Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grammatica Inglese
Uploaded by
Sara GalluccioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grammatica Inglese
Uploaded by
Sara GalluccioCopyright:
Available Formats
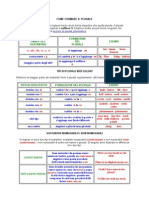
VERBS
Present simple
Si forma utilizzando la forma base del verbo. Il present simple si usa per azioni che si compiono abitualmente o frequentemente, per dare un suggerimento o un'istruzione,per indicare eventi programmati nel futuro.
Affirmative
I'm (am) English You !e "he# are English $e She It's (is) English I'm not (am not) English You !e "he# aren't (are not) English $e She It isn't (is not) English Am I English % Are #ou &e the# English % Is he she it English %
Negative
Question
Yes, I am 'o, I'm not Yes, #ou &e the# are. 'o, #ou &e the# aren't. Yes, he she it is. 'o, he she it isn't. Present continuous
Si forma utiliazzando il soggeto ( am are is (to be) ( forma base del verbo in ing. Si riferisce ad) azioni in corso di svolgimento in questo momento o in questo periodo,azioni di durata temporanea,si usa con always quando colui che parla vuole sottolineare un'azione che lo disturba poich* si ripete continuamente.
Short answers
Affirmative Negative Question
Sub+ect ( am are is ( &ith ( ,ing We're studying Sub+ect ( am not aren't not isn't ( &ith ( ,ing She isn't studying -m -re Is ( sub+ect ( verb ( ,ing % Are they studying ?
Short answers Yes, sub+ect ( am are is. 'o, sub+ect ( am aren't isn't. Yes, I am No, they aren't. Imperative
.er formare l'imperativo positivo usiamo il verbo senza il soggetto. .er formare la forma negativa dell'imperativo usiamo don't ( verbo. Esiste solo in seconda persona singolare e plurale. /iene usato per esprimere un comando ed impartire ordini, si usa anche per dare istruzioni, indicazioni.
Can Can't 0an 1 un verbo che funge da ausiliare e inoltre 1 uguale a tutte le persone. /iene utilizzato per indicare) Sapere, nel senso di saper fare qualche cosa.
Potere, quando la possibilit2 di compiere un3azione dipende dal soggetto.Potere, quando si chiede il permesso di fare qualche cosa (inglese parlato informale) oppure per dire ci4 che o non 1 consentito fare. Affirmative Negative Question S!ort answers Past simple I You $e She It !e You "he# can s&im I You $e She It !e You "he# can't (can not) s&im Can I You $e She It !e You "he# s&im % Yes, I You $e She It !e You "he# can. 'o, I You $e She It !e You "he# can't.
Il Simple Paste il tempo verbale inglese che esprime il concetto generale di unazione che si svolta nel passato e non ha pi nessun rapporto con il presente.
!ith the past simple &e often use the time e5pressions li6e) yesterday, yesterday morning/afternoon/evening, last night, the day efore yesterday, two/three/four days/wee!s/months/years ago, last wee!/month/year. Affirmative I $e She It was there. You !e "he# were there. Negative Question S!ort answers I $e She It wasn't (was not) there. You !e "he# weren't (were not) there. "as I $e She It there% "ere #ou &e the# there %
Yes, I he she it was. Yes, #ou &e the# were. 'o, I he she it wasn't. 'o, #ou &e the# weren't. Past continuous Si forma con soggetto ( &as &ere ( ing form. 7siamo il present continuouns 1 il tempo verbale che si utilizza per esprimere azioni che si sono svolte in un preciso preciso nel passato. Affirmative I $e She It was listening. You !e "he# were &atching. Negative Question S!ort answers I $e She It wasn't was not listening. You !e "he# weren't were not listening. "as I $e She It listening. "ere You !e "he# listening. Yes, I $e She It was. Yes, I $e She It wasn't. 'o, You !e "he# were. 'o, You !e "he# weren't.
Past Perfect Si forma con soggetto ( had ('d) ( participio passato past participle. Si usa per parlare di azioni che hanno avuto luogo prima di un certo tempo nel passato. Affirmative Sub+ect ( !a# ('#) ( past participle "hey had finished dinner. Negative Question S!ort answers Sub+ect ( !a# not (!a#n't) ( past participle "hey hadn't finished dinner. $a# ( sub+ect ( past participle #ad you finished dinner ?
Yes,sub+ect ( !a#. 'o, sub+ect ( !a#n't. Yes, I had. No, I hadn't. Coul# %Past simple of can& e was were a'le to Coul# si usa per esprimere un'abilit2 o capacit2 generale nel passato. Es) "he# could climb mountains. "as (si usa per la terza persona) were a'le to indicano un'abilit2 o capacit2 specifica nel passato con riferimento a un particolare momento o situazione. Alla forma negativa sia couldn't che &asn't &eren't albe to possono esprimere un'abilit2 o capacit2 sia generale che specifica nel passato. Affirmative I You $e She It !e You "he# coul# ( verb $e could spea6 English &hen he &as eight Negative Question S!ort answers I You $e She It !e You "he# She couldn't spea6 English &hen she &as eight Coul# I You $e She It !e You "he# ( verb 0ould the# spea6 English %
Yes, I You $e She It !e You "he# 'o, I You $e She It !e You "he# Yes, the# could8 'o, he couldn't. Regular an# irregular ver' Affirmative I You $e She It !e You "he# arrive# home I You $e She It !e You "he# #rove home Negative I You $e She It !e You "he# #i#n't (#i# not) arrive home. I You $e She It !e You "he# #i#n't (#i# not) #rive home. )i# I You $e She It !e You "he# arrive home % )i# I You $e She It !e You "he# #rive home % Yes, I You $e She It !e You "he# #i#. 'o, I You $e She It !e You "he# #i#n't.
Question S!ort answers
*uture+ 'e going to Si forma con soggetto ( be going to ( forma base del verbo. Si usa per esprimere il futuro intenzionale, azioni cio1 che si intende compiere nel futuro, l'azione 1 sempre premeditata. Affirmative I You $e She It !e You "he# ( am are is ( going to ( fall Negative Question S!ort answers I You $e She It !e You "he# ( am not aren't isn't ( going to ( fall Am Are Is I You $e She It !e You "he# ( going to ( fall %
Yes, I You $e She It !e You "he# ( am are is 'o, I You $e She It !e You "he# ( am not aren't isn't. Present Continuous Si forma con soggeto ( am are is (to be) ( forma base del verbo in ing. .u4 essere usato con significato di futuro per esprimere un programma preciso per il futuro, per realizzare il quale si 1 gi2 fatto qualcosa. Affirmative Negative Question Sub+ect ( am are is ( &ith ( ,ing I$m ta!ing an e%am in &'to er. Sub+ect ( am not aren't not isn't ( &ith ( ,ing I am not leaving y train tomorrow -m -re Is ( sub+ect ( verb ( ,ing % Are you leaving y train tomorrow?
Short answers Yes, sub+ect ( am are is. 'o, sub+ect ( am aren't isn't. Yes, I am No, they aren't. "ill s!all Si forma con soggetto ( &ill shall ( infinitive. Si usa &ill &on't per decisioni al momento, promesse, offerte, e suggerimenti. Si usa shall con I e &e per le offerte, e suggerimenti quando sono domande. Si usa &ill o going to per le previsioni. Affirmative I You $e She It !e You "he# ( will I'll have the stea! )instant decision*. You'll love the film+ ),redi'tion*. Negative I You $e She It !e You "he# + will not won't I won't tell any ody where you are )promise*. S!all I !e ( infinitive Shall I help you with you homewor! ? )offer*. Shall we eat out tonight ? )suggestion*
Question
Short answers
Yes, sub+ect ( &ill 'o, sub+ect ( &on't Yes, I will No, they won't Yes, sub+ect ( shall No, su -e't ( shan't Yes, I shall No, I shan't
Present perfect simple wit! for an# since E' formato da soggetto ( ver'o avere ( participio passato #el ver'o 'ase Il present perfect simple si usa per esprimere azioni o eventi avvenuti in un passato recente o non del tutto concluso, o che ha riferimento al presente. Il present perfect simple si usa anche con for e since) for per indicare la durata dell'azione (for five minute, for t&o #ears), since per indicare il momento in cui 1 iniziato l'azione o situazione (since 9:;<, since =anuar#). /iene tradotto in italiano con il presente Present perfect continuous con for e since E' formato da soggetto ( !ave ( 'een ( la forma in ing #el ver'o principale. Il present perfect continuous si usa per indicare la continuit2 di un'azione che ha effetti sul presente. Es) I've been stud#ing for hours and I'm e5hausted, ho studiato per ore e sono esausto. Il present perfect continuous si usa solo con i verbi che indicano un'azione e non con i verbi che indicano uno stato, un sentimento etc (es) believe, forget, li6e, love, hate , &ant). In questi casi il present perfect continuous diventa > es) I've believed ovvero soggetto ( !ave ( participio passato #el ver'o 'ase )ifferen,a su -uan#o usare present perfect continuous e present perfect simple $e's done his home&or6 > ha finito > present perfect simple. Esso si usa per indicare azioni o eventi completati in un tempo non precisato nel passato. Es) I've read t&o boo6s > ho letto due libri. $e's been &or6ing since seven > sta ancora lavorando. Esso si usa per indicare azioni o eventi che sono tuttora in corso. Es) I've been reading for t&o hours > leggo da due ore. .se# to Si usa used to per esprimere abitudini o situazioni passate che non sono pi? vere. Si forma con soggetto ( use# to ( ver'o 'ase al presente. 'ella forma negativa e interrogativa si usa did didn't. Es) "he# used to sing in a band > forma affermativa, I didn't use to have long hair > forma negativa, @id she use to &ear a school uniform % > forma interrogativa. Es. traduzione he used to ride a motorbi6e) ha usato una moto per andare lA. Question tags Si usano le question tags per chieder conferma di un'affermazione o di un fatto. Si forma con l'ausiliare appropriato della frase ( pronome. Es) You live in Bondon, #on't /ou 0 Se la frase 1 affermativa, la question tag 1 negativa e viceversa. Past perfect simple Il past perfect simple si forma con !a# ( participio passato. Il past perfect simple esprime un'azione avvenuta prima di un'altra azione passata. Si usa speso con il past simple o continuous per indicare ''anteriorit2''. Es) the man &ent to the police because he had lost his memor# > prima ha perso la memoria e poi 1 andato alla polizia.
You might also like
- Pillole di Inglese: 1.Avverbi 2.Pronomi Relativi 3.Verbi ModaliFrom EverandPillole di Inglese: 1.Avverbi 2.Pronomi Relativi 3.Verbi ModaliRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Corso di Tedesco Online Parte I: Articoli Struttura delle Frasi e Verbi principaliFrom EverandCorso di Tedesco Online Parte I: Articoli Struttura delle Frasi e Verbi principaliNo ratings yet
- Grammatica essenziale normativa della lingua tedescaFrom EverandGrammatica essenziale normativa della lingua tedescaNo ratings yet
- Grammatica Inglese A1 PDFDocument17 pagesGrammatica Inglese A1 PDFSamuela Lepori50% (2)
- Schema Dei Tempi in Inglese - Grammatica Ingles PDFDocument3 pagesSchema Dei Tempi in Inglese - Grammatica Ingles PDFcatubo80% (5)
- Learning English Together - Corso Base Di Inglese - 29 LezioniDocument38 pagesLearning English Together - Corso Base Di Inglese - 29 LezionistefanoallegrezzaNo ratings yet
- Oreste-Grammatica IngleseDocument38 pagesOreste-Grammatica IngleseCaterina De Lio100% (1)
- Grammatica IngleseDocument308 pagesGrammatica IngleseRodolfo JungeNo ratings yet
- Grammatica Inglese Di BaseDocument155 pagesGrammatica Inglese Di BaseKat ManduNo ratings yet
- Grammatica IngleseDocument12 pagesGrammatica IngleseGiorgio PredelliNo ratings yet
- Grammatica inglese avanzata con eserciziFrom EverandGrammatica inglese avanzata con eserciziRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Imparare l'inglese II con Testi paralleli - Racconti Brevi (Livello intermedio) Bilingue (Italiano - Inglese)From EverandImparare l'inglese II con Testi paralleli - Racconti Brevi (Livello intermedio) Bilingue (Italiano - Inglese)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Corso IngleseDocument103 pagesCorso Inglesepiemme76100% (2)
- Esercizi IngleseDocument20 pagesEsercizi IngleseSara CarboneNo ratings yet
- Esercizi Di Grammatica IngleseDocument196 pagesEsercizi Di Grammatica Ingleseesercizinglese.com100% (2)
- Inglese GrammaticaDocument86 pagesInglese GrammaticaBrenda Amelia Bohm100% (3)
- Corso Inglese AdvancedDocument13 pagesCorso Inglese Advanced8x8No ratings yet
- Inglese VeloceDocument267 pagesInglese VeloceFoundation for Africa100% (10)
- Lingua Inglese - GrammaticaDocument61 pagesLingua Inglese - Grammaticaraffican100% (1)
- Sos IngleseDocument21 pagesSos Inglesemassimo_rossi_5100% (1)
- Time on a Line. Il verbo inglese in 60 minutiFrom EverandTime on a Line. Il verbo inglese in 60 minutiRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Il contratto di agenzia - Normativa, Accordi Economici Collettivi, FormularioFrom EverandIl contratto di agenzia - Normativa, Accordi Economici Collettivi, FormularioNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation! Come pronunciare bene in IngleseFrom EverandPronunciation! Come pronunciare bene in IngleseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Grammatica IngleseDocument186 pagesGrammatica IngleseFrancesco Bernini100% (2)
- Grammatica IngleseDocument155 pagesGrammatica IngleseMaurizia TintiNo ratings yet
- Imparare l'arabo - Testo parallelo - Racconti Brevi (Italiano - Arabo)From EverandImparare l'arabo - Testo parallelo - Racconti Brevi (Italiano - Arabo)No ratings yet
- Grammatica IngleseDocument85 pagesGrammatica IngleseFrancesko EspositoNo ratings yet
- Inglese I-2Document3 pagesInglese I-2Francesca MarrucciNo ratings yet
- La Fonetica IngleseDocument5 pagesLa Fonetica IngleseEmanuele Femia100% (2)
- La Motivazione alla Formazione - leva per lo sviluppo personale ed organizzativoFrom EverandLa Motivazione alla Formazione - leva per lo sviluppo personale ed organizzativoNo ratings yet
- 3 Lezione PunteggiaturaDocument14 pages3 Lezione Punteggiaturateoden1976No ratings yet
- Tempi Verbali Inglesi e Loro Corrispondenti in ItalianoDocument3 pagesTempi Verbali Inglesi e Loro Corrispondenti in ItalianoAndreinaFranceschi67% (6)
- Inglese - Impara L'Inglese Velocemente e Senza Sforzo (Vol 2): Impara l'inglese con le storie iniziali, storie bilingue (testo parallelo in inglese e italiano) per principiantiFrom EverandInglese - Impara L'Inglese Velocemente e Senza Sforzo (Vol 2): Impara l'inglese con le storie iniziali, storie bilingue (testo parallelo in inglese e italiano) per principiantiRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Corso di Inglese: 200 Modi di dire - Idioms & Phrases (Vol. 2)From EverandCorso di Inglese: 200 Modi di dire - Idioms & Phrases (Vol. 2)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Riassunto Di ”Le 7 Regole Per Avere Successo”: Lezioni Fondamentali Per Il Cambiamento PersonaleFrom EverandRiassunto Di ”Le 7 Regole Per Avere Successo”: Lezioni Fondamentali Per Il Cambiamento PersonaleNo ratings yet
- Capire il Diritto Privato: Attraverso mappe concettuali e schemiFrom EverandCapire il Diritto Privato: Attraverso mappe concettuali e schemiNo ratings yet
- 100 Modi di Dire in Inglese (Vol. 2): Idioms & PhrasesFrom Everand100 Modi di Dire in Inglese (Vol. 2): Idioms & PhrasesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Test e quiz attitudinali e di logica per concorsi pubblici: Guida ai test psico-attitudinali per concorsi pubbliciFrom EverandTest e quiz attitudinali e di logica per concorsi pubblici: Guida ai test psico-attitudinali per concorsi pubbliciNo ratings yet
- Parole che confondiamo in inglese e vocabolario di livello avanzatoFrom EverandParole che confondiamo in inglese e vocabolario di livello avanzatoNo ratings yet
- Come ritrovare la voglia di studiare. Motivazione e metodo di studioFrom EverandCome ritrovare la voglia di studiare. Motivazione e metodo di studioNo ratings yet
- Spagnolo ( Spagnolo da zero ) I Verbi Spagnoli Più Comuni: Dalla A alla Z, i 100 verbi con traduzione, testo bilingue e frasi di esempioFrom EverandSpagnolo ( Spagnolo da zero ) I Verbi Spagnoli Più Comuni: Dalla A alla Z, i 100 verbi con traduzione, testo bilingue e frasi di esempioNo ratings yet
- Parla l'inglese magicamente! Speak English Magically! Rilassati! Anche tu puoi imparare l'inglese ora!From EverandParla l'inglese magicamente! Speak English Magically! Rilassati! Anche tu puoi imparare l'inglese ora!No ratings yet
- Corso Di A FranceseDocument167 pagesCorso Di A FranceseLuca Di Lotti100% (1)
- I Comuni RiassuntoDocument6 pagesI Comuni RiassuntoSara GalluccioNo ratings yet
- Appunti Di Economia PoliticaDocument4 pagesAppunti Di Economia PoliticaSara GalluccioNo ratings yet
- Frasi in Inglese EsempiDocument2 pagesFrasi in Inglese EsempiSara GalluccioNo ratings yet
- Compito Di IngleseDocument4 pagesCompito Di IngleseSara GalluccioNo ratings yet
- Appunti Italo Calvino Le Città InvisibiliDocument1 pageAppunti Italo Calvino Le Città InvisibiliSara GalluccioNo ratings yet
- 3) IMPERFETTO E PASSATO PROSSIMO-loescherDocument3 pages3) IMPERFETTO E PASSATO PROSSIMO-loescherEla CkNo ratings yet
- Tracce Ufficiali Discipline MusicaliDocument5 pagesTracce Ufficiali Discipline MusicaliViviana ApicellaNo ratings yet
- Opere Filosofiche, Teologiche e Matematiche by Niccolò Cusano, A C. Di E. Peroli PDFDocument3,133 pagesOpere Filosofiche, Teologiche e Matematiche by Niccolò Cusano, A C. Di E. Peroli PDFCristhian Espinal, SINo ratings yet
- Ludovico Ariosto - SatireDocument0 pagesLudovico Ariosto - SatiresbonaffinoNo ratings yet
- 1 Corinzi 13 AccordiDocument3 pages1 Corinzi 13 AccordiklitocelkupaNo ratings yet
- Fase20 33 1 1778 1 ItDocument38 pagesFase20 33 1 1778 1 ItEriflonaNo ratings yet
- Compresso 21 10 20 BROCH-S.CORTEZDocument44 pagesCompresso 21 10 20 BROCH-S.CORTEZGiuseppe ManganoNo ratings yet
- Analisi Fisher House, Louis KahnDocument13 pagesAnalisi Fisher House, Louis KahnFabio Angeloni75% (12)
- Giochi Per Il Mio Computer - 158 - 2009 - 08Document148 pagesGiochi Per Il Mio Computer - 158 - 2009 - 08Roberto JinxNo ratings yet
- Lista Incantesimi PaladinoDocument3 pagesLista Incantesimi PaladinoMarcoDiBellaNo ratings yet
- RadiocomandiDocument11 pagesRadiocomandialmanuclearNo ratings yet
- PIER LUIGI NERVI E IL SALE. IL MAGAZZINO SALI FOSFATI DI MARGHERITA DI SAVOIA - Rita Di GaetanoDocument8 pagesPIER LUIGI NERVI E IL SALE. IL MAGAZZINO SALI FOSFATI DI MARGHERITA DI SAVOIA - Rita Di GaetanoPLN_Project100% (2)
- Mosaico Italia - ChiaviDocument8 pagesMosaico Italia - ChiavimirenNo ratings yet
- Poesie Per Giorni Di Pioggia e Sole Di Edmond JabesDocument23 pagesPoesie Per Giorni Di Pioggia e Sole Di Edmond JabesMente Sugge SostanzaNo ratings yet
- Istruzioni SaxDocument2 pagesIstruzioni SaxMarco CesiNo ratings yet
- Quello BelloDocument4 pagesQuello BelloDolce LinguaNo ratings yet