does she go to?
Where do they work?
How often do you read books?
Im an announcer.
She goes to Little Womens School.
They work for a company.
I always read books.
Answers
SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE
Yes / No questions with Do
Does she go to Little Women School?
Do they work for a newspaper?
Does he like school?
Yes, she does.
Yes, they do.
Yes, he does.
Affrmative
No, she doesnt.
No, they dont.
No, he doesnt.
Negative
U
n
i
t
7
Lesson 3
68
Daily life 3
A. Complete the conversations. Then, practise with a partner.
B. In groups: Play a guessing game.
Here are twelve jobs. Choose a job from the list on the board. Mime action related to
the job. The group guesses the job.
1. A: What _______ you ________ ?
B : Im a ______________.
A: And __________ you study?
B: I study at _________.
A: ______ subjects _____ you like?
B: I like ____________.
2. A: What ______ your father ______ ?
B : Hes a ______. He ____ in a _______.
A: What about your uncle? ___ he work?
B: Yes, _______. He works in a _______.
A: ___________ he do?
B: He is a ______. He _____.
Writing
Read the passage about Sandra King, then complete column A in the table.
B. Fill column B with information about someone you know. Then use it to write a
paragraph on page 31 of your workbook.
Sandra King is a doctor at the Childrens hospital in Riyadh. She starts work at half
past seven in the morning. From 7:30 to 9:00 Sandra sees her patients, then she takes a
coffee break. At ten a.m., she starts her clinic. At two p.m., she goes home to have lunch
with her family. She likes to take a nap before she goes back to work at 4.30. Sandra
stays at work till 9:00 oclock in the evening.
Job
Place
City
A B
A
c
t
i
v
i
t
i
e
s
69
Phonics
Short i as in sit Short e as in set
A. Listen and repeat.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
sit
tins
pin
hid
big
bill
set
tens
pen
head
beg
bell
B.
C. Tick the word you recognize from the box above in each sen tence you hear.
D. Read the sentences. Put the underlined words in the right col umn.
- My uncle is a mechanic.
- He gets up very early in the morning.
- He has breakfast at six oclock.
- He listens to the Quran on his way to work.
- He has dinner with his family at seven oclock.
Short i sound is usually written as i
lip, milk, hint, fridge, bridge, his, six
Short i Short e
U
n
i
t
7
Lesson 4
70
Grammar Summary
Daily life 4
Time expressions
I
Soha and Layla
have a history lesson
start school
Rima
He / She
was born
studies
cooks
sleeps
ten oclock.
9.00 a.m.
the evening.
the afternoon.
the morning.
the 2nd of September.
weekdays.
before / after
at around
late / early
in
on
Adverbs of Frequency
always
usually
often
sometimes
seldom
rarely
never
I
They
go
goes
to work by car.
Bilal
He / She
A. Look at the activities below. Write as many questions as you can about each
one. (not less than two questions)
- read ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
- exercise ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
- visit friends or family ................................................................................................................................................................................................
- watch TV .................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
B. In pairs: Ask and answer each others questions.
Simple Present: Wh-and Yes / No questions with Do
Where
When
Do
Does
do
does
exercise
in the morning?
exercise
I / you / we / they
he / she
they / we
he / she
71
Daily life 4
C. Rewrite the sentences, using the adverbs.
1. He spends Thursday morning with his friends. (always)
...............................................................................................................................................................................
2. They go to the library and borrow some books. (usually)
...............................................................................................................................................................................
3. They let a week without reading a book. (never)
...............................................................................................................................................................................
4. They play table tennis to gether. (often)
...............................................................................................................................................................................
5. They have lunch in a restaurant. (rarely)
...............................................................................................................................................................................
Speaking
A. There are certain activities that you do daily. What are they? How much time do
you spend on each? Fill in the table.
activity time spent activity time spent
B. Look at Mahas time circle. Use the table above to make your own time circle.
Sleeping
Eating
R
e
a
d
i
n
g
P
r
a
y
i
n
g
W
ritin
g
L
e
tte
rs
F
a
m
i
l
y
F
r
i
e
n
d
s
S
w
i
m
m
i
n
g
V
e
ry
p
e
r s
o
n
a
l
TV
H
o
m
e
w
o
r
k
School
72
Lesson 4
C. In pairs: Ask about each others activities. What do you have in common?
D. Look at your time circle. Do you think you should change some of your daily
ac tivities to make better use of your time?
Reading
A. Look at Yassers picture. Where do you think he works? Fill in the table.
B. Read the paragraph about Yasser. Complete it with the words from the box.
Everyone, at the airport, knows Yasser. He is a ground steward for Saudi Airlines.
He checks passenger passports, tickets, etc. ....................................... weekdays, Yasser sleeps
most of the day and wakes up a little ....................................... 11:00 ....................................... the morning. He
has brunch (break fast and lunch) ....................................... 11:30 or 12:00. He watches television
...................................... the afternoon prayers. He leaves for work after nine oclock .......................................
night and re turns ....................................... in the morning, usually around 5 a.m. He hurries to the
mosque to pray and is never late for Fajr prayer.
before - around - in - early - late - on - at - after
What I know
K
What I learnt
L
What I want to know
W
.........................................................
.........................................................
.........................................................
.........................................................
.........................................................
.........................................................
.........................................................
.........................................................
.........................................................
.........................................................
.........................................................
.........................................................
73
Review
Review
Unit 8
74
In groups: Play Lie Detectors. Follow your teachers instructions.
Speaking
Listening
Listen to people talk about their jobs. As you listen to the tape, check the statements
that are true.
Huda
Huda works in an offce.
She knows how to type.
She types memos and letters.
People ask Huda for appointments.
Badr
Badr works only at night.
The restaurant is usually busy.
He has an easy job.
Badr works hard.
He gets tired at work.
He likes his job.
Abdullah
Abdullah starts at the same time every day.
He stays in shape by jogging and swimming.
Being in good shape is important for his job.
Abdullah likes his job.
He thinks his job is important.
Sometimes, he helps injured people.
Huda is a re cep tionist.
Badr is a waiter.
Abdullah is a frefghter.
U
n
i
t
8
Lesson 1
75
Vocabulary
A. Write at least fve items under each category.
Adverb of frequency Places Jobs Greeting
usually school teacher shake hands
B. In groups: Play Swing.
Team (1)
Choose a word either from the table above or one of your own. e.g. time Draw a box for
each letter.
Team (2)
Try to guess the word.
The team that guesses the words wins a point.
Lesson 1
76
Speaking
In groups: Take out a piece of paper. Divide it into six equal rows. Write
Who - Did - What - With whom - Where - When - at the top of each
row. Then, follow your teachers instructions.
Reading
A. How often do you go grocery shopping? Who do you go with?
Every Thursday, Maha and her family go shopping. They always visit the Red Sea
Hypermarket. Usually, Maha has her two brothers and her mother with her. Often, the
supermarket has special offers on Thursdays. Maha and her brothers love to taste the
different kinds of food that are on display. They begin by picking up dairy products, like
milk, cheese and butter. Then, they buy a variety of juices. Next, Mahas mother stops to
get fresh fruit and vegetables. She never buys meat from the su per mar ket. Maha loves to
choose things for the house. Her brothers love to drive the trolley through the chocolate
and cookie section. They always argue about which type of cornfakes to choose. Usually
the trolley gets full and they have to get a second one. Maha never forgets to check her
shopping list. She usually manages to buy all the items on the list. She rarely fnds the
check-out counter empty, as the queue at the cash ier is always long. Maha and her brothers
help to put everything in the car. They return home tired, but happy.
U
n
i
t
8
Lesson 2
77
Lesson 2
B. Rewrite the sentences below, replacing the underlined words in the passage with
the underlined words in the sentences.
1. Maha and her brothers try eating different kinds of food in the supermarket.
2. They start buying milk, cheese and butter.
3. Theres a long line so she has to wait to pay.
4. Mahas brothers fght about things to buy.
C. Put in the correct adverb of frequency.
1. The family needs two trolleys because they have a lot of groceries.
2. Mahas mother goes to the meat section at the Red Sea Hypermarket.
3. Maha checks the shopping list.
4. Mahas family shops at the same supermarket.
Always Usually Often Sometimes Never
%100
78
Speaking
In groups: Play Find the name. Follow your teachers instructions.
Vocabulary
Listening
A. Listen and circle the names you hear. Then, write them in the chart.
Salem - Dawood - Nadir - Jamlah
B. Where are they from? What are they doing? Listen and fll in the chart.
Write a verb that is used with each given words. Then, add one word for each verb.
1. homework /
2. holiday /
3. at home /
4. friends /
5. a programme /
Name On vacation? From?
Salem
U
n
i
t
8
Lesson 3
79
Phonics
Short vowels (a , i , o)
In groups:
A. Cut the set of cards at the back of your book page 89.
B. Read the words. Then, sort the cards according to their sound. Some words can
be put under more than one column.
a i e
C. Write the words that have completely different sounds.
Complete the conversation. Then, practise with a friend.
Noura :
Rania :
Noura :
Rania :
Noura :
Rania :
Noura :
Rania :
Noura :
Rania :
Hi, my name is Noura.
Hello Noura. Im Rania.
Nice party! Are you enjoying yourself?
Are you Hudas friend?
Im a student. Im in the eighth grade.
Nice meeting you, too.
Conversation
U
n
i
t
8
Lesson 4
80
Lesson 4
Speaking
In pairs: Ask questions to complete the paragraph about the historian Mohammad
Hussein Zaidan.
Student A : Turn to page 90.
Student B : Turn to page 91.
Writing
A. Choose two countries. Name a famous person from each country. On the time
line, write the events of his / her life.
B. Write a paragraph about one of the people you have chosen.
Communicative Activities Communicative Activities
Speaking,
Reading
&
Speaking,
Reading
&
Appendix A
Appendix A
82
V
a
n
c
o
u
v
e
r
N
e
w
Y
o
r
k
B
r
a
s
i
l
i
a
B
u
e
n
o
s
A
i
r
e
s
J
o
h
a
n
n
e
s
b
u
r
g
K
a
r
t
o
o
m
C
a
i
r
o
T
u
n
i
s
C
a
s
a
b
l
a
n
c
a
L
o
n
d
o
n
A
l
Q
u
d
s
K
a
r
a
c
h
i
B
a
n
g
k
o
k
S
y
d
n
e
y
B
e
i
j
n
g
T
o
k
y
o
a
h
e
a
d
b
e
h
i
n
d
83
V
a
n
c
o
u
v
e
r
N
e
w
Y
o
r
k
B
r
a
s
i
l
i
a
B
u
e
n
o
s
A
i
r
e
s
J
o
h
a
n
n
e
s
b
u
r
g
K
a
r
t
o
o
m
C
a
i
r
o
T
u
n
i
s
C
a
s
a
b
l
a
n
c
a
L
o
n
d
o
n
A
l
Q
u
d
s
K
a
r
a
c
h
i
B
a
n
g
k
o
k
S
y
d
n
e
y
B
e
i
j
n
g
a
h
e
a
d
b
e
h
i
n
d
T
o
k
y
o
P
a
r
i
s
84
Unit 5
Speaking
Student A
name
date of birth
place of birth
date journey started
place journey started
length of journey
duration of journey
date of death
Your traveller Your partners traveller
miles.
years.
Marco Polo was born in 1254 in Venice, Italy. In 1271, he travelled to Cathay,
China, with his father and uncle. They went from Venice to the Kingdom of Georgia.
When they reached Hormuz on the Arabian Gulf, they wanted to take a ship to
Cathay. They found ships to be unsafe, so they travelled by land. They took three
and a half years to fnish the 5600 mile- long journey. In 1275, they arrived to the
capital of China.
The Polos stayed in China for 17 years. Marco Polo became
very close to Kublai Khan, the ruler of China. The Polos
collected a lot of money and became very rich. They wanted
to leave the country before Kublai Khan died.
Marco Polo fnally arrived back in Venice in 1295. The sea
journey took two years and many people died on the ship.
A few years later Marco Polo wrote his book, The Travels of
Marco Polo . He died in 1324 when he was 70 years old.
85
Unit 5
Speaking
Student B
Ibn Battuta was born in 703 H in Tangier, Morocco. He travelled in 725 H when
he was 12 years. His main reason to travel was to go to Hajj, as all good Muslims
do. In Makkah, he decided to travel around the world. He travelled 7500 miles in
30 years and visited nearly 44 countries.
Ibn Battuta was the frst Muslim to visit every country ruled
by Muslims at that time. Among the places, he visited
Africa, Russia, India and China. He served the Chinese
Emperor, the Mongol Emperor and the Islamic Sultan.
During his journey, Ibn Battuta faced many dangers and had
many adventures. He also performed Hajj seven times. He returned to
Morocco in 755 H. He wrote the events of his journey in a book called
The Travels of Ibn Battuta. He died in 768 H at the age of 65.
name
date of birth
place of birth
date journey started
place journey started
length of journey
duration of journey
date of death
Your traveller Your partners traveller
miles.
years.
86
87
Unit 8
Lesson 1
Rules Sheet
9. The next player
takes the top
action cards.
10. The player with
no cards is the
winner.
5. Dont show it to
the others.
6. Ask the other
person.
7. The player chooses
a card and replies.
8. If its a good an swer,
throw away both
matching cards.
1. Deal out the
fre quency cards.
2. Look at your cards. 3. Put the action cards
down.
4. Player 1 takes the
top action card.
How often do
you...?
Everyday / on
Tues days / once
a week etc.
86
88
89
Unit 8
Lesson 1
Lie detectors
Action cards
smile cry shower do some exercise
tell a lie read a book clean the house stay up all night
drive too fast ride a horse Go to the park spend too much money
FREQUENCY CARDS
Every day
Once every fve
years
Always
Once a year
Twice a week
Once a week
Seldom
Sometimes
At weekends
Never
Often
On Monday
mornings
87
90
91
Unit 8
Lesson 3
Find the Name
A soldier who likes football.
A Philippino nurse.
A pilot who lives in Tabouk.
An Indian engineer who likes painting.
A 21 years-old student who likes reading.
A policeman from New-Zealand who likes cooking.
An Italian house wife.
A 50 years-old doctor.
A Japanese freman who likes karate.
A teacher who likes writing stories.
88
92
Unit 8
Lesson 4
stamp straight give
park speak kindergarten
camp write but
garage room cousin
mechanic plane until
bread sweets success
friend bull touch
health children memory
collected sit hospital
road important column
89
93
Unit 8
Lesson 4
Student A
(1)
(3)
(5)
(7)
(9)
(11)
(13)
(15)
90
Mohammad Hussein Zaidan was born in (1)..... His mother died when he was three
years old. He lived in (3) ............ with his father and grandmother who looked after him.
Mohammads father was a (5) .......... but he wanted to educate his son. Mohammad
went to a school called Al Raqia School in the morning and in the afternoon he stud ied
(7) .......... at the Holy Mosque. After graduating from school, he became a teacher.
In (9) ..........., he got married. He moved to Makkah in 1358. He wrote articles for
the newspaper and (11) ............ for the radio. He also wrote books on history and politics.
His most popular book Tamr wa Jamr was a collection of short articles about social
issues. His radio programme Kilma wa nos made him a house hold name. He died
in (15) .......... at the age of 87.
94
Unit 8
Lesson 4
Student B
(2) _____________________________________________________________________
(4) _____________________________________________________________________
(6) _____________________________________________________________________
(8) _____________________________________________________________________
(10) ____________________________________________________________________
(12) ____________________________________________________________________
(14) ____________________________________________________________________
(16) ____________________________________________________________________
Mohammad Hussein Zaidan was born in 1325. His (2) ........ died when he was
three years old. He lived in Madinah with his (4) ........................ who looked after him.
Mohammads father was a grocer but he wanted to educate his son. Mohammad
went to a school called (6) ............... in the morning and in the afternoon he
studied religion at the Holy Mosque. After graduating from school, he became
a (8) ........... In 1348, he got married. He moved to (10) .............. in 1358. He
wrote articles for the newspaper and programmes for the radio. He also wrote
(12) ............ on history and politics. His most popular book Tamr wa Jamr was a
collection of short articles about social issues. His radio programme (14) ..........
made him a household name. He died in 1412 at the age of (16) .................
91
92
Vocabulary
&
Expressions
Vocabulary
&
Expressions
Appendix B
Appendix B
93
Unit 1 Hobbies
Adjectives
favourite
Verbs
can / cant
cook
draw
go swimming
like
make (a dress)
play (tennis)
swim
use
sew
Nouns
Hobbies
cooking
drawing
sewing
bowling
listening to the radio
playing tennis
basketball
reading
swimming
collecting stamps
watching TV
writing
using a computer
writing
fshing
Other nouns
abilities (pl.)
free time
hobbies (pl.)
hobby
Conjunction
but
Language Use
Whats your hobby?
What do you like doing in your free time?
What can you do?
Can you..........?
I like ..........................
I can ..............
Yes, I can.
No, I cant
94
Unit 2 Time Around the world
Unit 3 Weekends
Nouns
airport
world
fight
Verbs
fy
arrive
Adverbs
ahead
behind
Time expressions
fve ( past / to )
ten ( past / to )
twenty ( past / to )
local time
Language Use
How many hours is ........ ahead / behind?
Its ....................
Adverbs
last ( night / week / month / year )
Language Use
Did you have a good weekend?
Did you have fun?
What did you do last ......?
Yes, I did.
We had a lot of fun.
I ...............
Nouns
Activities
horse back riding
walking
sailing
visiting family
collecting shells
going for picnics
other nouns
activity
weekend
beach
Verbs
drive to
fx
have ( a good time )
stay ( at my aunts house, in
bed, in a hotel )
take ( a walk )
Irregular past
did
went
drove
saw
had
drank
brought
ate
made
few
met
95
Unit 5 People
Nouns
college
prophet
found
shepherd
poet
scientist
artist
cook
pilot
Verbs
be born
die
get married
graduate
start college
invent
Adjectives
honest
truthful
famous
Language Use
Who( is / was ) ...............?
( Where / when ) was ............... born?
When did .............. die?
( He / she) is / was ...............
( He / she) was born in ............... .
( He / she) died in ...............
Adverbs
Times
A.D.
Ago
Hijra
Language Use
Introducting someone
This is ...... / these are ........
Hi, ........... Nice to meet you.
Exchanging personal information
Whats your name?
Im ........... / My name is ..........
Where are you from?
Im from ..............
Are you .............. ?
No, Im not. / Yes, I am.
Nouns
Nouns
hand shake
hug
parts of the body
cheek
chin
palm
back
other nouns
gestures
customs
tip
Verbs
Verbs
bow
greet
kiss
meet
pat
press
Unit 6 Greetings
96
Unit 7 Daily Life
Adjectives Nouns
Jobs
Announcer
Journalist
Secretary
Waiter
Other nouns
Daily routine
Schedule
activity
Verbs
Control (trafc)
eat out
look after
serve in
a restaurant
type
rarely
seldom
Language Use
Talking about routines
How often do you ........?
( Once / twice ) a week / month.
When do you .......... ?
I ( usually / sometimes ) ..........
( At / around ) ......... In the morning.
Where do you ........... ?
At ..........
Do they ........... ?
Yes, they do. / No, they dont.
Talking about work and school
What do you do?
I am a .........
Where do you work?
I work ( at / in / for ) ........
Which school do you go to?
I go to ...........
97
Vocabulary and Expressions / First Grade
Nouns
a pair of
apartment
apple
April
Arabic
arm
arm chair
art
August
autumn
back
backache
bag
Baghdad
bakers
banana
bank
barber shop
basketball
bathroom
beard
bed
bed cover
bedroom
beef
belt
blouse
book case
book store
bowling
boy
bread
breakfast
Britain
chart
cheese
hand
handbag
head
headache pain killer
headscarf
history
hot
house
humid
husband
India
ingredients
ink
Italian
Italy
jacket
January
Japan
Japanese
juice
July
June
key
kitchen
knee
knife
lamp
language
library
living room
leg
London
lunch
Makkah
Mall
Manama
mango
March
math
dresser
drycleaner
ear
earache
east
elevators
engineer
English
eraser
escalators
eyes
face
fan
farmer
father
February
fever
fag
four
fower shop
fu
food
fork
France
freezer
French
Friday
friend
furniture store
garage
garden
geography
girl
grandfather
grandmother
grocers
grocery
hair
chicken
children
closet
coffee
cold
college
colour
computer
brother
butchers
butter
cafe
cafeteria
Cairo
cake
capital city
carnation
carrots
cassette
centimetres
chair
cool
cough
cough medicine
country
curtain
customer
daughter
December
desk
dessert
dining room
dining table
dinner
dish
doctor
dress
dress shop
98
Pronouns
he
hers
his
I
whose
you
yours
they
this
we
it
mine
ours
she
that
theirs
these
Nouns
May
metre / kilo
milk
mirror
Monday
money
mosque
mother
moustache mouth
neck /shoulder
nest
New Delhi
nightstand
north
nose
November
nurse
occupation
October
offce
oil
one hundred
onions
orange
Palestine
parent
Paris
pear
pencil
pharmacy
pillow
plants
plate
playground
toothache
trousers
Tuesday
Turkey
Twenty one to
umbrella
uncle
uniform
van
vase
vice principal
visiting family
waiter
warm
Washington D C
watch
water
weather
Wednesday
west
where
wife
window
windy
winter
x-ray
yellow
zebra
shop/ store
shopping centre
shower
single/ king-size bed
sister
size
skirt
snowy
sock
socks
sofa
soldier
son
sore throat
south
spoon
spring
stomach
stomachache
stove
student
suitcase
summer
Sunday
sunglasses
sunny
table
tea
teacher
television
Thursday
toes
tomatoes
tooth - teeth
policeman
potatoes
principal
pyjamas
queue
rainy
refrigerator
region
religion
rest room sta tio nery
restaurants
rice
ring
Riyadh
Rome
room
roses
rug
ruler
salad
sandals
Saturday
Saudi Arabia
school
science
scientist
September
shepherd
shirt
shoes
99
Verbs
are
arrange
ate
brought
build
buy
circle
clean
close
come
cost
did
die
dont
drank
drove
sit down
sleep
stand up
stay (at my aunts house , in
bed, in a hotel)
stay ( in bed )
study
swim
teach
test
turn
wake up
walk
wash
watch
went
work
work on the computer
write
listen
listen to
look
look at
made
make ( a dress )
met
need
open
pick up
pray
put
put down
reach
reach school
sleep
read
repeat
saw
sit
eat
enjoy
exercise
few
fy
get clothes
get up
go
go ( to school / bed )
go out
had
have ( breakfast / lunch
dinner)
help
introduce
is
Adjectives
grey
healthy
her
his
how old
ill
Italian
its
large
long
lost
medium
medium
height (n)
Miss
Mr.
third
thirteenth
three
tidy
twelfth
twentieth
two
weight (n)
what
Whats the
matter?
white
who
yellow
young
seven
seventeenth
seventh
short
six
sixteenth
sixth
size
small
some
straight
tall
ten
tenth
their
thin
Mrs.
my
new
nice
nineteenth
ninth
old
one
orange
our
over weight
pink
Red
Saudi
second
see page...(v)
expensive
fair
fat
ffteenth
ffth
frst
four
fve
fourteenth
fourth
French
friendly
good
good looking
green
d better
any
bad
beautiful
better
big
black
blue
British
brown
cheap
com fortable
curly
dark
eighteenth
eighth
eleventh
100
Adverbs
always
at the back of
often
on the .... foor
sometimes
there
upstairs
usually
downstairs
here
never
Adverbs of place
at the back of
on the .... foor
Articles
a
an
the
Adverbs of place
fve ( past / to)
ten ( past / to )
twenty ( past / to )
local time
Phrases of quantity
a cup of .....
a piece of ......
a bottle of ......
a pot of ......
a glass of ......
Prepositions
be hind
be tween
in
in front
of
near
next to
on
oppo site
under
Language Use
What do you need?
What do you usually have ?
What is the time ?
What language do you speak?
What nationality are you?
Whats the date today?
Whats the weather like?
Whats your hobby?
Whats your name?
Whats your nationality?
When do you ... ...?
Where are you from?
Can you .... .... ....?
Did you have a good weekend?
Did you have fun?
Do you like ... ... ?
Do you need ... ... ?
Fine, thank you.
Good afternoon.
Good morning.
Hello,
Hi,
How are you?
How do you spend your day?
How much does it cost?
It costs ... ... riyals.
My name is -----
Nice to meet you
101
Appendix C Appendix C
Irregular Verbs
&
Spelling Rules
Irregular Verbs
&
Spelling Rules
102
Irregular Verbs
Present
(be) am/is/are
buy
come
cut
drive
fall
feel
get
give
grow
hear
keep
lose
put
quit
Par ti ciple
read
ridden
run
sold
set
sat
slept
spoken
spent
taken
taught
told
thought
worn
written
Past
read
rode
ran
sold
set
sat
slept
spoke
spent
took
taught
told
thought
wore
wrote
Present
read
ride
run
sell
set
sit
sleep
speak
spend
take
teach
tell
think
wear
write
Par ti ciple
been
bought
come
cut
driven
fallen
felt
got
given
grown
heard
kept
lost
put
quit
Past
was / were
bought
came
cut
drove
fell
felt
got
gave
grew
heard
kept
lost
put
quit
Pronunciation of Regular past forms
with /d/
studied
stayed
with /id/
invited
visited
with /t/
worked
watched
103
Comparatives
1. Most words just add -er and -est
long longer than the longest
cold colder than the coldest
fast faster than the fastest
2. Most words with silent -e add -r and -st
wide wider than the widest
late later than the latest
white whiter than the whitest
3. Some words double the last letter.
big bigger than the biggest
fat fatter than the fattest
hot hotter than the hottest
sad sadder than the saddest
4. Words with -y change to -ier and
-iest.
happy happier than the happiest
noisy noisier than the noisiest
thirsty thirstier than the thirstiest
windy windier than the windiest
B
Spelling rules
Plural nouns
1. Most words just add-s
1 pen
1 apple
1 room
2. Words with -s, -ch, -sh, and-x
add es.
1 box
1 bus
1 sandwich
1 crash
3. words with-o add -es.
1 potato
1 tomato
4. Words with -y change to -ies.
1 family
1 library
1 story
5. Words with -f change to -ves.
1 knife
1 wife
1 wolf
6. These words have no -s.
1 child
1 man
1 foot
2 pens
6 apples
10 rooms
2 boxes
3 buses
10 sand wiches
4 crashes
20 po ta toes
10 to ma toes
2 families
8 libraries
9 stories
6 knives
2 wives
5 wolves
2 children
10 men
20 feet
A
104
Adjectives Adverbs
1. Most words just add -ly.
quick
safe
slow
D
quickly
safely
slowly
happy
heavy
hungry
thirsty
happily
heavily
hungrily
thirstily
2. Words with -y take off the -y and add -ily.
Verbs
1. Most words just add -
eateats
arrivearrives
C
1. Most words just add -ed
cleancleaned
repeatrepeated
1. Most words just add -ing
laughlaughing
drinkdrinking
2. Word with -y change to -ies.
fy fies
studystudies
worry worries
2. Word with Silent -e add -d
smilesmiled
reviserevised
useused
2. Word with Silent -e take off
the e and add -ing
taketaking
scorescoring
changechanging
3. Words with -ch, -ss, -o and
-sh add -es.
teach teaches
cross crossess
go goes
fnish fnishes
3. Words with -y, change to -ied.
carrycarried
studystudied
worryworried
3. Some words double the last
letter
sitsitting
swimswimming
stopstopping
4. Some words double the last
letter
stopstopped
traveltravelled
adding -s adding -ed adding -ing
105
King Fahd National Library Cataloging-in Publication Data
Saudi Arabia. Ministry of Education
Say It In English-Second Year Intermediate Pupils Book Term 1 - Riyadh
126p. , 21x26 cm
ISBN : 9960-19-111-7
1 - English language - Study and teaching (intermediate)
SaudiArabia - Arabicspeakers
2 - English language - Textbooks
1 - Title
428.241 dc 0635/19
Ministry of Education, 1998 C
Say It In English
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Ministry of Education
Second Year Intermediate
Pupils Book
Term 1
All rights reserved
No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted,
in any form or by any means, without permission
of the Ministry of Education
1430 / 1431H Edition
2009 / 2010G Edition
You might also like
- اذاعة بمناسبة بداية الفصل الثانيDocument9 pagesاذاعة بمناسبة بداية الفصل الثانيrosefawazNo ratings yet
- جدول اختبار الفصل الدراسي الثاني الصف الثانيDocument1 pageجدول اختبار الفصل الدراسي الثاني الصف الثانيrosefawazNo ratings yet
- جدول اختبار الفصل الدراسي الثاني الصف الاولDocument1 pageجدول اختبار الفصل الدراسي الثاني الصف الاولrosefawazNo ratings yet
- 11Document9 pages11rosefawazNo ratings yet
- مركز مصادر التعلمDocument13 pagesمركز مصادر التعلمrosefawazNo ratings yet
- جدول اختبار الفصل الدراسي الثاني الصف الثالثDocument2 pagesجدول اختبار الفصل الدراسي الثاني الصف الثالثrosefawazNo ratings yet
- أسبوع المياه الصحيDocument5 pagesأسبوع المياه الصحيrosefawazNo ratings yet
- فنية ثاني متوسط ف2Document240 pagesفنية ثاني متوسط ف2rosefawazNo ratings yet
- دراسات اجتماعية ثاني متوسط ف2Document148 pagesدراسات اجتماعية ثاني متوسط ف2rosefawazNo ratings yet
- حديث ثاني متوسط ف2Document74 pagesحديث ثاني متوسط ف2rosefawazNo ratings yet
- تربية اسرية ثاني متوسط ف2Document84 pagesتربية اسرية ثاني متوسط ف2rosefawazNo ratings yet
- لغتي ثاني متوسط ف2Document272 pagesلغتي ثاني متوسط ف2rosefawazNo ratings yet
- فقه ثاني متوسط ف2Document80 pagesفقه ثاني متوسط ف2rosefawaz100% (1)
- توحيد ثاني متوسط ف1Document88 pagesتوحيد ثاني متوسط ف1rosefawazNo ratings yet
- دراسات اجتماعية ف1Document144 pagesدراسات اجتماعية ف1rosefawazNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- تربية اسريه ثاني متوسط ف1Document104 pagesتربية اسريه ثاني متوسط ف1rosefawazNo ratings yet
- فنيه ثاني متوسط ف1Document231 pagesفنيه ثاني متوسط ف1rosefawazNo ratings yet
- حديث ثاني متوسط ف1Document76 pagesحديث ثاني متوسط ف1rosefawazNo ratings yet
- حاسب ثاني متوسط ف1Document218 pagesحاسب ثاني متوسط ف1rosefawazNo ratings yet
- فقه ثاني متوسط ف1Document80 pagesفقه ثاني متوسط ف1rosefawaz100% (1)
- لغتي ثاني متوسط ف1Document272 pagesلغتي ثاني متوسط ف1rosefawazNo ratings yet
- رياضيات ثاني متوسط ف1Document175 pagesرياضيات ثاني متوسط ف1rosefawaz100% (1)
- توحيد ثاني متوسط ف2Document74 pagesتوحيد ثاني متوسط ف2rosefawazNo ratings yet
- انجليزي ثاني متوسط ف2Document144 pagesانجليزي ثاني متوسط ف2rosefawazNo ratings yet
- علوم ثاني متوسط ف1Document201 pagesعلوم ثاني متوسط ف1rosefawazNo ratings yet
- علوم اول متوسط ف2Document211 pagesعلوم اول متوسط ف2rosefawazNo ratings yet
- انجليزي اول متوسط ف2Document116 pagesانجليزي اول متوسط ف2rosefawazNo ratings yet
- لغتي اول متوسط ف1Document224 pagesلغتي اول متوسط ف1rosefawazNo ratings yet