Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Agnosias Aphasias
Uploaded by
gus_lionsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Agnosias Aphasias
Uploaded by
gus_lionsCopyright:
Available Formats
Agnosias, aphasias and other disorders of association cortex.
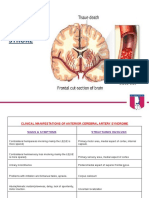
(It is assumed that the language areas are in the left cerebral hemisphere.) ________________________________________________________________________ Disorder Site of lesion ________________________________________________________________________ Agnosias Tactile agnosia: (including astereognosis) Cortical neglect: Left or right Anterior parietal lobe, posterior to primary somesthetic area Right (usually) superior parietal lobe; may extend to occipital lobe
Apperceptive visual agnosia: Acquired achromatopsia Prosopagnosia Left & right inferior occipital cortex Right (usually also left) inferior occipital and posterolateral temporal cortex Occipitotemporal cortex, bilaterally
Associative visual agnosia: Balint syndrome. Combination of: Visual disorientation Ocular apraxia Optic ataxia Auditory agnosia:
Left & right superior occipital cortex Posterior parietal cortex Posterior parietal cortex Posterior, superior temporal cortex, bilaterally Right posterior, superior temporal cortex
Amusia: Disordered control of movement Akinetic mutism:
Left and right supplementary and cingulate motor areas Left or right premotor area (positioning of limb) or anterior, inferior parietal cortex (due to astereognosis) Left angular gyrus
Apraxia:
Agraphia (without aphasia):
Behavioral and affective changes Acquired sociopathy: Ventromedial prefrontal cortex, usually bilaterally Either right inferior parietal cortex, or right inferior medial prefrontal cortex Left prefrontal cortex more often than other localized lesions
Anosognosia (and anosodiaphoria):
Depression:
Speech and language disorders Receptive (Wernicke's) aphasia: Left posterior, superior temporal cortex (Wernicke's area) Left parietal lobe, posterior to Wernicke's area
Anomic aphasia:
Transcortical aphasia: Receptive type: Expressive type: Alexia with agraphia Pure alexia (without agraphia):
Left middle temporal gyrus, inferior to Wernicke's area Left frontal lobe, anterior to Broca's area Wernickes area and left angular gyrus Left occipital lobe and associated commissural fibers either in the underlying white matter or in the splenium of the corpus callosum Left frontal operculum (Broca's area) Whole left perisylvian area (frontal, parietal & temporal opercula) Left inferior parietal lobe (supramarginal gyrus) and underlying arcuate fasciculus Head of left caudate nucleus
Expressive (Broca's) aphasia: Global aphasia:
Conduction aphasia:
Subcortical aphasia: Aprosodia:
Right perisylvian area (frontal, parietal & temporal opercula) ________________________________________________________________________
From Kiernan JA Barrs The Human Nervous System, 8 th ed. (Table 15-1) Copyright2005 Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore & Philadelphia
You might also like
- Disconnectionsyndrome 160606131019Document34 pagesDisconnectionsyndrome 160606131019Tamajyoti GhoshNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument17 pagesStrokeRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Disorders Caused by Lesions in Particular Parts of The Cerebral CortexDocument36 pagesNeurologic Disorders Caused by Lesions in Particular Parts of The Cerebral Cortexapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Parietal LobeDocument22 pagesParietal LobeAllisonNo ratings yet
- (Printing) Pass Medicine Notes - NeurologyDocument97 pages(Printing) Pass Medicine Notes - NeurologyJoanne HoNo ratings yet
- Aphasia Types and CausesDocument9 pagesAphasia Types and Causesdragtoss2No ratings yet
- 2020 - 10 - 29 - Εγκεφαλικά Ημισφαίρια και Αγγειακά Σύνδρομα - ΜήτσιαςDocument67 pages2020 - 10 - 29 - Εγκεφαλικά Ημισφαίρια και Αγγειακά Σύνδρομα - ΜήτσιαςΖέτα ΤσίρκαNo ratings yet
- Neurology Shelf Exam Review - Part 2.newDocument14 pagesNeurology Shelf Exam Review - Part 2.newyogurtNo ratings yet
- OCCLUSIONS & PATHOLOGIES OF THE CNS BLOOD SUPPLYDocument1 pageOCCLUSIONS & PATHOLOGIES OF THE CNS BLOOD SUPPLYFaye Stephanie CantagoNo ratings yet
- Neurology Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016Document158 pagesNeurology Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016Muhammad Haneef100% (2)
- 신경과 novel episode IDocument33 pages신경과 novel episode I김정우No ratings yet
- Kineto Lobii CerebraliDocument30 pagesKineto Lobii CerebraliMerry LeeNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience I - Neurologic History Taking and Examination (POBLETE)Document9 pagesNeuroscience I - Neurologic History Taking and Examination (POBLETE)Johanna Hamnia PobleteNo ratings yet
- Curs 4 Lobii CerebraliDocument51 pagesCurs 4 Lobii CerebraliRazilogo RazzyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy and Physiology of Brain in Regard With StrokeDocument62 pagesClinical Anatomy and Physiology of Brain in Regard With StrokePatricia Ann InneiazhiaNo ratings yet
- Apraxia 2Document25 pagesApraxia 2Vellardo AlbayNo ratings yet
- Curs 2 Lobii CerebraliDocument43 pagesCurs 2 Lobii CerebraliCarmen Maria100% (1)
- Stroke SindromDocument13 pagesStroke SindromEvi Andriani LestariNo ratings yet
- Parietal Lobe TestingDocument5 pagesParietal Lobe TestingvinodksahuNo ratings yet
- Temporal LobeDocument68 pagesTemporal LobeRupinder GillNo ratings yet
- Students Clinical Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesStudents Clinical Case Analysisjacc_282No ratings yet
- Diagnosis TopisDocument101 pagesDiagnosis TopisGita Nur SiwiNo ratings yet
- Apraxia, Agnosia and Disconnection SyndromesDocument65 pagesApraxia, Agnosia and Disconnection SyndromesDhawal Narang100% (1)
- Neurorehabilitation 1: Stroke, TBI, MS, PD, GBS, and ALS ExaminationDocument439 pagesNeurorehabilitation 1: Stroke, TBI, MS, PD, GBS, and ALS ExaminationDuncan D'AmicoNo ratings yet
- 1.13.2 Clinical Localization and History in NeurologyDocument42 pages1.13.2 Clinical Localization and History in Neurologyfikrah sharifNo ratings yet
- Stroke Syndromes GuideDocument4 pagesStroke Syndromes GuideUsman AR VainceNo ratings yet
- 3 Silhouet SignDocument79 pages3 Silhouet Signricky rdnNo ratings yet
- Clinical Neuroanatomy Part 1 (Original)Document80 pagesClinical Neuroanatomy Part 1 (Original)LEENo ratings yet
- Parietal LobeDocument29 pagesParietal LobeAdrishyaNo ratings yet
- Stroke Rehabilitation (Bayu) - EditDocument34 pagesStroke Rehabilitation (Bayu) - EditFinny BoekorsjomNo ratings yet
- Topical Diagnosis: Muhammad Iqbal BasriDocument80 pagesTopical Diagnosis: Muhammad Iqbal BasriMagfira Al HabsyiNo ratings yet
- Stroke RehabilitationDocument59 pagesStroke Rehabilitationnukareva100% (1)
- Clinicals of NeuroanatomyDocument9 pagesClinicals of Neuroanatomyaneeqahmed99No ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Sensory and Motor FunctionsDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Sensory and Motor FunctionsSpencer ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of BrainDocument29 pagesBlood Supply of Brainsalmankhan09215No ratings yet
- Cerebral Hemispheres Dysfunction and DiseaseDocument55 pagesCerebral Hemispheres Dysfunction and DiseasedrprasantNo ratings yet
- CLINICAL CASE ANALYSES: CEREBRUM AND HIGHER CORTICAL FUNCTIONDocument8 pagesCLINICAL CASE ANALYSES: CEREBRUM AND HIGHER CORTICAL FUNCTIONjacc_282No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab 1: Sectional Planes & TerminologyDocument9 pagesAnatomy Lab 1: Sectional Planes & TerminologyaliNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Cortex MappingDocument62 pagesCerebral Cortex MappingMORGAN LAMBERTNo ratings yet
- Cerebral hemisphere anatomy and functionsDocument83 pagesCerebral hemisphere anatomy and functionsAlokh Saha RajNo ratings yet
- Control of Movement by The Brain: Fakultas Kedokteran USUDocument12 pagesControl of Movement by The Brain: Fakultas Kedokteran USUWinda Adelia LubisNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Higher Cortical Visual Function: D Lelli, MD Feb 6, 2015Document21 pagesDisorders of Higher Cortical Visual Function: D Lelli, MD Feb 6, 2015helloNo ratings yet
- Parietal Lobe: Functional AnatomyDocument11 pagesParietal Lobe: Functional AnatomyILul Hidayat ARNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Cortex Areas and Their FunctionsDocument62 pagesCerebral Cortex Areas and Their FunctionsJ NNo ratings yet
- Stroke Syndromes: Hemiparesis (Faciobrachiocrural Weakness)Document7 pagesStroke Syndromes: Hemiparesis (Faciobrachiocrural Weakness)eko aNo ratings yet
- Neuro LesionsDocument7 pagesNeuro Lesionskep1313100% (5)
- Localization of sensory 肖争1 -student-2020Document49 pagesLocalization of sensory 肖争1 -student-2020mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- 4-TOPICAL DIAGNOSIS-clinical AnatomyDocument61 pages4-TOPICAL DIAGNOSIS-clinical AnatomyMuhammad SyauqadNo ratings yet
- Cortical Function: Dr. Paulus Anam Ong SP.S Dr. Yustiani Dikot SP.S (K) Bagian I.P. Saraf RSHS FKUPDocument78 pagesCortical Function: Dr. Paulus Anam Ong SP.S Dr. Yustiani Dikot SP.S (K) Bagian I.P. Saraf RSHS FKUPMuhammad Hamid MuktashimNo ratings yet
- Stroke Syndromes - MCA, ACA, ICA, PCA, Vertebrobasilar Artery SDocument3 pagesStroke Syndromes - MCA, ACA, ICA, PCA, Vertebrobasilar Artery Sabu_abdisysyaakirNo ratings yet
- 5 Major Stroke Syndromes: Recognition, Action & OutcomesDocument43 pages5 Major Stroke Syndromes: Recognition, Action & OutcomesweezerNo ratings yet
- Res 113Document197 pagesRes 113Belinda ELISHANo ratings yet
- Where Is The LesionDocument12 pagesWhere Is The LesionHo Yong WaiNo ratings yet
- CVA Ken Presentation FINALDocument110 pagesCVA Ken Presentation FINALJulia Salvio100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Total Anterior Circulation Infarction Left Middle Cerebral Artery (TACILMCA)Document2 pagesPathophysiology Total Anterior Circulation Infarction Left Middle Cerebral Artery (TACILMCA)PATHOSHOPPE100% (1)
- HemiplegiaDocument30 pagesHemiplegiasarguss14100% (1)
- CBIO261 Week 7 ActivityDocument1 pageCBIO261 Week 7 ActivityKaitlyn RobisonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linguistic Thought: LING 200Document22 pagesIntroduction To Linguistic Thought: LING 200Aivy Mae SanchezNo ratings yet