Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Painting Polynomials Up For Conference
Uploaded by
api-2474550010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesOriginal Title
painting polynomials up for conference
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesPainting Polynomials Up For Conference
Uploaded by
api-247455001Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Painting Polynomials Unit Plan
UNIT TITLE: Painting Polynomials
GRADE LEVEL(S): 9/10
ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS:
How to mix colors to find equal contrasts
How to manipulate water colors
How to manipulate acrylic paint
How multiplying polynomials is the same as using an area model
Mixing a scheme of colors can create harmony
How generic rectangles can be used to translate the area model for more frequent use.
How math can create order in an abstract work of art.
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS:
How do I mix colors using watercolors and acrylics?
How can I use an area model to multiply polynomials?
What are like terms and how do I combine them?
What patterns appear in multiplying polynomials?
How can I generalize the multiplication of polynomials?
How does adding one color affect the color harmonies the entire piece?
How does math create order in an abstract work of art?
GOALS AND EXPECTATIONS:
Art:
26B4D- Demonstrate knowledge and skills that communicate clear and focused ideas based on planning,
research and problem solving.
26A. 3E- Describe how the choices of tools/technologies and processes are used to create specific effects in the
arts.
Research topics and materials to create art.
Explore new materials to create art.
Math:
6.A- Demonstrate knowledge and use of numbers in their many representations in a broad range of theoretical
and practical settings.
6.B- Investigate, represent and solve problems using number facts, operations, and their properties, algorithms
and relationships.
7.C-Select and use appropriate technology, instruments and formulas to solve problems interpret results and
communicate findings.
8.D.- Use algebraic concepts and procedures to represent and solve problems.
4 Formulate and solve linear and quadratic equations and linear inequalities algebraically and investigate
nonlinear inequalities using graphs, tables, calculators and computers
MATERIALS, RESOURCES, AND TECHNOLOGY
Note cards for word wall (Vocabulary: monomial, binomial, polynomial)
Pencils
Scissors
Straight edge
Watercolors
Paint brushes
Newsprint
Watercolor paper
Mixing tray
Apron
Water cups
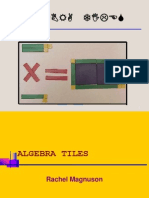
Algebra tiles
Overhead projector
CONNECT (or LESSON #1)
STAGE ONE: DESIRED RESULTS:
Students will know:
Area is the space taken up inside of a shape.
Areas of rectangles are found by multiplying the sides together.
Students will be able to:
Find many rectangles that have the same area.
Find area of rectangles using variables and constants.
_____________________________________________________________________________
STAGE TWO: ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE
Students will show many shapes that have the same areas both using constants and variables and turn it in for feedback.
STAGE THREE: LEARNING PLAN
Students will find many shapes and need to find the area of them. Students will also review the definition of
area, and be reminded of how to find area for many different shapes and figures.
Students will work with their groups to match the figures to each area. Students will then choose an area and
create at least four more figures that have the same area.
Some students will be challenged to do the same exercise with variables.
Students will check the work of their group, and then turn them in for a grade and feedback.
ATTEND (or LESSON #2)
STAGE ONE: DESIRED RESULTS:
Students will know:
That primary colors mix to secondary colors.
That secondary and primary colors can mix to tertiary colors
Which colors are complementaries of each other
That complementary colors mix to neutrals
That an ideal color mixing has equal contrast between each of the analogous colors (ie. Mixing blue and green
does not ensure blue green, so the contrast to blue and to green needs to be equal)
The qualities of using watercolors and acrylic paints
Students will be able to:
Identify primary, secondary, tertiary, and complimentary colors.
Mix all secondary and tertiary colors from the
_______________________________________________________________________
STAGE TWO: ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE
Students will turn in a color wheel, and the reference sheet they have made of each color scheme to be graded on a
rubric.
STAGE THREE: LEARNING PLAN
o Students will create a color wheel by making a circle and dividing it into twelve sections.
o Students will use primary colors in the appropriate places, and teacher will explain primary, secondary, and
tertiary colors. For the first activity they will be using watercolors.
o Students will then mix the secondary colors and put them into their appropriate places, making sure to use the
same amount of contrast between the primary colors.
o Students will mix tertiary colors making sure to show equal contrast between the secondary and primary in each
combination.
o Students will create the same exercise using acrylic colors.
o Teacher will explain each color scheme including complimentary, analogous, split complimentary, and
monochromatic.
o Students will use the media of their choice to show samples on a reference sheet.
IMAGINE (or LESSON #3)
STAGE ONE: DESIRED RESULTS:
Students will know:
o That finding the area involves multiplying, and to make an area model, a sum can be broken up and multiplied
appropriately.
o The area and dimensions of each algebra tile.
Students will be able to:
o Use algebra tiles to multiply binomials.
o Multiply variables and constants.
o Add like terms.
o Show any given binomial multiplication using algebra tiles.
o Effectively apply a negative to a problem
______________________________________________________________________________
STAGE TWO: ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE
Students will find binomial multiplication using algebra tiles, draw out the pictures, and turn it in for feedback as an exit
ticket.
STAGE THREE: LEARNING PLAN
o Teacher will introduce new vocabulary for this unit: monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial.
o Teacher will model doing a two digit number times a two digit number on the board using a generic rectangle
(so 13 times 16 by splitting 13 up to 10 and 3, and 16 to 10 and 6) and demonstrate how we can break things up
and multiply.
o Teacher will explain the lengths and areas of each algebra tiles.
o Teacher will demonstrate how to do a binomial multiplication problem using tiles on the overhead projector.
Students will follow along with their tiles and ask questions.
o Students will practice problems with their groups. Teacher will check answers with class and clarify
misunderstandings.
o Students will practice problems on their own and check them with an answer key.
INFORM (or LESSON #4)
STAGE ONE: DESIRED RESULTS:
Students will know:
o What a generic rectangle is and how to use it.
o That a multiplication problem done using algebra tiles can be translated to generic rectangles.
Students will be able to:
o Multiply polynomials using generic rectangles.
____________________________________________________________________________
STAGE TWO: ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE
o Students will turn in three problems as an exit ticket at the end of class for a grade. The exit ticket will include a
few variations of polynomials that need to be multiplied with a generic rectangle.
STAGE THREE: LEARNING PLAN
o Teacher will demonstrate another problem using tiles, and show how it can be translated to a generic rectangle,
much like our two digit multiplication problem.
o Students will try problems as a group.
o Students will work on generic rectangles on their own.
Differentiation:
o Students can continue doing problems with the tiles, or begin to draw out the tiles if the generic rectangles
arent making sense.
PRACTICE (or LESSON #5)
STAGE ONE: DESIRED RESULTS:
Students will know:
o That variations of polynomial problems can be done using generic rectangles.
Students will be able to:
o Do many variations of generic rectangle problems including monomials by binomials, trinomials by binomials,
trinomials by trinomials, using negatives, multiple variables, etc.
______________________________________________________________________________
STAGE TWO: ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE
Students will take a quiz at the end of class to turn in for a grade.
______________________________________________________________________________
STAGE THREE: LEARNING PLAN
o Teacher will demonstrate many forms of variation that can be used to multiply.
o Students will do Math Art where they are given a sheet of paper, and several practice problems. One student
will choose one problem, which everyone will do on his or her paper using some art material. The teacher will
check the problem for the class, and students will pass their papers, but not their art material, to another paper,
and complete the next problem. Students will do a total of 8 problems with their tables in this fashion.
o Students will choose five more problems to do on their own and check with the answer key. The teacher will
circulate during this time to clarify misunderstandings.
EXTEND (or LESSON #6)
STAGE ONE: DESIRED RESULTS:
Students will know:
o That the same problem can be done using many methods.
Students will be able to:
o Show polynomial multiplication in many ways.
o Measure out tiles and spaces consistently.
o How to create their own problem and find the answer.
o How to adjust their dimensions to use the most of their paper space.
______________________________________________________________________________
STAGE TWO: ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE
o Turn in a rough draft plan of their project for feedback.
STAGE THREE: LEARNING PLAN
o Students will create problems that incorporate negatives, constants, and multiple variables.
o Students will plan out sketches and decide what colors and dimensions they will decide to use on their final
project.
o Students will check each others problems before beginning their finals.
Enrichment Students can begin showing how to solve or evaluate equations using polynomials if they understand the
multiplication easily. They will also be pushed to work backwards. Given a polynomial, what would the two factors be?
Students can also choose from a list of problems instead.
REFINE (or LESSON #7)
STAGE ONE: DESIRED RESULTS:
Students will know:
o The advantages and disadvantages of each of the media.
o The components of finishing a piece of art
Students will be able to:
o Make a rough draft of their final problem in both acrylic and watercolor.
o Conduct a mini-critique
o Decide which material will be better for them to convey the problem
______________________________________________________________________________
STAGE TWO: ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE
Students will turn in their final project to be graded on a rubric.
STAGE THREE: LEARNING PLAN
o Students will create a smaller version of their project in both watercolor and acrylic paint.
o Students will conduct a mini-critique in order to decide which medium they want to use.
o Students will lightly measure and draw out their plan for the final project in pencil.
o Students will paint their final projects.
o Students will write an artist statement and turn it in.
PERFORM (or LESSON #8)
DESIRED RESULTS:
Students will know:
o That the thoughts and ideas of other observes strengthens and often guides artists.
Students will be able to:
o Critique other students work
o Self-assess and reflect on their own work.
o Multiply polynomials.
______________________________________________________________________________
STAGE TWO: ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE
o Students will turn in the factors and product of every students artwork.
o Students will be graded on their participation during the class critique.
STAGE THREE: LEARNING PLAN
o Students will mount their own work and artist statement throughout the room.
o Students will be given ten minutes as a mini-quiz, to walk around the room and observe work, writing down
both the factors and the product of the polynomial multiplications.
o Students will come back together and critique each students work. Each artist will be featured for five minutes.
Students will be allowed to share thoughts they had while they were walking around independently observing,
as well as what color schemes are represented, what elements and principles stand out, what aspects are
working well, and how the piece could improve.
You might also like
- Using Algebra Tiles From Polynomials To Factoring HandoutDocument13 pagesUsing Algebra Tiles From Polynomials To Factoring HandoutnoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2-1 3 1 Combining Like Terms With Algebra TilesDocument4 pagesActivity 2-1 3 1 Combining Like Terms With Algebra Tilesapi-288922072No ratings yet
- Algebra TilesDocument23 pagesAlgebra TilesLouNV100% (1)
- Y7 Elements of Art Unit ProgramDocument6 pagesY7 Elements of Art Unit Programapi-298785195No ratings yet
- Algebra Tiles: For A Concrete Introduction To The Abstract Concepts of Integers and AlgebraDocument43 pagesAlgebra Tiles: For A Concrete Introduction To The Abstract Concepts of Integers and Algebraismael63322100% (1)
- Algebra TilesDocument56 pagesAlgebra Tilesboostoberoi100% (1)
- Teach Algebra Using TilesDocument59 pagesTeach Algebra Using TilesManonmani PudhuezuthuNo ratings yet
- Basic Operations With Polynomials Using Algebra Tiles PDFDocument57 pagesBasic Operations With Polynomials Using Algebra Tiles PDFbaxreyn yareNo ratings yet
- Working With Algebra Tiles (Project)Document8 pagesWorking With Algebra Tiles (Project)Ruben Serna CNo ratings yet
- Using Math Manipulatives Full File Print With Markups9Document25 pagesUsing Math Manipulatives Full File Print With Markups9Kugan Mahendran Kgn100% (2)
- Combining Like Terms Algebra TilesDocument28 pagesCombining Like Terms Algebra TilesAntonio IJNo ratings yet
- Multiplying Fractions Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMultiplying Fractions Lesson Planapi-242060776100% (2)
- Art As A Form of CommunicationDocument16 pagesArt As A Form of Communicationapi-247455001100% (1)
- Painting Polynomials 12 5Document16 pagesPainting Polynomials 12 5api-2474550010% (1)
- Grade 4 MathDocument6 pagesGrade 4 Mathapi-252740604No ratings yet
- Scratchboard Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesScratchboard Lesson Planapi-251752385No ratings yet
- Warhol Color Scheme Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesWarhol Color Scheme Lesson PlanRebecca Randall Bryan Gallery, Coastal Carolina UniversityNo ratings yet
- Mosaics - Parts of The Whole Unit PlanDocument9 pagesMosaics - Parts of The Whole Unit Planapi-247455001100% (1)
- Notan Collages: Asymmetrical and Symmetrical BalanceDocument6 pagesNotan Collages: Asymmetrical and Symmetrical BalanceRebecca Randall Bryan Gallery, Coastal Carolina UniversityNo ratings yet
- Siop Lesson FinalDocument10 pagesSiop Lesson Finalapi-214081578No ratings yet
- 12 5 The Still Life Value and ScratchboardsDocument9 pages12 5 The Still Life Value and Scratchboardsapi-247455001100% (2)
- Elementary SchoolDocument19 pagesElementary Schoolraider00No ratings yet
- Adding Fractions Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesAdding Fractions Lesson Planapi-242060776100% (1)
- Introduction To Algebra Tiles AlgebraDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Algebra Tiles Algebrajes74No ratings yet
- Persona Empathy MapDocument2 pagesPersona Empathy Mapapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Guide: Specific Measurable Attainable Relevant - TimeDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Guide: Specific Measurable Attainable Relevant - Timeapi-525077971No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 Math Equal GroupsDocument12 pagesLesson Plan 3 Math Equal Groupsapi-143111550No ratings yet
- 6e Sample Lesson PlanDocument6 pages6e Sample Lesson Planapi-26271422575% (4)
- Unit 2 - Chuck Close Portrait Grid Drawing 12 5Document13 pagesUnit 2 - Chuck Close Portrait Grid Drawing 12 5api-247455001100% (3)
- Paintingpolynomialslp For ConferenceDocument2 pagesPaintingpolynomialslp For Conferenceapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Coordinate Plane Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesCoordinate Plane Lesson Planapi-272823486No ratings yet
- Edu 527 Unit PlanDocument5 pagesEdu 527 Unit Planapi-404033609No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document5 pagesLesson Plan 2Eton KirbyNo ratings yet
- LTM 632a RtapaDocument3 pagesLTM 632a Rtapaapi-300465966No ratings yet
- Math Lesson Plan AedDocument3 pagesMath Lesson Plan Aedapi-349671090No ratings yet
- Plants Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesPlants Lesson Planjalexislopez13No ratings yet
- 7 Amalgamation PDFDocument8 pages7 Amalgamation PDFMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Math 5th GradeDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Math 5th Gradeapi-273109703No ratings yet
- 1 Ma Measure AreaDocument7 pages1 Ma Measure Areaapi-207317283No ratings yet
- Area Word Problems Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesArea Word Problems Lesson Planapi-25164978250% (2)
- Math Lesson-ShapesDocument3 pagesMath Lesson-Shapesapi-206093485No ratings yet
- 02 Instructional Software Lesson Idea Template 2017 4Document6 pages02 Instructional Software Lesson Idea Template 2017 4api-361246102No ratings yet
- Romero Britto Color Theory Unit Lesson 5-Final PaintingDocument2 pagesRomero Britto Color Theory Unit Lesson 5-Final Paintingapi-252665872No ratings yet
- Edtech 506-Lesson 3Document3 pagesEdtech 506-Lesson 3api-293769922No ratings yet
- Siop Lesson For Optical IllusionDocument3 pagesSiop Lesson For Optical Illusionapi-375201971No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson PlansDocument16 pagesDaily Lesson Plansapi-250145674No ratings yet
- Elizabeth Alquicira - DL Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesElizabeth Alquicira - DL Lesson PlanElizabeth AlquiciraNo ratings yet
- BernDocument4 pagesBernAlvin Patrick PeñafloridaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 EdtpaDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Edtpaapi-323461891No ratings yet
- Unit Plan Matrix Math GeometryDocument4 pagesUnit Plan Matrix Math Geometryapi-242011119No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Day 1 of Similar Figures: Teachers: Bethany ConradDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Day 1 of Similar Figures: Teachers: Bethany Conradapi-193730631No ratings yet
- Math Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMath Lesson Planapi-243037695No ratings yet
- PBL Intervention OverviewDocument5 pagesPBL Intervention Overviewapi-268936426No ratings yet
- Week 3 Edma264Document3 pagesWeek 3 Edma264api-400302817No ratings yet
- Lesson FiveDocument4 pagesLesson FiveAlexandra KeresztesNo ratings yet
- W4 Volume, Area and CircumferenceDocument2 pagesW4 Volume, Area and CircumferenceShirlyn Navarro RamirezNo ratings yet
- Teraoka Pe3 Acei 2 3 EvidenceDocument11 pagesTeraoka Pe3 Acei 2 3 Evidenceapi-243091256No ratings yet
- Label The Sides and Fill in The Blanks!Document4 pagesLabel The Sides and Fill in The Blanks!Alexandra KeresztesNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Lesson Plan 16 6 16Document3 pagesMathematics Lesson Plan 16 6 16api-318806007No ratings yet
- Lesson OneDocument4 pagesLesson OneAlexandra KeresztesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document3 pagesLesson Plan 2api-371820420No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3Document4 pagesLesson Plan 3api-341104695No ratings yet
- But Wait, You Can Make It Easier! Multiply!Document4 pagesBut Wait, You Can Make It Easier! Multiply!Alexandra KeresztesNo ratings yet
- Painting With Colour: Kelsey Galbraith and Lacey Macleod Grade 7 ArtDocument20 pagesPainting With Colour: Kelsey Galbraith and Lacey Macleod Grade 7 Artapi-269658717No ratings yet
- Co-Teaching Lesson Plan (Inquiry)Document2 pagesCo-Teaching Lesson Plan (Inquiry)api-211261167No ratings yet
- KenteclothDocument2 pagesKenteclothapi-263381268No ratings yet
- Array Lesson Plan-2Document3 pagesArray Lesson Plan-2api-659399074No ratings yet
- Teaching Practice Task 4 - 0Document3 pagesTeaching Practice Task 4 - 0api-299621535No ratings yet
- Geometry Observation Lesson For Area and PerimeterDocument20 pagesGeometry Observation Lesson For Area and Perimeterapi-234842570No ratings yet
- Second Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesSecond Lesson Planapi-285000116No ratings yet
- Pattern RollDocument3 pagesPattern Rollapi-246531150No ratings yet
- 5 F A8 M Samenumeratorfracsw-Symbols WrefDocument2 pages5 F A8 M Samenumeratorfracsw-Symbols Wrefapi-291492450No ratings yet
- Melissa Miller - Byp Citizen of The YearDocument1 pageMelissa Miller - Byp Citizen of The Yearapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Melissa Miller Resume 3Document2 pagesMelissa Miller Resume 3api-247455001No ratings yet
- Mandalas 3rd - 5th Grade: Teacher Name(s) Grade(s) /content Area Content Area(s) Integrated Unit TitleDocument9 pagesMandalas 3rd - 5th Grade: Teacher Name(s) Grade(s) /content Area Content Area(s) Integrated Unit Titleapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Empathy Concepts MillerDocument3 pagesEmpathy Concepts Millerapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Miller Ux ResearchDocument15 pagesMiller Ux Researchapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Miller Journey Map ExerciseDocument1 pageMiller Journey Map Exerciseapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Miller Letter of Rec-4Document1 pageMiller Letter of Rec-4api-247455001No ratings yet
- Unit 2 3-5 Monsters Unit PlanDocument4 pagesUnit 2 3-5 Monsters Unit Planapi-247455001100% (1)
- Ceramics - Building A CommunityDocument6 pagesCeramics - Building A Communityapi-247455001No ratings yet
- NotanDocument5 pagesNotanapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Safety PostersDocument13 pagesSafety Postersapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Plaster Masks LP MillerDocument15 pagesPlaster Masks LP Millerapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Ed Tpa 2 - Drawing With ValueDocument10 pagesEd Tpa 2 - Drawing With Valueapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Letter of Reccomendation For Ms Miller 1Document1 pageLetter of Reccomendation For Ms Miller 1api-247455001No ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Art 1-ScratchboardDocument2 pagesUnit 7 - Art 1-Scratchboardapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Unit Plan - Art Literature - Greater Communication Through Discriptive Writing - Final Version With Notes-QuestionsDocument10 pagesUnit Plan - Art Literature - Greater Communication Through Discriptive Writing - Final Version With Notes-Questionsapi-247455001No ratings yet
- FLW Math IntegrationDocument3 pagesFLW Math Integrationapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Self PortraitsDocument12 pagesSelf Portraitsapi-247455001No ratings yet
- WildflowersDocument3 pagesWildflowersapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Ed Tpa 1 - Drawing Contour 1Document10 pagesEd Tpa 1 - Drawing Contour 1api-247455001No ratings yet
- From Shape To Form With Wire MillerDocument8 pagesFrom Shape To Form With Wire Millerapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Teachingautobiography Miller 2Document2 pagesTeachingautobiography Miller 2api-247455001No ratings yet
- Worksheet 10c Common FactorsDocument4 pagesWorksheet 10c Common Factorsapi-381868432No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Review Polynomial Worksheets PDFDocument9 pagesUnit 5 Review Polynomial Worksheets PDFMeagan JorgensonNo ratings yet
- Mathlinks9 CH 7 TextbookDocument20 pagesMathlinks9 CH 7 Textbookapi-171445363No ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan: Santiago National High SchoolDocument11 pagesWeekly Learning Plan: Santiago National High SchoolKENNEDY VAGAYNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the SquareDocument2 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations by Completing the SquareHaimen BuisanNo ratings yet
- Math7 Q2 Weeks5to8 Binded Ver1.0Document41 pagesMath7 Q2 Weeks5to8 Binded Ver1.0peachgirlgamersNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1 (Grade 7 - Q3)Document4 pagesSummative Test 1 (Grade 7 - Q3)Aljohn Beltran NerzaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Review-PolynomialsDocument9 pagesUnit 5 Review-Polynomialsapi-237494396No ratings yet
- Algebra Tiles and Distributive PropertyDocument4 pagesAlgebra Tiles and Distributive PropertyHarot KibreNo ratings yet
- U5 - PolynomialsDocument56 pagesU5 - PolynomialsmathclubNo ratings yet
- CL Second Verse Same As The First TeDocument28 pagesCL Second Verse Same As The First Teapi-261894355No ratings yet
- A Lesson Plan in Adding and Subtracting Integers Using Algebra TilesDocument4 pagesA Lesson Plan in Adding and Subtracting Integers Using Algebra TilesLesley NoreenNo ratings yet
- DLL-8 (Week 1, Day 5)Document9 pagesDLL-8 (Week 1, Day 5)MARISSA CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Math 10c I Can StatementsDocument7 pagesMath 10c I Can Statementsapi-302976262No ratings yet
- CL Second Verse Same As The First SeDocument18 pagesCL Second Verse Same As The First Seapi-2618943550% (1)
- Unit Plan Grade 10Document20 pagesUnit Plan Grade 10api-381868432No ratings yet
- Standards-Based Math Goals and Strategies K-6Document12 pagesStandards-Based Math Goals and Strategies K-6Dominic Torralba PaguioNo ratings yet
- MATH9 Chapter7 PDFDocument20 pagesMATH9 Chapter7 PDF700spymaster007No ratings yet
- How To Add and Subtract PolynomialsDocument13 pagesHow To Add and Subtract PolynomialsGeremyJustineBonifacioNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Lesson 25: Special Products Learning GuideDocument7 pagesGrade 7 Math Lesson 25: Special Products Learning GuideKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Lesson3-Factoring General Trinomials Condition 2Document5 pagesLesson3-Factoring General Trinomials Condition 2Shaquille Michael NaguitNo ratings yet
- Training Course 2 Algebra I PDFDocument40 pagesTraining Course 2 Algebra I PDFRichardoBrandonNo ratings yet