Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Salbutamol Drug Study Generic Name: Brand Name
Uploaded by
Lyn ConsingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Salbutamol Drug Study Generic Name: Brand Name
Uploaded by
Lyn ConsingCopyright:
Available Formats
Salbutamol Drug Study Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, airet, Novo-Salbutamol,Proventil HFA,
Gensalbutamol, Ventodisk, Ventolin HFA, Volmax, VoSpira ER Classification: Bronchodilator (therapeutic); adrenergics (pharmacologic) Indications 1. To control and prevent reversible airway obstruction caused by asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD)2. Quick relief for bronchospasm3. For the prevention of exerciseinduced bronchospasm4. Longterm control agent for patients with chronic or persistentbronchospasm Mechanism of Action It relieves nasal congestion and reversible bronchospasm by relaxing the smoothmuscles of the bronchioles. The relief from nasal congestion and bronchospasmis made possible by the following mechanism that takes place when Salbutamolis administered.1. First, it binds to the beta2-adrenergic receptors in the airway of the smoothmuscle which then leads to the activation of the adenyl cyclase andincreased levels of cyclic- 35-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP).2. When cAMP increases, kinases are activated.3. Kinases inhibit the phosphor ylation of myosin and decrease intracellular calcium.4. Decreased in intracellular calcium will result to the relaxation of the smoothmuscle airways. Contraindications 1. Hypersensitivity to adrenergic amines2. Hypersensitivity to fluorocarbons Precaution 1. Cardiac disease including coronary insufficiency, a history of stroke, coronary artery diseaseand cardiac arrhythmias2. Hypertension3. Hyperthyroidism4. Diabetes5. Glaucoma6. Geriatric patients older individuals are at higher risk for adverse reactionsand may require lower dosage7. Pregnancy especially near term8. Lactation9. Children less than 2 years of age because safety of its use has not beenestablished10. Excess inhaler use which may lead to tolerance and paradoxicalbronchospasm Side Effects and Adverse Reactions 1. Nervousness2. Restlessness3. Tremor 4. Headache5. Insomnia6. Chest pain7. Palpitations8. Angina9. Arrhythmias10. Hypertension11. Nausea and vomiting12. Hyperglycemia13. Hypokalemia Route and Dosage PO (Adults and Children more than 12 years): 2-4 mg 3-4 times a day or 4-8 mgof extended dose tablets twice a day.PO (Geriatric Patients): initial dose should not exceed 2 mg 3-4 times a day andmay be increased carefully up to 32 mg/dayPO (Children 6-12 years old): 2 mg 3-4 times a day or 4 mg as extended-releasetablets twice a day; may be carefully increased as needed but not to exceed 24mg/dayPO (Children 2-6 years old): 0.1 mg/kg 3 times a dayInhalation (Adults and children more
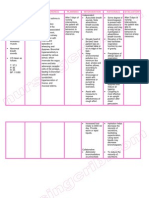
than 4 years of age): 2 inhalations every 4-6hoursInhalation (Children 2-12 years old): 0.1-0.15 mg/kg/dose 3-4 times a day D r u g N a m e A c t i o n I n d i c a t i o n C o n t r a i n d i c a t i onAdverseEffectNursing Considerations GenericName: amikacinsulfate Brand Name: Amikin Classification: Aminoglycoside Availableforms: *Infection:pediatric:50mg/ml,250mg/mlNSS:5mg/ml(500mInhibits proteinsynthesis bybindingdirectly to the30S ribosomalsub unit;bactericidal*Route: IVOnset:immediatePeak: 30mins.Duration: 812hrs.*Route: I.MOnset:unknownPeak: 1hr.Duration: 8-12hrs. Seriousinfectioncause bysensitiverestrainsof Pseudomonasaeruginusa, E.coli,Proteus,Klebsiella,staphylococcus Uncomplicated UTIcaused byorganismsusceptible to lesstoxicdrugs. Activetuberculosis, withotherantituberculotics Mycobacterium Contraindicatedinpatientshypersensitive todrug orotheraminogycosides. Usecautiously inpatientswithimpairedrenalfunctionorneuromusculardisorders, inneonatesandinfantsand inelderlypatients.CNS:neuromuscularblockadeEENT:-ototoxicity Obtain specimen for culture andsensitivity test before giving firstdose. Therapy may begin whileawaiting the results. Evaluate patients hearing beforeand during therapy if he will bereceiving drug for longer than 2weeks. Notify prescriber if patienthas tinnitus, vertigo, or hearing loss. Weigh patient and review renalfunction studies before therapybegins. Correct dehydration before therapybecause of increase risk of toxicity. Obtain blood for peak level 1 hourI.M injection and 30 mins. to 1 hourafter IV infusion ends; for troughlevels draw blood just before thenext dose. Dont
collect blood in aheparinized tube; heparin isincompatible with aminoglycosides. Peak drug levels more than 35mcg/ml and trough levels more than10 mcg/ml may linked to a higherrisk of toxicity Watch for signs and symptoms of super infection (especially URT),such as continued fever, chills, andincreased pulse rate. Name of drug General Action SpecificActionAdverse Effects Indication Contraindication NursingResponsibilitiesGenericName:Kalium duruleBrand Name: PotassiumChloride Classifications: electrolyticand water balance agent; replacementsolution Principalintracellular cation;essential for maintenanceof intracellular isotonicity,transmissionof nerveimpulses,contraction of cardiac,skeletal, andsmoothmuscles,maintenanceof normalkidneyfunction, andfor enzymeactivity.Plays aprominentrole in bothformationandcorrection of imbalancesin acid basemetabolism. GI: Nausea, vomiting,diarrhea, abdominaldistension. BodyWhole: Pain, mentalconfusion, irritability,listlessness, paresthesias of extremities,muscleweaknessand heaviness of limbs, difficulty inswallowing, flaccid paralysis. Urogenital: Oliguria, anuria. Hematologic: Hyperkalemia. Respiratory: Respiratorydistress. CV: Hypotension,bradycardia; cardiacdepression, arrhythmias, or arrest; altered sensitivity todigitalis glycosides. ECGchanges in hyperkalemia:Tenting (peaking) of T wave(especially in right precordialleads), lowering of R withdeepening of S waves anddepression of RST;prolonged P-R interval,widened QRS complex,decreased amplitude anddisappearance of P waves,prolonged Q-T interval,To preventand treatpotassiumdeficitsecondary todiuretic or corticosteroidtherapy. Alsoindicatedwhenpotassium isdepleted byseverevomiting,diarrhea;intestinaldrainage,fistulas,
or malabsorption;prolongeddiuresis,diabeticacidosis.Effective in thetreatment of hypokalemicalkalosis(chloride, notthegluconate). . Severe renalimpairment;severehemolyticreactions;untreated Addisons disease; crushsyndrome;earlypostoperativeoliguria (exceptduring GIdrainage);adynamicileus; acutedehydration;heat cramps,hyperkalemia,patientsreceivingpotassiumsparingdiuretics,digitalisintoxicationwith AVconductiondisturbance.Monitor I&Oratio and patternin patientsreceiving theparenteral drug.If oliguriaoccurs, stopinfusionpromptly andnotifyphysician.Lab test:Frequent serumelectrolytes arewarranted.
Monitor for andreport signs of GI ulceration(esophageal or epigastric painor hematemesis).
Monitor patientsreceivingparenteralpotassiumclosely
You might also like
- Salbuterol Generic NameDocument4 pagesSalbuterol Generic NamejunieNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument7 pagesGeneric NameGia Bautista-AmbasingNo ratings yet
- Symph A To Mimetic SDocument27 pagesSymph A To Mimetic Sjl frusaNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol for Asthma and COPD ReliefDocument5 pagesSalbutamol for Asthma and COPD ReliefFildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayNo ratings yet
- SalbutamolDocument1 pageSalbutamolMonica Lyka BancaleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Upper Respiratory TractDocument7 pagesAnatomy of the Upper Respiratory TractGladys NacionNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- Bronchodilators Guide for Asthma and COPDDocument5 pagesBronchodilators Guide for Asthma and COPDdeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsdeepika kushwah100% (1)
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Asthma 2 Copd 2Document6 pagesAsthma 2 Copd 2Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Parmacon Ass EdtDocument5 pagesParmacon Ass EdtMalcolm SharfNo ratings yet
- Adult: PO Acute Bronchospasm 2-4 MG 3-4 Times/day, Up To 8 MG 3-4 Times/day. AsDocument3 pagesAdult: PO Acute Bronchospasm 2-4 MG 3-4 Times/day, Up To 8 MG 3-4 Times/day. AswidiyaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Gentamicin Sulfate and SalbutamolDocument7 pagesDrug Study Gentamicin Sulfate and SalbutamolEduardNo ratings yet
- 33-36 Medications PDFDocument15 pages33-36 Medications PDFJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- Key Drug Information: AlbuterolDocument1 pageKey Drug Information: Albuterolamaliea234No ratings yet
- Salbutamol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSalbutamol Drug StudyClaire Go Tajarros82% (11)
- COPD - Drug FormularyDocument32 pagesCOPD - Drug FormularyCharles BayogNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GentamicinDocument3 pagesDrug Study GentamicinEARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia and Concious SedationDocument43 pagesLocal Anesthesia and Concious Sedationpawi18No ratings yet
- Generic Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicDocument7 pagesGeneric Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- My Paper That Is Due Today!Document11 pagesMy Paper That Is Due Today!Nic CochranNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ON Cabergolin EDocument4 pagesDrug Study ON Cabergolin ESimran SimzNo ratings yet
- SalbutamolDocument2 pagesSalbutamolMarck Vincent Garcia OngNo ratings yet
- Organophosphate Poisoning 2Document12 pagesOrganophosphate Poisoning 2Diana MurguiaNo ratings yet
- ALBUTEROL (Salbutamol)Document4 pagesALBUTEROL (Salbutamol)GLen CaniedoNo ratings yet
- Protocol for managing pesticide poisoningDocument6 pagesProtocol for managing pesticide poisoningJesicca SNo ratings yet
- PLASIL antiemetics classificationDocument5 pagesPLASIL antiemetics classificationAbby MontealegreNo ratings yet
- Salbutamolbidosonide ParacetamolcefexineDocument8 pagesSalbutamolbidosonide ParacetamolcefexineAlter BadonNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Brand Name, Classifications, Indications and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesDexamethasone Brand Name, Classifications, Indications and Nursing ConsiderationsChristine Joy CamachoNo ratings yet
- Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesNursing ResponsibilitiesMaureen Joy Cascayan EspirituNo ratings yet
- FINAL COVID19 1 April 2021Document14 pagesFINAL COVID19 1 April 2021Wleed KhledNo ratings yet
- Meptin® Swinghaler®: Dry Powder InhalerDocument9 pagesMeptin® Swinghaler®: Dry Powder InhalerYusuf HadiNo ratings yet
- For Drug Recitation 1Document33 pagesFor Drug Recitation 1Abigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyJhann0% (1)
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyjennachristy03100% (3)
- Iligan - DiazepamDocument6 pagesIligan - DiazepamJamaicah IliganNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document8 pagesDrug Study 2rey_tengNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: PART 1: To Be Completed Prior To Clinical ExperienceDocument5 pagesDrug Study: PART 1: To Be Completed Prior To Clinical ExperienceFrozanSNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCarson BirthNo ratings yet
- ACUTE ASTHMA ATTACK EMERGENCY TREATMENTDocument31 pagesACUTE ASTHMA ATTACK EMERGENCY TREATMENTMuneeb YounisNo ratings yet
- Status Epilepticus - APLSDocument3 pagesStatus Epilepticus - APLSMuhammadafif SholehuddinNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug Prsentation: By, Rachel - J BSC Nursing 2 Year College of Nursing, Christian Fellowship HospitalDocument33 pagesMetoprolol Drug Prsentation: By, Rachel - J BSC Nursing 2 Year College of Nursing, Christian Fellowship HospitalRachel JohnNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY CASE - Sol - GargantielDocument4 pagesRESPIRATORY CASE - Sol - GargantielMaryglen GargantielNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- EMA ProtocolsDocument14 pagesEMA ProtocolsMattNo ratings yet
- The Biochemical Pathway of Paraquat ToxicityDocument16 pagesThe Biochemical Pathway of Paraquat ToxicitysuderiNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Drug StudyDocument15 pagesEmergency Drugs Drug StudyCathrine Sandile Tangwara100% (1)
- Opiates (E.g. Codeine, Heroin, Pethidine, Morphine, Methadone)Document7 pagesOpiates (E.g. Codeine, Heroin, Pethidine, Morphine, Methadone)Ali HussnainNo ratings yet
- BricanylDocument4 pagesBricanylianecunarNo ratings yet
- KGD 2 IvanDocument92 pagesKGD 2 IvanrikarikaNo ratings yet
- Carboprost Drug Study for Postpartum Bleeding and AbortionDocument4 pagesCarboprost Drug Study for Postpartum Bleeding and Abortionshadow gonzalez100% (1)
- GentDocument2 pagesGentOxford666No ratings yet
- TB medications overviewDocument7 pagesTB medications overviewANNIE SHINE MAGSACAYNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: ActionDocument22 pagesGeneric Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: Actionp_dawg100% (14)
- JoyDocument1 pageJoyLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing Edited Royal PentagonDocument49 pagesMaternity Nursing Edited Royal PentagonRichard Ines Valino95% (38)
- NURSING RESEARCH Nursing Research - Kerlinger - The Systematic, EmpiricalDocument32 pagesNURSING RESEARCH Nursing Research - Kerlinger - The Systematic, Empiricalrizaustria100% (3)
- NLE ReviewerDocument246 pagesNLE Reviewerblazegomez99% (69)
- Psych NursingDocument28 pagesPsych NursingLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Communicable Dse ReviewerDocument13 pagesCommunicable Dse ReviewerRichard Ines Valino100% (29)
- Psych NursingDocument28 pagesPsych NursingLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- MenstruationDocument25 pagesMenstruationLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Medicare Proposes Small Payment Increases for Outpatient Departments, ASCsDocument2 pagesMedicare Proposes Small Payment Increases for Outpatient Departments, ASCsLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Certificate of AttendanceDocument1 pageCertificate of AttendanceLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Case Study FormatDocument2 pagesCase Study Formatalieze11100% (1)
- Drugs For Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesDrugs For Liver CirrhosisLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Maternity NursingDocument23 pagesMaternity NursingLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Anti TuberculosisagentsDocument24 pagesAnti TuberculosisagentsLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- URLDocument21 pagesURLLyn Consing100% (3)
- Formal Place SettingDocument8 pagesFormal Place SettingLyn Consing100% (1)
- Anti TuberculosisagentsDocument24 pagesAnti TuberculosisagentsLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Seven principles of good practice in health educationDocument7 pagesSeven principles of good practice in health educationLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- EquipmentsDocument1 pageEquipmentsLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- URL and HTMLDocument4 pagesURL and HTMLLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- EquipmentsDocument1 pageEquipmentsLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Dosage: Route:: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument21 pagesDosage: Route:: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LCPDocument3 pagesDrug Study LCPalleen_viaNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseMaria MarquezNo ratings yet
- NCP-Drug Study 2Document4 pagesNCP-Drug Study 2hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Andrian Alfa Heru Cupriyanti Irmawati Yusuf Juwita Sari Lutfi Umaimah Rina AyuniDocument34 pagesAndrian Alfa Heru Cupriyanti Irmawati Yusuf Juwita Sari Lutfi Umaimah Rina AyuniPaulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedDocument42 pagesLecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Bam Slam Drug CardDocument4 pagesBam Slam Drug CardLeticia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Copydrugstudy 03Document61 pagesCopydrugstudy 03Ishtar LovernNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPRyan John Bito-onNo ratings yet
- Bronchodilator & Other Drugs Used in AsthmaDocument15 pagesBronchodilator & Other Drugs Used in AsthmaGenta JagadNo ratings yet
- Materi Dr. Darmawan B. Setyanto, Sp.A (K)Document42 pagesMateri Dr. Darmawan B. Setyanto, Sp.A (K)deddyNo ratings yet
- Ventolin DrugstudyDocument1 pageVentolin DrugstudyMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- Waiters Salmeterol PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Salmeterol PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic and Cholinergic SummaryDocument2 pagesAdrenergic and Cholinergic Summaryhashman0689No ratings yet
- Researchers Discover Cause of Asthmatic Lung Spasms - Rutgers UniversityDocument3 pagesResearchers Discover Cause of Asthmatic Lung Spasms - Rutgers UniversityA.No ratings yet
- Bronchospasm During Anaesthesia Update 2011Document5 pagesBronchospasm During Anaesthesia Update 2011hy3pjb1984No ratings yet
- 1 Pharmacy Practice Therapeutics OTC Drugs Q&A Content Ver1Document123 pages1 Pharmacy Practice Therapeutics OTC Drugs Q&A Content Ver1bhaveshnidhi64100% (1)
- Drug Study (Seretide)Document1 pageDrug Study (Seretide)Rene John Francisco100% (1)
- Metered Dose InhalersDocument2 pagesMetered Dose InhalersTepperoniNo ratings yet
- Pil 6902Document4 pagesPil 6902kovi mNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients On Lower Respiratory System Drugs Presented by Donnahae Rhoden SalmonDocument39 pagesCare of Patients On Lower Respiratory System Drugs Presented by Donnahae Rhoden SalmonKishi CopelandNo ratings yet
- Askep in EnglishDocument9 pagesAskep in EnglishnoviNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Bronchial Asthmaderic93% (60)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studypaulkris_14100% (1)
- Respiratory Drugs XL Chart 3Document2 pagesRespiratory Drugs XL Chart 3cdp1587100% (1)
- Anti Acid OsDocument13 pagesAnti Acid OsnicolaslanchNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationkrish_tartNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline Is Used To TreatDocument4 pagesTerbutaline Is Used To TreatCendaña LorelynNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia in An Asthmatic Patient: Collin Clinton Cheng, MD Janette T. Fusilero-Pascual, MDDocument96 pagesAnesthesia in An Asthmatic Patient: Collin Clinton Cheng, MD Janette T. Fusilero-Pascual, MDNicole BiduaNo ratings yet