Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Urea
Uploaded by
ryadav_257018Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Urea
Uploaded by
ryadav_257018Copyright:
Available Formats
UREA
IFFCO's Urea is not merely a source of 46% of nutrient nitrogen for crops, but it is an integral part of millions of farmers in India. A bag of IFFCO's urea is a constant source of confidence and is a trusted companion for Indian farmer. Urea is the most important nitrogenous fertiliser in the country because of its high N content (46%N). Besides its use in the crops, it is used as a cattle feed supplement to replace a part of protein requirements. It has also numerous industrial uses notably for production of plastics. Specification of urea as per Fertiliser 1. Moisture % by weight, maximum 2. Total N % by weight (on dry basis) minimum 3. Biuret % by weight, maximum 4. Particle size Control Order 1.0 46.0 1.5 90% of the material shall pass through 2.8 mm IS sieve and not less than 80% by weight shall be retained on 1 mm IS sieve.
If urea is applied to bare soil surface significant quantities of ammonia may be lost by volatilisation because of its rapid hydrolysis to ammonium carbonate. The hydrolysis of urea can be altered by the use of several compound called urease inhibitors. These inhibitors inactivate the enzyme and thereby prevent the rapid hydrolysis of urea when it is added to soil. The rapid hydrolysis of urea in soils is also responsible for ammonia injury to seedlings if large quantities of this material placed with or too close to the seed. Proper placement of fertiliser urea with respect to seed can eliminate this difficulty.
NPK
As far as Indian farmer is concerned, IFFCO's NPK/DAP is not just a source of crucial nutrients N, P, K for the crops, but is an integral part of his/her quest for nurturing mother earth. The bountiful crop that results from this care is an enough reason for the graceful bags of IFFCO NPK/DAP bags to be an integral part of the farmers' family. The two grades of NPK produced by IFFCO, 10:26:26 and 12:32:16, indicating the content of N, P, K proportion, are tailor made to supply the exact composition required for replenishment of the soil.
NPK/DAP DIAMMONIUM PHOSPHATE
It is the most popular phosphatic fertiliser because of its high analysis and good physical properties. The composition of pure salt of DAP is N-21.19% and P205 -53.76%. Fertiliser grade DAP is 18:46:0.
NPK COMPLEX GRADES
NPK complex fertilisers produced at Kandla are DAP based grades. At present two grades Grade I 10:26:26 and Grade II 12:32:16 are produced. Granular NPK complexes are free flowing and do not pose any problem during handling and storage. However, exposure of material for long period to very high humidity may cause caking. Therefore, NPK complexes are bagged in quality tested HDPE bags to prevent ingress of moisture. Specifications Of DAP/NPK Complex As Per DAP NPKNPKFertiliser Control Order 10:26:26 12:32:16 1. Moisture % by weight, maximum 1.5 1.0 1.0 2. Total N % by weight, minimum 18.0 10.0 12.0 3. Ammoniacal N % by weight, minimum 15.5 7.0 9.0 4. N in the form of urea, % by weight, maximum 2.5 3.0 3.0 5. Neutral ammonium citrate soluble phosphates (as 46.0 26.0 32.0 P2O5) % by weight, minimum 6. Water soluble phosphates (as P2O5) % by 41.0 22.1 27.2 weight, minimum 7. Water soluble potash (as K2O) % by weight, -26.0 16.0 minimum 8. Particle size 90% of the material will be between 1 mm and 4 mm IS sieve and not more than 5% will be below 1 mm size. Typical Composition Of DAP/NPK Complex Grades (By Weight) 1. Moisture 2. Diammonium phosphate 3. Muriate of Potash 4. Urea 5. Filler (silica sand) DAP 0.90 87.53 -3.09 8.48 NPK10:26:26 0.88 50.04 43.98 1.50 3.60 NPK12:32:16 0.85 62.68 26.88 1.63 7.96
Secondary/Micro Nutrients 1. Sulphur as S 2. IRON AS FE 3. Aluminium as AI 4. Calcium as Ca 5. Magnesium as Mg 6. Zinc as Zn (ppm) 7. Copper as Cu
DAP 0.48 0.31 0.32 0.12 0.26 103 55
NPK10:26:26 0.88 0.40 0.52 0.11 0.34 98 32
NPK12:32:16 0.66 0.25 0.18 0.09 0.31 88 27
Atomic weight
C=12, H=1, O=16, N=14, P=31, K=39, Ca=40, S=32, C1=35.
CONVERSION FACTORS
P to P2O5 = 2.29; P205 to P = 0.44 K to K2O = 1.2; K2O to K= 0.83
BIO FERTILISERS
Biofertilisers are capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen when suitable crops are inoculated with them. Biofertilisers are low cost, effective, environmental friendly and renewable source of plant nutrients to supplement fertilisers. Integration of chemical, organic and biological sources of plant nutrients and their management is necessary for maintaining soil health for sustainable agriculture. The bacterial organisms present in the biofertiliser either fix atmospheric nitrogen or solubilise insoluble forms of soil phosphate. The range of nitrogen fixed per ha/year varies from crop to crop; it is 80 - 85 kg for cow pea, 50 - 60 kg for groundnut, 60 - 80 kg for soybean and 50 - 55 kg for moongbean.
PRICES OF IFFCO FERTILISERS (W.E.F. 1ST' APRIL, 2013)
( Rs. PMT ) UREA NPK-I (10:26:26)
NP NPK-II APS (12:32:16) (20:20:0:13) (28:28:0)
DAP DAP(Imp.) Neem (18:46:00) (18:46:00) Coated Urea 22500 22,500 5680.87
5412.63
20900
21000
18000
22000
You might also like
- The Potential Use of Rock Phosphate in Sudan for Sustainable Agricultural ProductionFrom EverandThe Potential Use of Rock Phosphate in Sudan for Sustainable Agricultural ProductionNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectDocument12 pagesSciencedirect Sciencedirect Sciencedirectnovita evi handayaniNo ratings yet
- Diammonium Phosphate (DAP) Production ProcessDocument10 pagesDiammonium Phosphate (DAP) Production ProcessGlobal PMC100% (1)
- NPK Production Technologies Fertilizer FocusDocument6 pagesNPK Production Technologies Fertilizer FocusELIO BARRIOS IBARRANo ratings yet
- Internship project report on fertilizer manufacturingDocument79 pagesInternship project report on fertilizer manufacturingBharath Vr100% (1)
- FertilizersDocument7 pagesFertilizersshazeen shoaibNo ratings yet
- Soil Science MCQDocument6 pagesSoil Science MCQSonam RanaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Fertilizer Materials: Potassium Nitrate (KNODocument4 pagesInorganic Fertilizer Materials: Potassium Nitrate (KNOChitanga BiembaNo ratings yet
- FertilisationDocument22 pagesFertilisationvaishu2488No ratings yet
- Scientific Authenticity of Nano Liquid Urea: Why in News?Document3 pagesScientific Authenticity of Nano Liquid Urea: Why in News?MohitNo ratings yet
- E Ifc 47 December 2016 HRDocument34 pagesE Ifc 47 December 2016 HRqadriranaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Yara Fertilizer Industry HandbookDocument46 pages2014 Yara Fertilizer Industry HandbookMarcusWerteck100% (1)
- IFFCODocument107 pagesIFFCODSGNo ratings yet
- W F O T N ?: Hat Is in Ertilizer Ther HAN UtrientsDocument5 pagesW F O T N ?: Hat Is in Ertilizer Ther HAN UtrientsalejandrorubilarNo ratings yet
- Diammonium Phosphate: 3500 Parkway Lane, Suite 550 Norcross, Georgia 30092-2844 USA Phone (770) 447-0335Document1 pageDiammonium Phosphate: 3500 Parkway Lane, Suite 550 Norcross, Georgia 30092-2844 USA Phone (770) 447-0335Sushil ChandnaniNo ratings yet
- DuofosDocument2 pagesDuofosGrignion100% (1)
- NP Nutrients and Their Role in Plant GrowthDocument36 pagesNP Nutrients and Their Role in Plant GrowthGustia MiaandimiNo ratings yet
- Specifications of UREA 46 GRANULADODocument2 pagesSpecifications of UREA 46 GRANULADOMartí Vilà VallsNo ratings yet
- NovaTec Pro 147172TEDocument6 pagesNovaTec Pro 147172TEMichele LamNo ratings yet
- NovaTec Solub NKMax 16816Document8 pagesNovaTec Solub NKMax 16816Kifah ZaidanNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology - A Recent Approach For Enhancement of Phosphorus in CropsDocument4 pagesNanotechnology - A Recent Approach For Enhancement of Phosphorus in CropsRashmi C M RashmiNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Nitrogen NotesDocument20 pagesFertilizer Nitrogen NotesAmal ShajuNo ratings yet
- Yara FertilizersDocument16 pagesYara FertilizersBeeLive Health100% (2)
- Commodity Part 2Document8 pagesCommodity Part 2Kristine MangilogNo ratings yet
- 8 Fertilizer IndustryDocument24 pages8 Fertilizer IndustryNida TasneemNo ratings yet
- 10-20-10 Liquid Fertilizer Manufacturing ProcessDocument2 pages10-20-10 Liquid Fertilizer Manufacturing ProcessFernando Nieto OchoaNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Industry Handbook Describes Essential Plant NutrientsDocument46 pagesFertilizer Industry Handbook Describes Essential Plant Nutrientskaspersky2009No ratings yet
- Nano Fertilizers Role in Sustainable Agriculture-2Document19 pagesNano Fertilizers Role in Sustainable Agriculture-2SujanNo ratings yet
- Rock PhosphateDocument2 pagesRock PhosphateGrignionNo ratings yet
- Crop Nutrition Management With Nano Fertilizers 1Document3 pagesCrop Nutrition Management With Nano Fertilizers 1Fitri SukmawatiNo ratings yet
- FertahiDocument36 pagesFertahiYonatan AdiNo ratings yet
- Mxdfertilizer PPAH PDFDocument4 pagesMxdfertilizer PPAH PDFASDFG21No ratings yet
- NPK Fertilizer Manufacturing ProcessDocument5 pagesNPK Fertilizer Manufacturing ProcessEmuskNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments Fertilizer ProductionDocument56 pagesRecent Developments Fertilizer ProductionLinh TranNo ratings yet
- The Fertilizer IndustryDocument24 pagesThe Fertilizer IndustryNesmar Walet NobleNo ratings yet
- Residual Effect of Phosphorus Fertilizer in A Low-Humic Andosol With Low Extractable PhosphorusDocument8 pagesResidual Effect of Phosphorus Fertilizer in A Low-Humic Andosol With Low Extractable Phosphorusramdhana karimahNo ratings yet
- MKP Map UpDocument5 pagesMKP Map Upfertilizer exporterNo ratings yet
- Almeida 2020Document9 pagesAlmeida 2020Nautam ParasanaNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Nutrients GuideDocument10 pagesFertilizer Nutrients GuideEirojram MarjorieNo ratings yet
- Compost BasicsOfOnFarmComposting PDFDocument9 pagesCompost BasicsOfOnFarmComposting PDFAngel PerezNo ratings yet
- About FertilizersDocument8 pagesAbout FertilizersGovind ManglaniNo ratings yet
- B 1b Use of Manure Plant CellDocument6 pagesB 1b Use of Manure Plant Celltaphesh48No ratings yet
- Efficacy of NPK and Cow Dung Combinations On Perfomance of Chilli Pepper (Capiscum Annuum L) and Their Influence On Soil PropertiesDocument5 pagesEfficacy of NPK and Cow Dung Combinations On Perfomance of Chilli Pepper (Capiscum Annuum L) and Their Influence On Soil PropertiesIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- NPK FertilizerDocument11 pagesNPK FertilizerShivaniNo ratings yet
- Water HoldingDocument10 pagesWater HoldingYonatan AdiNo ratings yet
- Market-Brief-Fertilizers June2019 enDocument8 pagesMarket-Brief-Fertilizers June2019 enASDFG21No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2352186422004138 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S2352186422004138 MainAgus Prihanto PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Sec 2Document71 pagesSec 2katherinerbNo ratings yet
- Review Article On BiofertilizersDocument17 pagesReview Article On Biofertilizersnet_set71% (7)
- Urea Impregnated HAP Encapsulated FertilizerDocument13 pagesUrea Impregnated HAP Encapsulated Fertilizergabriel rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Application With and Without Zinc Sulphate (Znso) and NPK Levels On The Growth and Yield Performance of High Protein Corn (Zea Mays L)Document10 pagesApplication With and Without Zinc Sulphate (Znso) and NPK Levels On The Growth and Yield Performance of High Protein Corn (Zea Mays L)TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- 42 IJEAB-OCT-2016-23-Efficacy of Organic Products As Black Pepper Foliar FertilizerDocument7 pages42 IJEAB-OCT-2016-23-Efficacy of Organic Products As Black Pepper Foliar Fertilizerrudy.cahyadi.gunawanNo ratings yet
- OMF compost improves growth and yield of beans in saline soilDocument11 pagesOMF compost improves growth and yield of beans in saline soilRomel LigmayoNo ratings yet
- Single Super PhosphateDocument3 pagesSingle Super PhosphateHafiz AtiqNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Organic Compound FertilizersDocument9 pagesManufacturing Organic Compound FertilizersSamer MaroufNo ratings yet
- IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering - The Utilization of Banana Peel in the Fermentation Liquid in Food Waste CompostingDocument8 pagesIOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering - The Utilization of Banana Peel in the Fermentation Liquid in Food Waste CompostingRozyvell MontañoNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument7 pages1 SMAmmar RasyiqNo ratings yet
- NPK fertilizer composition, manufacturing processDocument11 pagesNPK fertilizer composition, manufacturing processmajidNo ratings yet
- Yara Brasil PDFDocument91 pagesYara Brasil PDFChristopher GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mubarak 2013Document10 pagesMubarak 2013Ahmed MustafaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of SwimmingDocument7 pagesFundamentals of SwimmingSheila Mae Lira100% (1)
- Brosur Sy135cDocument9 pagesBrosur Sy135cDenny KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Etabloc Technical DataDocument108 pagesEtabloc Technical Dataedward ksbNo ratings yet
- Kultura I InteligencijaDocument15 pagesKultura I InteligencijaToni JandricNo ratings yet
- Kathrein 80010375Document2 pagesKathrein 80010375klamar5No ratings yet
- LearnEnglish Video Zone How These Women Changed Science ForeverDocument3 pagesLearnEnglish Video Zone How These Women Changed Science ForeverDaniella MensatoNo ratings yet
- RC Design IIDocument58 pagesRC Design IIvenkatesh19701No ratings yet
- 2017 Scoring Materials Math g6Document119 pages2017 Scoring Materials Math g6KRANo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Manually Operated ReaperDocument8 pagesDesign and Development of Manually Operated ReaperIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Unchained MelodeeDocument93 pagesUnchained MelodeeRafael Cornholio RodriguezNo ratings yet
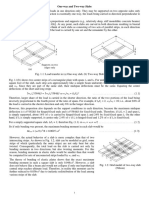
- Equations 2Document8 pagesEquations 2Patrick ValdezNo ratings yet
- EAPP w2Document13 pagesEAPP w2Elijah AquinoNo ratings yet
- Volvo g900 Modelos PDFDocument952 pagesVolvo g900 Modelos PDFAdrianDumescu100% (3)
- Mast Bending Stress Calculation: Antenna 1Document6 pagesMast Bending Stress Calculation: Antenna 1Vinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 The Communist Manifesto As International Relations TheoryDocument12 pagesChapter 14 The Communist Manifesto As International Relations TheoryLaurindo Paulo Ribeiro TchinhamaNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Chemtech Reviewer PRDocument1 pageToaz - Info Chemtech Reviewer PRchristy janioNo ratings yet
- ChecklistsDocument1 pageChecklistsnotme2120No ratings yet
- MC BreakdownDocument5 pagesMC BreakdownThane SnymanNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls of HIV Infection - Dr. Rizqi Amalia, Sp.ADocument46 pagesPitfalls of HIV Infection - Dr. Rizqi Amalia, Sp.AandreknhNo ratings yet
- Ross 308 AP Broiler PO2019-EN PDFDocument16 pagesRoss 308 AP Broiler PO2019-EN PDFJORGE GALVISNo ratings yet
- Calculator For SW Density Changes - Effect of List On Ships DraftDocument3 pagesCalculator For SW Density Changes - Effect of List On Ships DraftHein Thurein KyawNo ratings yet
- Project Information for 2x660 MW Lube Oil PumpsDocument93 pagesProject Information for 2x660 MW Lube Oil PumpsghostamirNo ratings yet
- CalderaDocument56 pagesCalderaEsteban TapiaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Torch and Consumables Catalog: For Mechanized Plasma SystemsDocument64 pages2019 Torch and Consumables Catalog: For Mechanized Plasma SystemsRaj DomadiyaNo ratings yet
- WPS Ernicu 7 R1 3 6 PDFDocument4 pagesWPS Ernicu 7 R1 3 6 PDFandresNo ratings yet
- Energy Analysis of Closed Systems BreakdownDocument31 pagesEnergy Analysis of Closed Systems Breakdownايات امجد امجدNo ratings yet
- BASIC IMMUNOLOGY TERMSDocument2 pagesBASIC IMMUNOLOGY TERMSAnnicoldjohn LariozaNo ratings yet
- Swami Brahmananda - The Spiritual Son of Sri RamakrishnaDocument7 pagesSwami Brahmananda - The Spiritual Son of Sri RamakrishnaEstudante da Vedanta100% (2)
- ASSIGNMENTDocument10 pagesASSIGNMENTKoleen Lopez ÜNo ratings yet
- Din en 1320-1996Document18 pagesDin en 1320-1996edcam13No ratings yet
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationFrom EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Transmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualFrom EverandTransmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationFrom EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo ratings yet
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignFrom EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (137)
- Advanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignFrom EverandAdvanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Siting and Layout of FacilitiesFrom EverandGuidelines for Siting and Layout of FacilitiesNo ratings yet
- Process Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentFrom EverandProcess Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentNo ratings yet
- Marine Structural Design CalculationsFrom EverandMarine Structural Design CalculationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Guidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyFrom EverandGuidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsFrom EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataFrom EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Guidelines for Enabling Conditions and Conditional Modifiers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Enabling Conditions and Conditional Modifiers in Layer of Protection AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Perfume Engineering: Design, Performance and ClassificationFrom EverandPerfume Engineering: Design, Performance and ClassificationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Guidelines for Developing Quantitative Safety Risk CriteriaFrom EverandGuidelines for Developing Quantitative Safety Risk CriteriaNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)