Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group Policy
Group Policy
Uploaded by
Petar PoparaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group Policy
Group Policy
Uploaded by
Petar PoparaCopyright:
Available Formats
2
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Introduction to Group Policy ..................................................................................................................... 3
Exercise 1 Group Policy Benefits ........................................................................................................................4 Exercise 2 Group Policy Objects vs. Group Policy Object Links........................................................................6 Exercise 3 Processing Order of Group Policy......................................................................................................8 Exercise 4 Introducing the Group Policy Management Console .......................................................................11 Exercise 5 Creating a New GPO for Finance Users...........................................................................................13 Exercise 6 Using the Group Policy Object Editor..............................................................................................15 Exercise 7 Using Group Policy to Secure Desktops ..........................................................................................18
Introduction to Group Policy
Introduction to Group Policy
Objectives After completing this lab, you know more about:
� �
The Benefits of Group Policy. The Difference between Group Policy Objects (GPOs) and Group Policy Object Links. The Processing Order of Group Policy. The Group Policy Management Console. Creating New GPOs. Using the Group Policy Object Editor. Using Group Policy to Secure Desktops
� � � � �
Scenario
These labs provide an introduction to Group Policy and associated terms and technologies. Windows Server 2003 also includes improvements to Group Policy and those improvements will be outlined during lab. Group Policy enables you to better manage users and desktops with fewer resources. You will see examples of using Group Policy to manage a desktop environment. We will create and edit a Group Policy Object to see the basics of using Group Policy. Group Policy can be targeted at several levels. You will see how to target a Group Policy Object so it applies at the appropriate level in your organization. Finally, you will be introduced to the Group Policy Management Console. This tool improves upon the old Windows 2000 based tools used for managing Group Policy.
Estimated time to complete this lab: 45 minutes
Introduction to Group Policy
Computers used in these Labs:
SEA-DC-01
WRK-SEA-001
Exercise 1 Group Policy Benefits
Scenario
You can manage computers centrally through Active Directory and Group Policy. Using Group Policy to deliver managed computing environments allows you to work more efficiently because of the centralized, one-to-many management it enables. Complete this Exercise using:
SEA-DC-01
Tasks
1.
Detailed steps
a.
Open Group Policy Management.
Click the SEA-DC-01 link in the My Machines browser. Press Right-ALT + DEL.
b. Click in the virtual machine window. c.
d. Log on as Administrator with a password of Passw0rd.
Group Policy offers wide-scale management of users and workstations.
e. f. 2.
On the desktop, double-click Group Policy Management. The Group Policy Management window appears.
Investigate the organization of Group Policy.
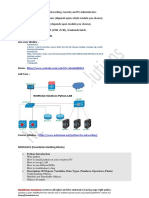
Group Policy can be applied at site, domain, and organizational unit levels to reduce overall management costs.
a.
In the console-pane, expand Forest: contoso.com and click Sites. Expand contoso.com and click Sales and Marketing.
b. Expand Domains and click contoso.com. c.
d. Expand Sales and Marketing and click Sales Team. 3.
Observe setting for installing a program through Group Policy.
Group Policy offers a high degree of flexibility, allowing you to customize configurations, such as delivering a specific piece of software to users based on their membership in an OU.
a.
In the console-pane, expand Finance and click Install Excel 2003.
b. In the details-pane, click the Settings tab and click show all.
Introduction to Group Policy Initiate a program installation. In this case, Group Policy will initiate the installation Microsoft Excel 2003 to users that are members of the Finance OU.
4.
You can see the source file location on the network server, and later, we will see MS Excel installed on the workstation.
a.
Navigate to User Configuration | Software Settings | Assigned Applications | Microsoft Office Excel 2003 | Deployment Information and notice that the Deployment Source is \\SEA-DC01\Office\EXCEL11.msi.
b. Minimize Group Policy Management. 5.
Look at details about a user in Active Directory Users and Computers.
Finance User is a member of the Finance OU and will have Excel installed on their system via the Install MS Excel 2003 Group Policy when they logon onto the domain. Again, this will be demonstrated later in this session.
a.
On the desktop, double-click Active Directory Users and Computers. maximize the window.
b. The Active Directory Users and Computers window appears; c.
In the console-pane, expand contoso.com and click Finance. Minimize Active Directory Users and Computers.
d. In the details-pane, click Finance User. e. 6.
Look at policies for various GPOs.
Because Group Policy defines the settings and allowed actions for users and computers, it can create desktops that are tailored to users job responsibilities and level of experience with computers.
a.
Restore Group Policy Management. Under Sales and Marketing, hover the mouse over the linked group policies.
b. In the console-pane, click Sales and Marketing. c.
The Sales and Marketing OU has a number of linked Group Policies that are defined to configure computers that are members of this OU.
d. Hover the mouse over Marketing Security.
Note that you can use Group Policy to secure user workstations.
e. 7.
Minimize Group Policy Management.
View setting for the Servers OU.
Besides users and workstations, servers can be managed via Group Policy through server-specific operational and security settings.
a.
Restore Active Directory Users and Computers.
b. In the console-pane, click Servers.
In this case, a Servers OU has been created to house all servers for the consoto.com domain.
c.
In the details-pane, hover the mouse over the listed servers.
d. Close Active Directory Users and Computers. 8.
View the GPO that is linked to another OU.
a.
Restore Group Policy Management. Security.
b. In the console-pane, expand Servers and hover the mouse over Server
A group policy called Server Security has been linked to the Servers OU and will configure all member computers with a security related settings.
Introduction to Group Policy
Exercise 2 Group Policy Objects vs. Group Policy Object Links
Scenario
Group Policy Objects, or GPOs, are not useful until they are linked to a site, domain, or OU. This is called the Scope of Management or SOM. The settings defined in a GPO are only applied when the GPO is linked to one or more SOMs. The link is not a component of the GPO; it is a component of the SOM to which it is linked. In the Group Policy Management Console tree view, GPO-links on a given SOM are shown as child nodes of that container. The Group Policy Management Console, or GPMC, greatly improved distinguishing a group policy object from a group policy object link. Complete this Exercise using:
SEA-DC-01
Tasks
1.
Detailed steps
a.
View Group Policy Object Container.
In the console-pane, click Group Policy Objects.
b. In the details-pane, hover the mouse over the listed group policies.
All Group Policy objects reside in the Group Policy Objects container. Note that all of the group policies shown earlier are listed in the detailspane of the container.
2.
View additional GPO details.
a.
In the details-pane, hover the mouse over the GPO Status and WMI Filter columns.
Additional details, such as if the GPOs are enabled, and if there are WMI filters applied to the GPOs, are shown in the details-pane.
b. In the console-pane, expand Group Policy Objects and hover the
mouse over the group policies. The group policies are also child objects underneath the Group Policy Objects container
3.
View a GPO-link.
a.
Under Group Policy Objects, click Marketing Security. Hover the mouse over the details-pane.
b. In the details pane, click the Settings tab. c.
The GPMC user interface distinguishes between GPO-links and GPOs as follows: The first difference is location in the console tree. Actual GPOs are always shown under the Group Policy Objects node for a given domain. Here is the Server Security Group Policy object shown earlier in the demonstration.
4.
View a GPO child.
a.
In the console-pane, under Sales and Marketing, click Marketing Security.
Introduction to Group Policy
b. Hover the mouse over the details-pane.
GPO-links appear as child nodes of a site, domain, or OU. The Server Security group policy object has been linked to the Servers OU. Note the contents of the details panes for GPOs and GPO-link are identical.
5.
View GPO-link shortcut icons.
a.
In the console-pane, under Sales and Marketing, hover the mouse over Marketing Security. Security.
b. Under Group Policy Objects, hover the mouse over Marketing
The icons for GPO links have a shortcut icon to indicate that they are pointers to another object. For example, note the Server Security GPO-link. The icon for this link has a shortcut icon to differentiate it from the icon for the actual Server Security GPO under Group Policy Objects.
6.
View backup, restore, and other options in the context menu.
a.
Under Group Policy Objects, right-click Marketing Security and hover the mouse over Back Up and Restore from Backup.
The context menu that appears when you right-click in the tree view is different depending on whether you are managing a GPO-link or a GPO. Right clicking a GPO exposes options that are primarily relevant for the actual GPO, such as Backup and Restore.
b. Click in the details-pane to close the context menu.
7.
View additional options.
Right clicking a GPO-link exposes options that are relevant to managing the link, such as Enforced and Link Enabled. Note that some options, such as Edit are available on both context menus.
a.
Under Sales and Marketing, right-click Marketing Security and hover the mouse over Enforced. Click in the details-pane to close the context menu.
b. Hover the mouse over Edit. c.
d. Minimize Group Policy Management.
Introduction to Group Policy
Exercise 3 Processing Order of Group Policy
Scenario
The scope of Group Policy includes the local GPO that all computers and GPOs apply at Active Directory sites, domains, and OUs. As mentioned earlier, each of these different targeting options is called a Scope of Management, or SOM. A GPO becomes useful only after it is linked to a SOMthe settings in the GPO are then applied according to the scope. GPOs are processed in the order of local, site, domain, and then OU. As a result, a computer or user receives the policy settings of the last Active Directory container processedthat is, a policy applied later overwrites policy applied earlier. Complete this Exercise using:
SEA-DC-01
WRK-SEA-001
Tasks Complete the following 2 tasks on: WRK-SEA-001
1.
Detailed steps
a.
Click the WRK-SEA-001 link in the My Machines browser. Press Right-ALT + DEL. Passw0rd.
b. Click in the virtual machine window. c.
Logon to the workstation as Administrator.
d. Log on as SEA-WRK-01\Administrator with the password
The first policy applied is the local computer policy. This policy applies to the machine regardless of who logs onto the computer. The settings applied to the computer are as defined by the Local Security Policy.
2.
View security settings.
a.
On the desktop, double-click Local Security Policy.
These policies are the default policies for Windows XP.
b. The Local Security Settings window appears; maximize the window. c.
In the console-pane, expand Security Settings | Local Policies and click Security Options.
Security Policies can be defined on the local machine. This is useful for workstations that are not members of a domain. Example settings include who can access this system over the network, who can logon locally, and who has backup and restore rights.
d. Hover the mouse over the details-pane. e. f.
Close Local Security Policy. Log off SEA-WRK-01.
Introduction to Group Policy Complete the following 8 tasks on: SEA-DC-01
3.
a.
Click the SEA-DC-01 link in the My Machines browser.
b. Restore Group Policy Management.
Site-based group policies are applied next. Our workstation would receive policy settings defined on a group policy that is linked to the site container. For example, a GPO might be linked to an Active Directory site to specify policy settings for proxy settings and network-related settings that are specific to that site.
Go back to Group Policy Management.
4.
Enable Show Sites on the site container to link a GPO to a site. Link the Site Group Policy to the Sites container.
a.
In the console-pane, right-click Sites and click Show Sites. click OK.
b. The Show Sites window appears; check Default-First-Site-Name and a.
5.
Expand Sites and right-click Default-First-Site-Name and click Link an Existing GPO. OK.
b. The Select GPO window appears; click Site Group Policy and click
Note that you cannot create and link group policies in one step on the site container.
6.
View Group Policy settings for the site.
a.
Expand Default-First-Site-Name and hover the mouse over Site Group Policy.
All users and workstations in the site will inherit policy settings defined at this level unless the GPO is configured for exception management. Exception management will be discussed later in this lab.
7.
View Domain Policies.
a.
In the console-pane, under contoso.com, click Default Domain Policy.
Domain-based policies are processed next.
b. On the Settings tab, click show all.
By default, the Default Domain policy is automatically created and linked to the domain container and used by all domain controllers in the domain. This will be applied to all objects in the domain.
8.
View Account Policies/Password Policies
a.
Navigate to Computer Configuration | Windows Settings | Security Settings | Account Policies/Password Policies and hover the mouse over the Account Policies/Password policy settings.
Settings have already been configured for this policy. Note the strong security settings on the Password policy. Again, all users and workstations in the domain will inherit policy settings defined at this level unless the GPO is configured for exception management.
9.
View OU policies.
a.
In the console-pane, click Sales and Marketing.
Organizational Unit policies are processed next.
b. Hover the mouse over the linked group policies in the details pane.
If a workstation or user is a member of the Marketing and Sales Team OU, they will receive any settings defined in a group policy object that is linked to the Marketing and Sales Team OU unless the GPO or OU is configured for exception management.
10. View child organizational a.
In the console-pane, click Sales Team.
unit-based group policies.
Finally, child organizational unit-based group policies are processed.
10
Introduction to Group Policy
b. Hover the mouse over the linked group policies in the details pane.
If a workstation or user is a member of the Sales Team OU, they receive any settings defined in a group policy object that is linked to the Sales Team OU unless the GPO or OU is configured for exception management.
Introduction to Group Policy
11
Exercise 4 Introducing the Group Policy Management Console
Scenario
Now that youve gotten a quick tour of Group Policy and seen some of its capabilities, lets take a more detailed look at the primary tool use to manage Group Policy the Group Policy Management Console, or GPMC. You should use the GPMC for managing Group Policy because it offers simplified management and additional functionality such as full access to Group Policy creation and linking. The main point of this exercise is to familiarize you with the GPMC. Specific management of Group Policy will be further presented in upcoming Webcast sessions. Complete this Exercise using:
SEA-DC-01
Tasks
1.
Detailed steps
a.
Open GPMC.
In the console-pane, under Forest: contoso.com, click Domains.
We can then view other forests and domains for which our account has permissions. By default it connects to PDC Emulator of the Domain in which the machine resides.
b. In the details pane, hover the mouse over SEA-DC-01.contoso.com. 2.
View Domain Controller options.
a.
In the console pane, right-click contoso.com and click Change Domain Controller. over the window as you view the options.
b. The Change Domain Controller window appears; hover the mouse
The GPMC can connect to any domain controller within the domain. The best practice is to use the PDC Emulator to avoid conflicts in case an object is edited by two parties simultaneously. However, if you are in a remote site, you can connect to a local domain controller to perform Group Policy management to improve performance.
c. 3.
Click Cancel. In the console tree, under Sites, hover the mouse over Default-FirstSite-Name.
View Site options.
a.
As we have already seen, sites are not shown by default. This helps to speed up console performance by not having it enumerate site information. Earlier, we enabled sites to be shown.
4.
View Group Policy Modeling options.
a.
In the console-pane, click Group Policy Modeling.
Group Policy Modeling is a new Group Policy management feature. This allows you to simulate policy settings applied to users and computers via Group Policy before actually applying the policies. This feature is known as Resultant Set of Policy Planning Mode in Windows Server 2003. This feature requires at least one domain controller in the forest running
12
Introduction to Group Policy Windows 2003, since the simulation is performed by the Resultant Set of Policy Provider service that is only present on domain controllers running Windows Server 2003.
5.
View Group Policy Results options.
a.
In the console-pane, click Group Policy Results.
Group Policy Results allows to you to access the Resultant Set of Policy Logging Mode capabilities. Group Policy Results represents the actual resultant set of policy that is applied to a given user and computer. You can only obtain Group Policy Results data from computers that are running Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 and later.
Introduction to Group Policy
13
Exercise 5 Creating a New GPO for Finance Users
Scenario
The Administrative Template Extension is used by the Group Policy Object Editor to configure the settings in a Group Policy Object. GPOs are settings that are applied by modifying the registry on target clients. Creating a GPO is an excellent way to introduce you to Group Policy object features. Lets say that the Finance department needs Internet Explorer settings defined for Finance users. Complete this Exercise using:
SEA-DC-01
Tasks
1.
Detailed steps
a.
Create a link to a GPO.
In the console-pane, right-click Finance and click Create and Link a GPO here.
b. The New GPO dialog box appears; type Finance Users and click OK.
A new GPO-link titled Finance Users will appear in the Linked Group Policy Objects tab.
c.
In the console tree, under Finance, click Finance Users.
Remember the actual GPO is in Group Policy Objects, where all GPOs for the domain reside.
2.
View GPO properties.
a.
In the details pane, ensure that the Scope tab is selected.
The Scope tab shows Links, Security Filtering and WMI Filtering. Filtering can be used to further refine who receives GPO settings. Filtering will be presented in later Webcasts.
b. In the details pane, in the Links section, hover the mouse over
Finance. The Links section shows the container where the GPO-link resides; in this case it is the Finance OU. You can also see if the link is Enforced, if the link is Enabled, and the path to the container.
c.
Under Enforced, hover the mouse over No. Under Path, hover the mouse over Contoso.com/Finance. Hover the mouse over Security Filtering.
d. Under Link Enabled, hover the mouse over Yes. e. 3.
View Security Filtering options.
a.
Security Filtering allows you to add security groups to the GPO to filter who receives the GPO settings. Authenticated Users are listed here. That means all authenticated users on the domain have rights regarding this group policy object. Security Filtering will also be presented in a later Webcast.
14
Introduction to Group Policy View WMI Filtering Options. Hover the mouse over WMI Filtering.
4.
a.
WMI Filtering is used to further refine application of the GPO using scripts to filter potential targets based on devices. WMI filters can only be applied to Windows Server 2003 or Windows XP. Windows 2000 machines will disregard any WMI Filtering. Advanced WMI Filters will be created and applied to prevent the application of a group policy object on specific clients based on computer configuration in future Webcasts.
5.
View the Details Tab.
a.
Click the Details tab. Domain
b. Hover the mouse over the following objects as you view them: c.
The domain where the GPO resides.
d. Owner
The owner of the GPO.
e.
Created Modified User version
The creation date of the GPO.
f.
The last time the GPO was modified.
g.
The User version of the GPO. This is the portion of the policy settings applied to the user.
h. Computer version
The Computer version of the GPO. This is the portion of the policy settings applied to the computer.
i.
Unique ID
The Unique ID of the GPO. This is the GPOs GUID Globally Unique Identifier.
6.
View Computer configuration settings.
a.
Expand the GPO Status drop-down menu and hover the mouse Computer configuration settings disabled.
To make GPOs more efficient, you can filter settings based on user or computer settings.
b. Click the mouse on the details tab to close the drop-down menu. 7.
View the Settings tab.
a.
Click the Settings tab.
Use the settings tab to display settings for the group policy object. Here we can see that there arent yet any defined settings for the Finance Users GPO. We will edit the Finance Users GPO to configure Internet Explorer settings shortly.
8.
View the Delegation tab.
a.
Click the Delegation tab.
The Delegation tab is where the GPO can be delegated to users or groups other than Domain Admins for administrative purposes. GPO Delegation will be discussed in a future Webcast.
Introduction to Group Policy
15
Exercise 6 Using the Group Policy Object Editor
Scenario
Group Policy settings are edited using the Group Policy Object Editor. All policy settings created by the Group Policy Object Editor are stored in a GPO. Complete this Exercise using:
SEA-DC-01
WRK-SEA-001
Tasks Complete the following 8 tasks on: SEA-DC-01
1.
Detailed steps
a.
In the console tree, under contoso.com, click Default Domain Policy. The Group Policy Object Editor window appears.
b. Right-click Default Domain Policy and click Edit. c.
Open the Group Policy Object Editor.
The Group Policy Object Editor is used to define the settings in a Group Policy Object. The Group Policy Object Editor uses administrative template files to display settings. Administrative Template files, or .adm files, are used to populate user interface settings in the Group Policy Object Editor, enabling administrators to manage registry-based policy settings. An entire future Webcast session will be dedicated to .adm files at a later date. Editing the Default Domain Policy should help you understand the difference between using the GPMC to manage GPOs and using the Group Policy Object Editor to define the settings.
2.
Use User Configuration.
a.
In the console tree, expand User Configuration | Administrative Templates and click System. welcome screen at logon.
b. In the details pane, double-click Dont display the Getting Started c.
The Dont display the Getting Started welcome screen at logon Properties window appears; click the Explain tab and hover the mouse over the contents.
We will edit the User Configuration to define a policy that will prevent the Getting Started Welcome Screen from being displayed when users logon. This is a Domain Policy, so it will be applied to all users in the domain. You can click the Explain tab to view more information on any setting.
d. Click the Setting tab and click Enabled and click OK. 3.
Close Group Policy Object Editor.
a.
Close the Group Policy Object Editor.
Settings are automatically saved when you close the Group Policy Object
16
Introduction to Group Policy Editor
4.
Open another Group Policy Object Editor.
Next, we will edit the Finance Users GPO that we created earlier in order to configure Internet Explorer settings for members of this OU.
a.
In the console tree, under Finance, right-click Finance Users and click Edit. window.
b. The Group Policy Object Editor window appears; maximize the 5.
Change the Disable the Connections page Properties.
a.
Expand User Configuration | Administrative Templates | Windows Components | Internet Explorer and click Internet Control Panel.
We will change Internet Explorer for Finance Users by hiding the Connections tab in the Internet Options panel.
b. In the details pane, double-click Disable the Connections page.
Opening the Disable the Connections page Properties uses the inetres.adm file to display the settings. Again, adm files will be further discussed in a future Webcast.
c.
The Disable the Connections page Properties window appears; click Enabled and click OK.
d. Scroll the window to the right and hover the mouse over Enabled. 6.
Change AutoSave configuration so that users will not be able to store passwords using autocomplete.
a.
Navigate to User Configuration | Administrative Templates | Windows Components and click Internet Explorer. AutoComplete to save passwords.
b. In the details-pane, scroll down and double-click Do not Allow c.
The Do not Allow AutoComplete to save passwords Properties window appears; click Enabled.
d. Click Previous Setting. 7. 8.
Disable AutoComplete for forms a well. Prevent finance users from changing their home page.
a. a.
The Disable AutoComplete for forms Properties window appears; click Enabled and click OK. In the details-pane, scroll up and double-click Disable changing home page settings. appears; click Enabled and click OK.
b. The Disable changing home page settings Properties window c.
Close Group Policy Object Editor.
d. Close Group Policy Management.
Complete the following 10 tasks on: WRK-SEA-001
9.
a.
Click the WRK-SEA-001 link in the My Machines browser. Press Right-ALT + DEL.
b. Click in the virtual machine window. c.
Log on to the client workstation as FinanceUser, a user object that resides in the Finance OU, to see the Group Policy settings applied from the Finance Users GPO.
d. Logon as Contoso\FinanceUser with the password Passw0rd.
10. View GPUpdate help.
a.
On the desktop, double-click Command Prompt. more and press Enter.
b. The Command Prompt window appears; type GPUpdate /help |
Introduction to Group Policy
17
Running GPUpdate.exe will force the latest settings to our client. GPUdate.exe on Windows XP replaces the Secedit /refreshpolicy formerly used on Windows 2000 clients. If we type help after GPUdate we will see a list of options that can be run with the tool.
c.
Hover the mouse over options as they appear.
d. Press spacebar to display more pages of help. 11. Force GPUpdate. a.
Scroll window down to get to prompt; type GPUpdate /force and press Enter.
By running GPUdate with the force option, this forces the client to compare its files to see if it has the latest GPtO settings in its cache or if it needs to reapply settings.
b. Wait until Policy Refresh has completed appears. c.
At Certain Computer policies are enabled that can only run during start up type Y and press Enter.
d. The system will reboot, this may take a moment.
Earlier, we saw the Install Excel 2003 GPO linked to the Finance OU. This GPO is now going to be applied to our workstation. The Install Excel 2003 GPO contained computer-based settings that will require a reboot for them to take affect so we will reboot the workstation to receive the changes.
12. Restart and allow Excel
2003 to install.
When the computer restarts, you will notice that you are prevented from logging in immediately while Excel 2003 is automatically installed. Again, this is a result of a GPO being applied to the computer.
a.
Click in the virtual machine window. Logon as Contoso\FinanceUser with the password Passw0rd.
b. Press Right-ALT + DEL. c.
It could take several minutes for the installation to finish.
13. View Internet Explorer a.
Properties and verify that the Group Policy has taken effect.
14. View AutoComplete
Click Start, right-click Internet Explorer and click Internet Properties. tabs to show Connections tab is missing.
b. The Internet Properties window appears; hover the mouse over the a.
Click the Content tab and click AutoComplete. Forms and click Cancel.
settings and verify that the Group Policy has taken effect.
15. Finally, notice that Finance
b. The AutoComplete Settings window appears; hover the mouse over
a.
Click the General tab; hover the mouse over Address. Do not log off FinanceUser.
Users cannot change their home page settings.
b. Click Cancel. c.
18
Introduction to Group Policy
Exercise 7 Using Group Policy to Secure Desktops
Scenario
You should use Group Policy to efficiently manage your desktop environment. A good example if this is preventing users from making system level changes on their desktops by using Group Policy to push secured settings to target machines. Complete this Exercise using:
SEA-DC-01
WRK-SEA-001
Tasks Complete the following 5 tasks on: SEA-DC-01
1.
Detailed steps
a.
Click the SEA-DC-01 link in the My Machines browser. The Group Policy Management window appears. click Edit.
b. On the desktop, double-click Group Policy Management. c.
Open another Group Policy Object Editor.
d. In the console-pane, under Finance, right-click Finance Users and
Now we will further edit the Finance Users GPO by configuring settings that will reduce the number of usergenerated problems by preventing them from accessing certain desktop features.
2.
Remove the Run command from the start menu to prevent users from circumventing application shortcuts and to make it more difficult to run programs such as the registry editor. Prohibit access to the control panel. This will prevent finance users from making system changes to their system configuration. Finally, we will configure Folder Redirection for Finance Users, ensuring they will have access to their files regardless of which desktop they log onto.
a.
The Group Policy Object Editor appears; maximize the window. click Start Menu and Taskbar.
b. Navigate to User Configuration | Administrative Templates and c.
In the details pane, double-click Remove Run menu from Start Menu. appears; click Enabled and click OK.
d. The Remove Run menu from Start Menu Properties window a.
3.
Navigate to User Configuration | Administrative Templates and click Control Panel. The Prohibit access to the Control Panel window appears; click Enabled and click OK. In the console tree, navigate to User Configuration | Windows Settings and click Folder Redirection. The My Documents Properties dialog box appears; next to Settings, expand the drop-down menu and click Basic Redirect everyones folder to the same location.
b. In the details-pane, double-click Prohibit access to the Control Panel. c. a.
4.
b. In the details-pane, right-click My Documents and click Properties. c.
We will be configuring Basic redirection for the My Documents folder.
Introduction to Group Policy Basic redirection redirects everyones folder to the same location.
19
Advance redirection redirects allows us to specify locations for various users or groups.
5.
Specify the folder redirection path.
a.
Next to Target Folder Location, hover the mouse over Create a folder for each user under the root path.
Each user has their own folder in the Profiles directory on the domain controller.
b. For Root Path, type \\SEA-DC-01\profiles.
Notice the example path given at the bottom of the My Documents Properties window.
c.
Hover the mouse over \\SEA-DC-01\profiles\Clair\My Documents and click OK. Close Group Policy Management. Click the WRK-SEA-001 link in the My Machines browser. Contoso\FinanceUser with the password Passw0rd.
d. Close Group Policy Object Editor. e.
Complete the following 3 tasks on: WRK-SEA-001
6.
a.
b. Log off the WRK-SEA-001 computer and log back on as c.
Attempt to use the Run command.
On WRK - SEA -001, click Start and notice that the Run command is no longer available.
If it still available, log off and log back on again. This may occur if not enough time passes after you changed the GPO.
a. a.
7. 8.
Attempt to access the Control Panel. View the location of the My Documents folder.
Notice that the Control Panel is no longer accessible. Right-click My Documents and click Properties. the mouse in the field and scroll to the left to show the new location.
b. The My Documents Properties window appears; next to Target, click
The My Documents folder resides on the domain controller.
c.
Click Cancel.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Learner Guide Era 4 MscitDocument103 pagesLearner Guide Era 4 MscitAaditya RoyNo ratings yet
- Daily, Weekly and Monthly Responsibilities For Oracle Applications DbasDocument21 pagesDaily, Weekly and Monthly Responsibilities For Oracle Applications DbasVikrant ThapaNo ratings yet
- Visa Preparing For Psd2 Sca Publication Version 1-1-05!12!18 002 FinalDocument30 pagesVisa Preparing For Psd2 Sca Publication Version 1-1-05!12!18 002 FinalRohitNo ratings yet
- Python For Networking, Security and F5 AdministratorsDocument4 pagesPython For Networking, Security and F5 AdministratorsSantanuNo ratings yet
- Leica SpiderQC FLYDocument2 pagesLeica SpiderQC FLYSahrul nasNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design Practical FileDocument49 pagesCompiler Design Practical FileDHRITI SALUJANo ratings yet
- Exam Taken by CTIDocument43 pagesExam Taken by CTIAdi OrbachinNo ratings yet
- Error Correcting Codes - Hamming CodesDocument3 pagesError Correcting Codes - Hamming Codesatina tehreemNo ratings yet
- %SASDIFF: A SAS Macro For Differential File ComparisonDocument8 pages%SASDIFF: A SAS Macro For Differential File ComparisonmihirhotaNo ratings yet
- ECE NAS Practical1 (Sayed Ramish Ali) PDFDocument21 pagesECE NAS Practical1 (Sayed Ramish Ali) PDF037SAYED RAMISH ALINo ratings yet
- CassandraDocument5 pagesCassandraSheshikanth DonNo ratings yet
- CS42L42 Ds1083a2Document180 pagesCS42L42 Ds1083a2joseph zhangNo ratings yet
- Labvolt Series 9063: Data Acquisition and Control InterfaceDocument2 pagesLabvolt Series 9063: Data Acquisition and Control Interfaceollata kalanoNo ratings yet
- Prudhvi Raj Gadamsetty: Java DeveloperDocument2 pagesPrudhvi Raj Gadamsetty: Java DeveloperKrishNo ratings yet
- Role of Computer in ElectronicsDocument11 pagesRole of Computer in ElectronicsNabeel Raja100% (1)
- Multiple and Bicriteria Scheduling - A Literature SurveyDocument17 pagesMultiple and Bicriteria Scheduling - A Literature SurveybizNo ratings yet
- MAXBridge CPE 33 User Guide Rev 3.5 EngDocument54 pagesMAXBridge CPE 33 User Guide Rev 3.5 EngashaharaNo ratings yet
- 2 DataModeling RelationalModeling 2012Document2 pages2 DataModeling RelationalModeling 2012Ksatria AFKNo ratings yet
- MachXO3L StarterKit UGDocument28 pagesMachXO3L StarterKit UGDavid ParkerNo ratings yet
- Drone Forensics FieldDocument13 pagesDrone Forensics FieldyannikNo ratings yet
- Architecang and Sizing Your Splunk Deployment: Simeon YepDocument47 pagesArchitecang and Sizing Your Splunk Deployment: Simeon YepSecurisq NetworksNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:09: Name Tarun Shetty Class Be Extc B Batch B2 Roll No. 54Document9 pagesExperiment No:09: Name Tarun Shetty Class Be Extc B Batch B2 Roll No. 54Dikshit ShettyNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Project ReportDocument30 pagesSummer Training Project ReportYaman VermaNo ratings yet
- Python All The Fun of The FairDocument4 pagesPython All The Fun of The FairsdfgNo ratings yet
- VM400 Commissioning 7EN02-0417-02Document6 pagesVM400 Commissioning 7EN02-0417-0201666754614No ratings yet
- Personal Notes On The Network Simulator NS-3: Mubashir Husain RehmaniDocument6 pagesPersonal Notes On The Network Simulator NS-3: Mubashir Husain RehmaniNakul VyasNo ratings yet
- Library Management SystemDocument15 pagesLibrary Management SystemMugeshNo ratings yet
- What Is Software Architecture: BITS PilaniDocument39 pagesWhat Is Software Architecture: BITS PilaniTejaswini SandapollaNo ratings yet
- Cobol-Complete-Notes 1Document37 pagesCobol-Complete-Notes 1Satish KodiNo ratings yet
- Project Title: - Bitcoin: Debre Markos UniversityDocument11 pagesProject Title: - Bitcoin: Debre Markos Universityalehegn manayeNo ratings yet