Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul Sains Tambahan Bab 1 Ting 4
Uploaded by
Mimah ZakariaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul Sains Tambahan Bab 1 Ting 4
Uploaded by
Mimah ZakariaCopyright:
Available Formats
~ 1 ~
MODUL
SAINS TAMBAHAN
TINGKATAN 4
SET I
1.1 Kuantiti Fizik
1.2 Proses pengukuran
1.3 Tenaga
1.4 Haba
1.5 Elektrik
1.6 Sumber tenaga
~ 2 ~
SET I : BAHAGIAN A
1 Figure shows a vernier calipers used to measure a block of wood.
Rajah menunjukkan angkup vernier yang sedang digunakan untuk mengukur blok
kayu.
(b)
a) i) Name the part labelled X?
Nama kan bahagian berlabel X?
..
[1 mark]
ii) State the function of X ?
Nyatakan fungsi bagi X?
..
[1 mark ]
b) Zero error reading is taken before the vernier calliper is used to measure the
length of wood.
Bacaan ralat sifar ditentukan sebelum angkup vernier digunakan untuk
mengukur ketebalan blok kayu..
i) What does zero error mean?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan ralat sifar?
..
[1 mark]
Block of wood
X
(a)
~ 3 ~
ii) What is the reading of the error in figure above?
Berapakah bacaan ralat sifar yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah di atas?
...
[1 mark]
c) i) Calculate the length of wood?
Kira ketebalan blok kayu?
[2 marks]
ii) The length of wood are measured at several different parts. The readings taken
were 0.90 cm, 0.84 cm, 0.79 cm and 0.91 cm. Calculate the average length of
wood.
Panjang kayu diukur di beberapa bahagian yang berbeza. Bacaan yang
diperolehi adalah 0.90 cm, 0.84 cm, 0.79 cm dan 0.91 cm. Kirakan purata
panjang kayu.
[2 marks]
2. A student measures the thickness of a glass block using measuring instrument K, L
and M. For each instrument, the thickness is measured at three different parts. The
results are shown in the table below.
Seorang pelajar mengukur ketebalan satu blok kaca dengan menggunakan alat
pengukur K, L dan M. Bagi setiap alat pengukur, ketebalan diukur pada tiga
bahagian berbeza. Keputusan yang diperolehi ditunjukkan dalam jadual di bawah.
Measuring
Instrument/
Alat pengukur
Reading (cm)
1 2 3
K 2.0 2.2 2.1
L 2.12 2.13 2.12
M 2.131 2.133 2.121
~ 4 ~
a) Why does the thickness of the glass block is measured three times?
Mengapa ketebalan blok kaca diukur sebanyak tiga kali?
..
[1 mark]
b) Consistency, accuracy and sensitivity of a measuring instrument is
important in measurement.
Ketekalan. Ketepatan dan kepekaan satu alat pengukur adalah penting dalam
pengukuran.
Based on the table shown, state a measuring instrument which is the most
Berdasarkan jadual, nyatakan alat yang manakah memberikan bacaan yang
paling
(i) consistent : ........................................................
persis
(ii) sensitive : ........................................................
peka
[2 marks]
c) Based on the table above which measuring instruments represents
Berdasarkan jadual di atas, alat pengukuran manakah yang mewakili
(i) metre ruler? : ..........................................
pembaris meter?
(ii) micrometer screw gauge? : .............................
tolok skru micrometer?
[2 marks]
d) State the average reading for measuring instrument K.
Nyatakan bacaan purata bagi alat pengukur K.
.
[2 marks]
~ 5 ~
3. The table shows the physical quantities and their units.
Jadual menunjukkan kuantiti fizik dan unit masing-masing.
Physical quantity Relation with base quantities SI unit Name of the unit
volume Length (m) x length (m) x length (m) none
velocity ms
-1
none
force Mass (kg) x acceleration (ms
-2
) N
Electric charge Current (ampere) x time (s) Coulomb
(a) What is meant by physical quantity?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan kuantiti fizik?
..
[1 mark]
(b) Complete the table above.
Lengkapkan jadual di atas.
[2 marks]
(c) State the base quantity and derived quantity used to derive physical quantity
force.
Nyatakan kuantiti asas dan kuantiti terbitan yang digunakan untuk
menerbitkan kuantiti fizik bagi daya
Base quantity :..
Derived quantity : .
[2 marks]
(d) Density is defined as mass per unit volume.What is the unit for density?
Ketumpatan ditakrifkan sebagai jisim per unit isipadu. Apakah unit bagi
ketumpatan?
[1 mark ]
~ 6 ~
4. The SI units and symbols for some base and derived quantities are shown in the table
below.
Unit SI dan simbol beberapa kuantiti asas dan terbitan ditunjukkan dalam jadual
dibawah.
Quantity Symbol SI unit Symbol for the unit.
Length l metre m
mass m
Velocity v Metre per second
Force F Newton N
Temperature K
Based on the table above, answer the following questions.
Berdasarkan jadual di atas, jawab soalan-soalan di bawah.
(a) (i) Classify these quantities into base and derived quantities.
Kelaskan kuantiti tersebut kepada kuanti asas dan kuantiti terbitan.
Base quantity: ..
Derived quantity: .................
[2 marks]
(ii) Complete the table above.
Lengkapkan jadual di atas.
[2 marks]
(b) What is meant by derived quantity?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan kuantiti terbitan?
..
..
[1 mark]
(c) Given that Force = mass x acceleration and Acceleration = velocity/time.
What is the derived unit of force?
Diberi Daya=jisim x pecutan dan Pecutan=halaju/masa.
Apakah unit terbitan bagi daya?
[2 marks]
~ 7 ~
(e) A stone has mass 500 g and volume 20 cm
3
.
Calculate the density of the stone.
Seketul batu mempunyai jisim 500 g dan isipadunya adalah 20 cm
3
.
Hitung ketumpatan batu tersebut .
[2 marks]
5. The electric current (I) passing through a conductor varies as the voltage (V) across
the resistor changes.The diagram below shows a graph of voltage against the electric
current. Based on the graph answer the questions below.
Arus elektrik (I) yang melalui satu konduktor berubah-ubah dengan perubahan beza
keupayaan (V) merentasi satu perintang.Gambar rajah di bawah menunjukkan graf
beza keupayaan melawan arus elektrik. Berdasarkan graf itu jawab soalan di bawah.
5
Y
X
4
0
~ 8 ~
(a) Name axes X and Y.
Namakan paksi-paksi X dan Y.
(i) X: .
(ii) Y: .
[2 marks]
(b) What is the relationship between voltage and current?
Apakah hubungan diantara beza keupayaan (V) dan arus (I)?
[1 mark]
(c) The gradient of this graph is given as R. Calculate R.
Kecerunan graf diberi sebagai R. Hitung R.
[2 marks ]
(d) The SI unit for current is ampere (A) and voltage is Volt (V). What is the SI
unit of R?
Unit SI bagi arus adalah Ampere(A) dan beza keupayaan adalah Volt(V).
Apakah unit SI bagi R?
..
[1 mark]
~ 9 ~
6. Table 1 below shows two sets of reading obtained by two students P and Q when
measuring the diameter of a metal rod.
Jadual 2 di bawah menunjukkan dua set bacaan yang diperolehi oleh pelajar P dan Q
semasa mengukur diameter sebatang rod logam.
Student P (mm) Student Q (mm)
2.76 2.75
2.75 2.74
2.78 2.75
2.74 2.76
2.77 2.75
Table 1 // Jadual 1
(a) What is the type of measuring instrument used by the two students?
Apakah jenis alat pengukuran yang digunakan oleh kedua-dua pelajar
tersebut?
..
[1 mark]
(b) Calculate the average diameter of the metal rod as measured by
Hitung diameter purata bagi rod logam yang diukur oleh
(i) Student P : ..
(ii) Student Q : ....
[2 marks]
(c) The actual diameter of the metal rod is 2.74 mm. Which set of reading shown
in Table 1 is more accurate?
Diameter sebenar bagi rod logam ialah 2.74 mm. Set bacaan yang manakah
dalam Jadual 1 lebih jitu?
..
[1 mark]
(d) Why did the students measure the diameter of the metal rod five times?
Mengapakah pelajar-pelajar itu mengukur diameter rod logam sebanyak lima
kali?
[1 mark]
~ 10 ~
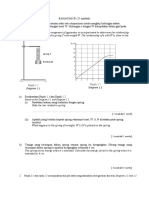
7. The diagram shows a ball of mass 0.5 kg is falling down at the height of 7.0 m.
Rajah menunjukkan sebiji bola yang berjisim 0.5 kg jatuh dari ketinggian 7.0 m.
[Given : g = 10 ms
-2
, P.E = mgh, K.E = mv
2
]
(a) Name two forms of energy that involved when the ball falling down.
Namakan dua bentuk tenaga yang terlibat apabila bola itu jatuh ke bawah.
(i) ..
(ii) .
[2 marks]
(b) State the changes of energy during the ball falling down.
Nyatakan perubahan bentuk tenaga semasa bola itu jatuh.
......
[1 mark]
(c) Name the principle involves in the changes of energy.
Namakan prinsip yang terlibat dalam perubahan tenaga.
......
[1 mark]
(d) By using the principle named in 2(c), calculate the maximum velocity of the
ball.
Dengan menggunakan prinsip di 2 (c), hitung halaju maksimum bola
tersebut.
[2 marks]
Ball
P
7.0 m
~ 11 ~
8. The diagram shows a simple pendulum swings between position W and position Z
repeatedly. The swing started at position W.
Rajah menunjukkan bandul ringkas berayun dari kedudukan W ke kedudukan Z
secara berulang. Ayunan bermula di kedudukan W.
(a) What is meant by potential energy?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan tenaga keupayaan?
.
[1 mark]
(b) State the labeled position where the pendulum bob has,
Nyatakan kedudukan berlabel dimana ladung itu mempunyai ,
(i) zero kinetic energy.
tenaga kinetik sifar.
[1 mark]
(ii) minimum potential energy.
tenaga keupayaan minimum.
.
[1 mark]
(c) The mass of the pendulum bob is 2.1 kg.
Calculate the potential energy of the pendulum bob at W.
Jisim bagi ladung ialah 2.1 kg. Hitung tenaga keupayaan bagi ladung pada
kedudukan W.
[Given, potential energy = mgh and g = 10 m s
-1
]
[2 marks]
X
Y
W
Z
Pendulum
bob
1.5 m
~ 12 ~
(d) Why does the pendulum bob unable to return to its initial position W after one
complete swing?
Mengapakah ladung tidak kembali ke kedudukan asal, W selepas satu
ayunan lengkap?
..
[1mark]
9. The diagram shows a box with mass of 10 kg hanging at 10 m height above the
ground.
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan sebuah kotak berjisim 10 kg berada pada ketinggian 10
m dari permukaan bumi.
(a) Name the energy of the box.
Namakan tenaga yang dipunyai oleh kotak itu.
..
[1 mark]
(b) Calculate the energy named in 2(a).
Hitung tenaga yang dinamakan di 2(a).
[Given / Diberi: PE = mgh; g = 10 m s
-2
]
[2 marks]
Box / Kotak
10 m
Rope / Tali
~ 13 ~
(c) The rope is cut and the box falls on the ground. Explain what happens to the
energy named in 2(a) during the fall of box.
Tali itu dipotong dan kotak itu jatuh ke bumi. Terangkan apa yang berlaku
kepada tenaga di 2(a) semasa kotak itu sedang jatuh ke bawah.
..
..
..
[2 marks]
(d) State one factor that affects the energy named in 2(a).
Nyatakan satu faktor yang mempengaruhi tenaga yang dinamakan di 2(a)
..............................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
~ 14 ~
10. The diagram shows the graph of temperature against time for the solid P. Solid P with
2 kg mass is heated using a 150 W heater. [Given: Q = ml]
Rajah menunjukkan graf suhu melawan masa bagi pepejal P. Pepejal P berjisim 2 kg
dipanaskan dengan pemanas 150 W.
(a) What is the state of P at BC?
Apakah keadaan P pada BC?
.
[ 1 mark]
(b) State the melting point of the solid P
Nyatakan takat lebur bagi pepejal P
..
[1 mark]
(c) (i) Name the process which occurs at BC.
Namakan proses yang berlaku pada BC.
.
[1 mark]
(ii) Explain why the temperature remains constant at BC.
Terangkan mengapa suhu pada BC tidak berubah
..........
......
[2 marks]
Temperature/
0
C
0
A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
20
40
60
80
100
B
C
D
Time/minute
~ 15 ~
Time/ min
(d) Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion for solid P.
Hitung haba pendam pelakuran bagi pepejal P
[2 marks]
(e) Draw a graph of cooling curve in the space below when the liquid P is cooled.
Lukis graf penyejukan dalam ruang di bawah apabila cecair P disejukkan.
[1 mark]
Temperature/
o
C.
~ 16 ~
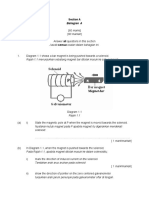
11. Diagram 2.1 shows a liquid-in-glass thermometer.
Rajah 2.1 menunjukkan satu termometer cecair-dalamkaca.
Diagram 2.1
(a) (i) Name liquid S used in the thermometer.
Namakan cecair S yang digunakan dalam termometer .
..............................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
(ii) State the physical change in liquid S when the temperature increases.
Nyatakan perubahan sifat fizikal pada cecair bila suhu bertambah.
..............................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
(b) Diagram 2.2 shows two types of thermometer.
Rajah 2.2 menunjukkan dua jenis termometer.
(i) Which thermometer is more sensitive?
Termometer yang manakah yang lebih peka ?
..............................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
(ii) State one reason for your answer in 2(b) (i).
Nyatakan satu sebab bagi jawapan di 1 (b) (i).
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
Diagram 2.2
Liquid S
~ 17 ~
c) State how to increase the sensitivity of the liquid-in-glass thermometer.
Nyatakan bagaimana kepekaan termometer cecair dalam kaca boleh
ditingkatkan.
.
.
[2 marks]
BAHAGIAN B
1. (a) (i) What is the definition of heat and temperature?
Apakah definisi bagi haba dan suhu ?
(ii) List two differences between heat and temperature.
Senaraikan dua perbezaan antara haba dan suhu.
(iii) Explain when does thermal equilibrium is achieved if a hot water is
mixed with a cool water,
Terangkan bila keseimbangan terma akan dicapai jika air panas
dicampurkan ke dalam air sejuk,
[7 marks]
(b) Describe how a mercury thermometer can measure the temperature of a hot
water by using the principle of expansion of a liquid.
Huraikan bagaimana termometer merkuri dapat mengukur suhu air panas
dengan menggunakan prinsip pengembangan cecair.
[5 marks]
(c) What is the meaning that the specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg
-1o
C
-1
Apakah maksud muatan haba tentu bagi air adalah 4200 J kg
-1o
C
-1
?
[3 marks]
(d) An electric kettle contains 2 kg of water. It takes 5 minutes to heat the water.
The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 Jkg
-1o
C
-1
. Assume all the energy
supplied is used to heat the water. Given : [Q = mc; Q= Pt].
Sebuah cerek elektrik mengandungi 2 kg air. Ia mengambil masa 5 minit untuk
memanaskan air. Muatan haba tentu bagi air 4200 Jkg
-1o
C
-1
. Andaikan semua
tenaga digunakan untuk memanaskan air.
(i) Calculate the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of
water from 30
o
C to 100
o
C.
Hitung jumlah tenaga yang diperlukan untuk menaikkan suhu air dari
30
o
C ke 100
o
C.
~ 18 ~
(ii) Calculate the power of the kettle.
Hitung kuasa bagi cerek elektrik itu. [5 marks]
You might also like
- Bab 2 - Daya Dan Gerakan K1 PDFDocument13 pagesBab 2 - Daya Dan Gerakan K1 PDFHafizasharin Othman0% (1)
- Modul Cemerlang PDFDocument15 pagesModul Cemerlang PDFNahiza Suhimin0% (1)
- Soalan Amali Sains FizikDocument6 pagesSoalan Amali Sains FizikLoi Lai FongNo ratings yet
- A - Penjelmaan K2Document2 pagesA - Penjelmaan K2sofiyyahNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 Pep Awal Tahun SPM Terengganu 2020 - SoalanDocument22 pagesKertas 2 Pep Awal Tahun SPM Terengganu 2020 - SoalansyazaqilahNo ratings yet
- Soalan Pembelauan Bab 06 GelombangDocument2 pagesSoalan Pembelauan Bab 06 GelombangA. SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- F4 Physics Final Exam Paper 2 2013Document30 pagesF4 Physics Final Exam Paper 2 2013MadAm JaJaNo ratings yet
- 1penyelesaian SegitigaDocument6 pages1penyelesaian Segitigarosli87No ratings yet
- Kertas Percubaan Kimia SPM 2013 Kertas 2Document16 pagesKertas Percubaan Kimia SPM 2013 Kertas 2Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- S55 B2Document8 pagesS55 B2Henerita Ray100% (1)
- Math SPM Trial 2018 Kedah P2&Ans PDFDocument53 pagesMath SPM Trial 2018 Kedah P2&Ans PDFLalitha ManiamNo ratings yet
- Set 1 - Kertas 1Document26 pagesSet 1 - Kertas 1fae noorzanNo ratings yet
- 13a1 - (4M) - Graf Jasad Hitam#d21Document4 pages13a1 - (4M) - Graf Jasad Hitam#d21izzat fuatNo ratings yet
- Soalan Trial NegeriDocument26 pagesSoalan Trial NegeriSharuNo ratings yet
- Amali 2 FizikDocument7 pagesAmali 2 Fizikrush9945No ratings yet
- Novel Silir DaksinaDocument6 pagesNovel Silir DaksinaMelody EreenzzNo ratings yet
- Soalan Latihan 5ADocument5 pagesSoalan Latihan 5AGeraldJoelBillih100% (1)
- Kelantan - Add Maths K1K2 Dan Skema K1K2 Trial SPM 2020Document77 pagesKelantan - Add Maths K1K2 Dan Skema K1K2 Trial SPM 2020Faizilanor SutiaraNo ratings yet
- Sintaksis SPMDocument4 pagesSintaksis SPMAnonymous TAncYyH2No ratings yet
- 3.modul Induk t5 JPN Perak EditedDocument138 pages3.modul Induk t5 JPN Perak Editednfaizah1100% (1)
- Set 6 Modul Halus Fizik F5B3 2018Document23 pagesSet 6 Modul Halus Fizik F5B3 2018ctzamrah100% (1)
- LAPORAN AMALI NelsonDocument12 pagesLAPORAN AMALI NelsonNelson BernardNo ratings yet
- Program Gempur T4Document49 pagesProgram Gempur T4Mahfuzah MahyuddinNo ratings yet
- Indeks Dan LogDocument29 pagesIndeks Dan LogSHOBASINI A/P SANGARAM MoeNo ratings yet
- 022 Mel 42 Final Matematik t4 Fasa 2 Dlp-10-18Document9 pages022 Mel 42 Final Matematik t4 Fasa 2 Dlp-10-18mardhiah88No ratings yet
- Instrumen Contoh Soalan AmaliDocument19 pagesInstrumen Contoh Soalan AmaliZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Gelombang Elektromagnet AssgDocument12 pagesGelombang Elektromagnet AssgRoslisalmiahNo ratings yet
- Trial BIO 2 2021 - 220310 - 222853 KedahDocument23 pagesTrial BIO 2 2021 - 220310 - 222853 KedahSHARIFAH BINTI MOHAMAD HADI MoeNo ratings yet
- Soalan FizikDocument16 pagesSoalan FizikFirdaus Ahmad0% (1)
- Ask 2.0Document3 pagesAsk 2.0Sasha TioNo ratings yet
- Fizik 1 Trial SPM SBP 2006Document27 pagesFizik 1 Trial SPM SBP 2006nani98No ratings yet
- 2.2 Graf Gerakan 2020 JawapanDocument10 pages2.2 Graf Gerakan 2020 JawapanMUHAMAD ZANDAR BIN ZAKARIA KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- W5 2020 Penang Addmath (Module 1) K1 SoalanDocument18 pagesW5 2020 Penang Addmath (Module 1) K1 SoalanJacelynNo ratings yet
- Skema Percubaan Biologi k2Document19 pagesSkema Percubaan Biologi k2ABDULLAH ZAWAWI BIN TAIB MoeNo ratings yet
- Skema Soalan Kertas 2 BM Ting.5Document14 pagesSkema Soalan Kertas 2 BM Ting.5Balkis Semera Lot Ulu100% (1)
- Ujian Bab10Document17 pagesUjian Bab10anon_383714618No ratings yet
- Bengkel Misi Mengapai A+ JKD Fizik 2016Document25 pagesBengkel Misi Mengapai A+ JKD Fizik 2016aimarashidNo ratings yet
- Quiz - T4 BAB 6 ANCAMAN KOMUNIS & PERISYTIHARAAN DARURAT (Copy)Document6 pagesQuiz - T4 BAB 6 ANCAMAN KOMUNIS & PERISYTIHARAAN DARURAT (Copy)rodiNo ratings yet
- SPM Trial 2015 Physics Qa PerakDocument83 pagesSPM Trial 2015 Physics Qa PerakJinyuanLowNo ratings yet
- SK 2018 T4Document13 pagesSK 2018 T4Andeli Md Zin0% (1)
- 1 BulatanDocument9 pages1 BulatanlhmooNo ratings yet
- Unit 8Document8 pagesUnit 8AhmadShayuti arNo ratings yet
- 072 MODUL GEMILANG A+ KIMIA TINGKATAN 5 - Skema-1-17Document17 pages072 MODUL GEMILANG A+ KIMIA TINGKATAN 5 - Skema-1-17NUR A'LIAH MAISARAH BINTI ZAINUDDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- 2.6 ImpulsDocument9 pages2.6 ImpulsNorliha JamilNo ratings yet
- Bab 6.4 PembelauanDocument8 pagesBab 6.4 PembelauanNiekey JohnNo ratings yet
- Latihan Resonans Dan PelembapanDocument4 pagesLatihan Resonans Dan PelembapanChewLee TanNo ratings yet
- Jawapan 3 Elektromagnet (Transformer) - PKPDocument12 pagesJawapan 3 Elektromagnet (Transformer) - PKPalizNo ratings yet
- 71 Soalan Untuk Gapai Gred Kualiti Math SPM: Hak MilikDocument18 pages71 Soalan Untuk Gapai Gred Kualiti Math SPM: Hak Milikmuhammad4fadzelyNo ratings yet
- SPM Kimia Skema Kim k3 Set2Document9 pagesSPM Kimia Skema Kim k3 Set2api-3841296No ratings yet
- Kertas Amali Fizik 2021Document5 pagesKertas Amali Fizik 2021YUSFALINA BINTI MOHD YUSOFF Moe100% (1)
- Modul 1 - K1Document26 pagesModul 1 - K1Suhaila Salleh100% (1)
- WkqaDocument46 pagesWkqaunknown :)100% (1)
- Soalan 4-jDocument74 pagesSoalan 4-jZainon KhalidNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 Matematik Pat f4Document11 pagesKertas 2 Matematik Pat f4Yanie HarianiNo ratings yet
- Latihan 2 Fizik F4Document13 pagesLatihan 2 Fizik F4nisaNo ratings yet
- Pat Sains 2019Document5 pagesPat Sains 2019rehansuwarni50% (2)
- Ulangkaji Form 4 k2Document4 pagesUlangkaji Form 4 k2sikhafizNo ratings yet
- Fizik Kertas 2 KBAT 2016Document25 pagesFizik Kertas 2 KBAT 2016Tan Teik SoonNo ratings yet
- BAHAGIAN B-Tov 1Document6 pagesBAHAGIAN B-Tov 1Mohammad Haidil MisiranNo ratings yet
- FoRM 5 2014Document21 pagesFoRM 5 2014Mohd Tarmizi Mohd NorNo ratings yet
- Aturcara Flowery RetroDocument2 pagesAturcara Flowery RetroMimah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Aturcara Majlis Jasamu DisanjungDocument2 pagesAturcara Majlis Jasamu DisanjungMimah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Takwim Panitia Sains 2018Document1 pageTakwim Panitia Sains 2018Mimah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- RPT Kimia f5 2016Document6 pagesRPT Kimia f5 2016Mimah ZakariaNo ratings yet