Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dental Anatomy
Uploaded by
ritchie19952006Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dental Anatomy
Uploaded by
ritchie19952006Copyright:
Available Formats
Dental Anatomy
OBJECTIVES/RATIONALE
It is important to know the anatomy of the tooth to effectively communicate information
with the dentist. The student will utilize dental terminology associated with dental
charting.
TEKS 121.5 (c) 1G, 2A, 3E, 3F, 6A, TAKS ELA 1, 4
Science 2
KEY POINTS
I. Face and Oral Cavity
A. Maxillary and Mandibular arches
B. Anterior Teeth
1. Incisors located at the front of the mouth include the central and lateral
incisors.
2. Cuspids/Canines Sharp points tear food that is too tough for the incisors
have the longest root.
C. Posterior Teeth
1. Premolars/Bicuspids located next to the cuspids/canines
2. Molars located next to the bicuspids the largest teeth in the mouth
II. Identification of Teeth
A. Name and Location
1. Deciduous Teeth
2. Permanent Teeth
B. Letter and Number
1. Universal Method deciduous/permanent teeth are identified by letter and
permanent teeth are identified by number
a. Deciduous teeth begin lettering with the right second molar in the
maxillary arch it is labeled A continue lettering from upper right to
upper left, then lower left to lower right the last molar on the right
mandibular arch is labeled T
b. Permanent Teeth begin numbering with the right third molar in the
maxillary arch it is numbered 1 continue numbering from upper
right to upper left, then lower left to lower right the last molar on the
right mandibular arch is numbered 32
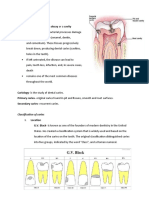
III. Anatomy of the tooth
A. Crown outer surface covered with enamel the enamel is a protective sheet
made of calcium and phosphorus that protects the dentin of the tooth
B. CEJ (Cementum Enamel J unction) junction between enamel and cementum
C. Root
1. covered with cementum
2. lies below the gingival/gums
3. holds the tooth in the bony sockets of the jaw
4. a tooth may have more than one root
a. mandibular molars have two roots
b. maxillary molars have three roots
D. Dentin makes up the bulk of the tooth contains dentinal tubules
E. Cementum hard, thin shell that covers the root
F. Pulp soft tissue inside the hard wall of enamel and dentin has veins,
arteries, and nerve tissue that nourish the tooth and sense pain
G. Apex the very tip of each root
IV. Surrounding Tissues
A. Alveolar processes form the boney sockets that hold and support the teeth in
position
B. Gingiva/gums cover the alveolar bone protect the tooth and deeper tissues
from injury or infection
C. Gingival sulcus the open space between gingival/gums and a tooth
D. Periodontal ligaments / periodontal membranes
1. Small fibers anchored in the cementum and attached to the alveolus
2. Act as a shock absorber for the tooth
V. Dental Terminology
A. Anterior teeth incisors and the cuspids
1. labial surface that touches the lips facial towards the front of the face
2. lingual surface faces toward the tongue
3. incisal edge of the tooth that we bite with
4. distal surface away from midline
5. mesial surface toward the midline
B. Posterior teeth bicuspids and molars
1. Buccal surface that touch the cheeks
2. Lingual surface facing toward the face
3. Occlusal large chewing surface where food is ground
4. Distal surface toward the back of the oral cavity
5. Mesial surface toward the front of the oral cavity
ACTIVITIES
I. Chart existing dental restorations in a partners mouth.
MATERIALS NEEDED
Light source
Mouth mirrors
Dental Chart
Answers Key Terms
Identification of Deciduous Teeth
Identification of Permanent Teeth
ASSESSMENT
Successful charting
ACCOMMODATIONS
For reinforcement, the student will define Key Terms.
For enrichment, the student will review and report on a case study found at
http://www.dent.ohio-state.edu/teaching/CasesSample/Default.htm
REFLECTIONS
Key Terms
Alvelous -
Apex -
Buccal -
Cementum -
Crown -
Cuspal -
Dentin -
Enamel -
Frenum -
Gingivae /Gums -
Nerves -
Periodontal membrane/ligament -
Pulp -
Pulp Chamber -
Root -
Answers - Key Terms
Alvelous - A opening in the jaw-bone in which a tooth is attached.
Apex - The very bottom each root
Buccal - The tooth surface which is next to your cheeks. Usually only posterior teeth
touch your cheeks, so people usually use the term "buccal" only when talking about the
back teeth.
Cementum - A bony substance covering the root of a tooth.
Crown - the visible part of a tooth.
Cuspal - The chewing or tearing points of the cuspids, bicuspids, and molars.
Dentin - The calcium part of a tooth below the enamel containing the pulp chamber and
root canals.
Enamel - A hard ceramic which covers the exposed part of teeth.
Frenum - Small pieces of pink colored skin that attach the lips, cheeks and tongue to the
mouth.
Gingivae /Gums - the soft tissue that surrounds the base of the teeth.
Nerves - nerves transmit signals (conveying messages like hot, cold, or pain) to and from
the brain.
Periodontal membrane/ligament - the fleshy tissue between tooth and the tooth socket;
it holds the tooth in place. The fibers of the periodontal membrane are embedded within
the cementum.
Pulp -The soft inner structure of a tooth, consisting of nerve and blood vessels
Pulp Chamber - The very inner part of your tooth containing nerve cells and blood
vessels.
Root - the anchor of a tooth that extends into the jawbone. The number of roots ranges
from one to three
Parts of the Tooth
Identification of Deciduous Teeth
Maxillary Teeth
2 central incisors in the center next to midline
2 lateral incisors next to the central incisors
2 cuspids just under the ala wing of the nose
There are no Bicuspids in the deciduous dentition
2 primary first molars
2 primary second molars
Mandibular Teeth
2 central incisors in the center next to midline
2 lateral incisors next to the central incisors
2 cuspids just under the ala wing of the nose
There are no Bicuspids in the deciduous dentition
2 primary first molars
2 primary second molars
Identification of Permanent Teeth
Maxillary Teeth
2 central incisors in the center next to the midline
2 lateral incisors next to the central incisors
2 cuspids under the ala next to the lateral incisors
2 first premolars/bicuspids next to the cuspids
2 second premolar/bicuspids next to the first bicuspids
2 first molars next to the second bicuspid
2 second molars next to the first molar
2 third molars or wisdom teeth in the back of the mouth
Mandibular Teeth
2 central incisors in the center next to the midline
2 lateral incisors next to the central incisors
2 cuspids under the corner of the nose next to the lateral incisors
2 first premolars/bicuspids next to the cuspids
2 second premolar/bicuspids next to the first bicuspids
2 first molars next to the second bicuspid
2 second molars next to the first molar
2 third molars or wisdom teeth in the back of the mouth
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Dental CariesDocument6 pagesDental CariesJerryboy69No ratings yet
- VITA en Viktor Fuergut Broschuere Screen enDocument8 pagesVITA en Viktor Fuergut Broschuere Screen enHamidNo ratings yet
- Bleaching Depth of A 35% Hydrogen Peroxide Based in Office Product A Study in Vitro Sulieman Et Al., 2005Document8 pagesBleaching Depth of A 35% Hydrogen Peroxide Based in Office Product A Study in Vitro Sulieman Et Al., 2005EugenioNo ratings yet
- CamouflageDocument81 pagesCamouflageRohini TondaNo ratings yet
- 18 Interrelationship of Orthodontics With Periodontics and Restorative DentistryDocument25 pages18 Interrelationship of Orthodontics With Periodontics and Restorative DentistrySriAduri100% (1)
- Cieszynski' Rule of IsometryDocument5 pagesCieszynski' Rule of Isometrynishant_tewari_1No ratings yet
- An Alternative Technique of Bleaching Vital ToothDocument3 pagesAn Alternative Technique of Bleaching Vital ToothMissyNo ratings yet
- Classification of Malocclusion: Presented By, DR - Dharampal Singh, Dept. of OrthodonticsDocument104 pagesClassification of Malocclusion: Presented By, DR - Dharampal Singh, Dept. of OrthodonticsDharampal SinghNo ratings yet
- Arch Width and Form - A ReviewDocument9 pagesArch Width and Form - A ReviewMafe SalazarNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Dentistr1 Board QuestionsDocument5 pagesPediatric Dentistr1 Board QuestionsMohammed NabeelNo ratings yet
- Discrepancy Index Scoring SystemDocument26 pagesDiscrepancy Index Scoring SystemJohn PulgarinNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Stability of A Class III Malocclusion With Severe Anterior Open Bite and Bilateral Posterior Crossbite in A Hyperdivergent PatientDocument14 pagesLong-Term Stability of A Class III Malocclusion With Severe Anterior Open Bite and Bilateral Posterior Crossbite in A Hyperdivergent PatientErna NaharuddinNo ratings yet
- Dental Implant Therapy in A Patient With Acromegaly: A Clinical ReportDocument6 pagesDental Implant Therapy in A Patient With Acromegaly: A Clinical ReportAkanksha MahajanNo ratings yet
- Occlusion 2Document48 pagesOcclusion 2Dr Hajar Al samomiNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Approach Strategy For The Diagnosis Treatment and Evaluation of ExternalDocument27 pagesA Clinical Approach Strategy For The Diagnosis Treatment and Evaluation of Externaltrain.with.asadhamoodNo ratings yet
- Active and Retentive Components of Ras 1-3-2011 TuesdayDocument15 pagesActive and Retentive Components of Ras 1-3-2011 TuesdayJustin SameulNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Oral Histology and Embryology. James Avery, 2 EditionDocument29 pagesEssentials of Oral Histology and Embryology. James Avery, 2 EditionAde Dian KaruniaNo ratings yet
- ProsthoDocument15 pagesProsthoMaryam IsrarNo ratings yet
- COMPLEX NON SKELETAL PROBLEMS in PREADOLESCENT CHILDREN - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Document14 pagesCOMPLEX NON SKELETAL PROBLEMS in PREADOLESCENT CHILDREN - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Vinnie SinghNo ratings yet
- Leeway Space of NanceDocument11 pagesLeeway Space of NanceGauriNo ratings yet
- Underline and Correct 15 Errors in Subject Verb AgreementDocument2 pagesUnderline and Correct 15 Errors in Subject Verb AgreementkrishnachivukulaNo ratings yet
- ORAL REHABILITATION Clinical Determination of OcclusionDocument177 pagesORAL REHABILITATION Clinical Determination of OcclusionGabriel CabralNo ratings yet
- TWICARE PhotosDocument9 pagesTWICARE PhotosDr. Amir MoradiNo ratings yet
- Interarch Relationships of Teeth Pag. 3-12Document11 pagesInterarch Relationships of Teeth Pag. 3-12Elena SabinaNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Commonly Used Dental Terms: 14212 Ambaum Boulevard Southwest Suite #101, Burien, WA 98166Document10 pagesGlossary of Commonly Used Dental Terms: 14212 Ambaum Boulevard Southwest Suite #101, Burien, WA 98166Mayra RojasNo ratings yet
- Excellence in Loops - Some ReflectionsDocument3 pagesExcellence in Loops - Some ReflectionsKanish Aggarwal100% (2)
- Nikki Atack Postgraduate Notes in Orthodontics University of Bristol 2018Document340 pagesNikki Atack Postgraduate Notes in Orthodontics University of Bristol 2018rare44costanNo ratings yet
- Veneers. Fantasy. Risk. Success SampleDocument59 pagesVeneers. Fantasy. Risk. Success SampleDental Technician ЗУБНЫЕ ТЕХНИКИ100% (1)
- Laporan UniversalDocument113 pagesLaporan UniversalEsty Indah PNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Classification of Dental CariesDocument4 pagesLecture 2-Classification of Dental CariesAli Al-Qudsi100% (3)