Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 14 - Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP
Uploaded by
bingyang0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
412 views5 pagesOperations Management
Original Title
Chapter 14_ Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOperations Management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
412 views5 pagesChapter 14 - Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP
Uploaded by
bingyangOperations Management
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Multiple Choice
This activity contains 17 questions.
The list of quantities of components, ingredients, and materials required to produce a
product is the
engineering change notice.
bill-of-materials.
master schedule.
purchase order.
____________ allows a segment of the master schedule to be designated as "not to
be rescheduled."
Regenerative MRP
Time fence
System nervousness
Pegging
A lot-sizing technique that generates exactly what was required to meet the plan is
economic order quantity.
lot-for-lot.
the Wagner-Whitin algorithm.
part period balancing.
Breaking up the order and running part of it ahead of schedule is known as
operations splitting.
lot splitting.
overlapping.
pegging.
The difference between a gross material requirements plan (gross MRP) and a net
material requirements plan (net MRP) is
the net MRP includes consideration of the inventory on hand, whereas the gross
MRP does not.
the gross MRP includes consideration of the inventory on hand, whereas the net
MRP does not.
the gross MRP doesn't take taxes into account, whereas the net MRP includes the
tax considerations.
the gross MRP may not be computerized, but the net MRP must be computerized.
A phantom bill-of-materials is a bill-of-materials developed for
a module that is a major component of a final product.
a final product for which production is to be discontinued.
the purpose of grouping subassemblies when we wish to issue "kits" for later use.
a subassembly that exists only temporarily.
Which of the following lot-sizing techniques is likely to prove the most complex to
use?
part period balancing (PPB)
the Wagner-Whitin algorithm
economic order quantity (EOQ)
lot-for-lot
When a bill-of-materials is used in order to assign an artificial parent to a bill-of-
materials, it is usually called a
pick list.
planning bill-of-materials.
phantom bill-of-materials.
modular bill-of-materials.
The operations manager has several tools available to deal with MRP system
nervousness. Those tools are
time fences and pegging.
buckets with back flush.
pseudo bills and kits.
net and gross requirements.
An MRP system that provides feedback to the capacity plan, master production
schedule, and production plans is called
load report.
system nervousness.
lot-sizing.
closed-loop MRP.
A time-phased stock-replenishment plan for all levels of a supply chain is called
ERP.
MRP II.
MRP.
DRP.
Which of the following is an advantage of ERP?
requires major changes to the company and its processes
is simple enough that companies have an easy time adjusting to it
creates commonality of databases
is very inexpensive to purchase
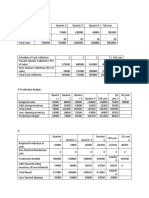
Use the product structure tree and the inventory records to determine how many
item Cs should be ordered in order to produce 20 phones.
Item
On-
Hand
A 5
B 5
C 5
D 25
E 4
F 20
105
120
115
97
Use the product structure tree and the lead time information (in weeks) to determine
when an order for Fs should be placed to deliver phones in week 10 if the phones
require 2 weeks to assemble. Assume there is no starting inventory for any
component or end item.
Item
Lead
Time
A 2
B 1
C 3
D 2
E 3
F 2
week 3
week 2
week 5
week 4
A(n) ________ system provides feedback to the capacity plan, master production
schedule and production plan.
load
closed-loop
Wagner-Whitin
efficient consumer response
Which of these pieces of information isNOTcontained in a bill of material?
raw materials to be used
quantities of components
physical dimensions
lead times
A report that shows the resource requirements in a work center for all currently
assigned work as well as all planned and expected orders is a
MRP II report.
back flush report.
closed-loop report.
load report.
You might also like
- Moodle 2 Word TemplateDocument9 pagesMoodle 2 Word TemplateinamNo ratings yet
- Strategic Service Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandStrategic Service Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- ch09 Numericals (1) - PM MbaDocument52 pagesch09 Numericals (1) - PM MbaDimanshu BakshiNo ratings yet
- Value Chain Management Capability A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandValue Chain Management Capability A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Moodle Teacher ManualDocument34 pagesMoodle Teacher ManualHarryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 - WarehousingDocument37 pagesChapter 09 - WarehousingKashif Niaz MeoNo ratings yet
- Home Work Chapter 1 To 12Document50 pagesHome Work Chapter 1 To 12Haha JohnNgNo ratings yet
- Bozarth ch03Document59 pagesBozarth ch03Judith FajardoNo ratings yet
- Exercise Book Level 3 - Update 2023 FULLDocument62 pagesExercise Book Level 3 - Update 2023 FULLCrazzyguy ForuNo ratings yet
- Become A Supply Chain With Scpro: SuperstarDocument46 pagesBecome A Supply Chain With Scpro: SuperstarVuNo ratings yet
- Lean Accounting, Costs of Quality & Target Costing: Oleh: Suyanto, MBA., Dipl. ResDocument47 pagesLean Accounting, Costs of Quality & Target Costing: Oleh: Suyanto, MBA., Dipl. ResrikiNo ratings yet
- Management and Cost Accounting: Colin DruryDocument14 pagesManagement and Cost Accounting: Colin DruryUmar SulemanNo ratings yet
- Ch08 - InventoryDocument112 pagesCh08 - InventoryAdam Yans JrNo ratings yet
- Ch-05 Material Inventory Controls (Online Class)Document6 pagesCh-05 Material Inventory Controls (Online Class)shayan zamanNo ratings yet
- P&G Case Study - Full PDFDocument10 pagesP&G Case Study - Full PDFeeit_nizamNo ratings yet
- Chapter06 - Internal Analysis PDFDocument21 pagesChapter06 - Internal Analysis PDFRovi Rohhimatul Chasanah100% (1)
- I. Aligning The Resources With The Strategic Plan (37%)Document17 pagesI. Aligning The Resources With The Strategic Plan (37%)Javed ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Ch01-Casesstudy For UMADocument3 pagesCh01-Casesstudy For UMAjklbnm12345100% (1)
- CPIM Part 1 Section D PDFDocument2 pagesCPIM Part 1 Section D PDFSaurabhNo ratings yet
- 01 BSCM PPT v3.0 VCDocument32 pages01 BSCM PPT v3.0 VCpkj009No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: The Master Schedule Discussion Questions and ProblemsDocument3 pagesChapter 4: The Master Schedule Discussion Questions and ProblemsAmeen Mohamed AlameenNo ratings yet
- Supply-ChainDocument61 pagesSupply-ChainJackson TeohNo ratings yet
- TB1000 FileOverviewDocument3 pagesTB1000 FileOverviewWilbert AcostaNo ratings yet
- DMAIC Process Used For Academic Case Analysis: Article SubmissionDocument14 pagesDMAIC Process Used For Academic Case Analysis: Article SubmissionAnand ViharNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - The Project in The Organization StructureDocument7 pagesModule 5 - The Project in The Organization StructureJeng AndradeNo ratings yet
- 3PL WMS IntegrationORACLE01Document33 pages3PL WMS IntegrationORACLE01Jorge DeaThrider VazquezNo ratings yet
- Supply Chains A Managers GuideDocument193 pagesSupply Chains A Managers GuideLoredana Mihaela BobeicaNo ratings yet
- APICS BSCM Sample TestDocument21 pagesAPICS BSCM Sample TestAhmedBYNo ratings yet
- m5zn - Chapter 12Document22 pagesm5zn - Chapter 12Виталий БогачевNo ratings yet
- Research On Warehouse Management System Based On Association RulesDocument5 pagesResearch On Warehouse Management System Based On Association RulesSubhan Riyandi100% (1)
- Using APQC Metrics - Claude Lanouette - CBPADocument4 pagesUsing APQC Metrics - Claude Lanouette - CBPAgong688665No ratings yet
- KEI APICS CPIM Information Booklet 2010.01Document30 pagesKEI APICS CPIM Information Booklet 2010.01mkasi2k9No ratings yet
- Course Outline - ToM - Dr. Rameez KhalidDocument1 pageCourse Outline - ToM - Dr. Rameez KhalidAbid ButtNo ratings yet
- Sales Budget AssignmentDocument2 pagesSales Budget Assignmentsardar hussainNo ratings yet
- Chap 2-Product Process and ScheduleDocument67 pagesChap 2-Product Process and Schedulemuath wardatNo ratings yet
- 04 BSCM v4.1Document57 pages04 BSCM v4.1Baher LotfyNo ratings yet
- Notes - SCMDocument96 pagesNotes - SCMDavid BusinelliNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem 1 - Max's Slice Problem - Week 4 Practice Problems - CTLDocument5 pagesPractice Problem 1 - Max's Slice Problem - Week 4 Practice Problems - CTLSrinivasa RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Products and ProcessesDocument7 pagesChapter 14 Products and ProcessesKamble AbhijitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Materials Management BookDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Materials Management Bookka5227No ratings yet
- CH 12Document12 pagesCH 12Renz AlconeraNo ratings yet
- CH 18 MRPDocument37 pagesCH 18 MRPEric F. IrawanNo ratings yet
- School of EngineeringDocument11 pagesSchool of EngineeringJoyce ChoyNo ratings yet
- A Study On Manufacturing Resources Planning of Tamilnadu Cement Corportation Limited at AriyalurDocument25 pagesA Study On Manufacturing Resources Planning of Tamilnadu Cement Corportation Limited at Ariyalurk eswariNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Computer Aided Production Production Planning and Planning and Control Control (Lecture #11) (Lecture #11)Document43 pagesComputer Aided Computer Aided Production Production Planning and Planning and Control Control (Lecture #11) (Lecture #11)Sreedhar PugalendhiNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - Pull vs. Push System: StructureDocument69 pagesUnit 9 - Pull vs. Push System: StructuresreerajNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Resource PlanningDocument8 pagesAggregate Resource PlanningAbhishek ThakurNo ratings yet
- What Is Needed? How Much Is Needed? When Is It Needed?Document3 pagesWhat Is Needed? How Much Is Needed? When Is It Needed?DeviNo ratings yet
- CH 5 MRPDocument20 pagesCH 5 MRPahsanzia62No ratings yet
- OM Unit 4Document87 pagesOM Unit 4Aswiny SNo ratings yet
- Materials Requirement PlanningDocument12 pagesMaterials Requirement PlanningJoju JohnyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document42 pagesChapter 06razi haiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Material Requirements PlanningDocument3 pagesChapter 13 - Material Requirements Planninghello_khayNo ratings yet
- What Is MRPDocument15 pagesWhat Is MRPParag Narkhede100% (1)
- 4 International DAAAM Conference: MRP Systems ResearchDocument4 pages4 International DAAAM Conference: MRP Systems Researchsanam20191No ratings yet
- Lean Operations: MRP vs. JitDocument32 pagesLean Operations: MRP vs. JitSamantha SiauNo ratings yet
- Materials Requirements PlanningDocument20 pagesMaterials Requirements PlanningMohamad FakihNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument4 pagesSupply Chain ManagementEmelieKatharineNo ratings yet
- Resumen de La Academia de PPDocument63 pagesResumen de La Academia de PPÁlvarez JavierNo ratings yet
- Topic 9-MRP+ERPDocument4 pagesTopic 9-MRP+ERPbingyangNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Revision QuestionsDocument3 pagesMacroeconomics Revision Questionsbingyang0% (1)
- DHL Global Forwarding HR AnalystDocument2 pagesDHL Global Forwarding HR AnalystbingyangNo ratings yet
- Samp MidDocument8 pagesSamp MidbingyangNo ratings yet
- BUS007 2014 U3 Student - Oral PresentationsDocument25 pagesBUS007 2014 U3 Student - Oral PresentationsbingyangNo ratings yet
- OM Study Guide Lessons 1-12Document122 pagesOM Study Guide Lessons 1-12bingyang75% (4)
- Things To Take Note of Before PresentationDocument6 pagesThings To Take Note of Before PresentationbingyangNo ratings yet
- B 1Document1 pageB 1bingyangNo ratings yet
- DMSAF BUS101 End of Course Assessment Group Jan 2014Document5 pagesDMSAF BUS101 End of Course Assessment Group Jan 2014bingyangNo ratings yet
- CompTIA - Testinside.sy0 201.v3.29.by - DavidDocument224 pagesCompTIA - Testinside.sy0 201.v3.29.by - DavidbingyangNo ratings yet
- LPIC Preguntas IDocument15 pagesLPIC Preguntas ILluniNo ratings yet
- CSCE 515:: TCP Client/Server ExampleDocument5 pagesCSCE 515:: TCP Client/Server Examplebingyang100% (1)
- Popular CultureDocument6 pagesPopular CultureAmritaNo ratings yet
- Scuba Diving - Technical Terms MK IDocument107 pagesScuba Diving - Technical Terms MK IJoachim MikkelsenNo ratings yet
- Mwangi, Thyne, Rao - 2013 - Extensive Experimental Wettability Study in Sandstone and Carbonate-Oil-Brine Systems Part 1 - Screening ToDocument7 pagesMwangi, Thyne, Rao - 2013 - Extensive Experimental Wettability Study in Sandstone and Carbonate-Oil-Brine Systems Part 1 - Screening ToMateo AponteNo ratings yet
- Sindarin-English Dictionary - 2nd EditionDocument192 pagesSindarin-English Dictionary - 2nd EditionNea Tan100% (1)
- En LF Drivers 10nw76 8Document3 pagesEn LF Drivers 10nw76 8ChrisNo ratings yet
- Sermo 13 de Tempore (2 Feb in Praes)Document1 pageSermo 13 de Tempore (2 Feb in Praes)GeorgesEdouardNo ratings yet
- 1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016Document3 pages1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016api-292307509No ratings yet
- BTL Info CNC ProgrammDocument132 pagesBTL Info CNC ProgrammdieulafaitNo ratings yet
- PECI 405 ECPP 7th Sem CivilDocument96 pagesPECI 405 ECPP 7th Sem CivilYasaswi AkkirajuNo ratings yet
- EXP1POSTLABDocument13 pagesEXP1POSTLABGiane MagimotNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 With Solution MathematicsDocument17 pagesPaper 2 With Solution MathematicsFaiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Adminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDocument3 pagesAdminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDenise CastroNo ratings yet
- Jib Crane Assembly ManualDocument76 pagesJib Crane Assembly ManualRobert Cumpa100% (1)
- EB-300 310 Service ManualDocument32 pagesEB-300 310 Service ManualVictor ArizagaNo ratings yet
- 132kV Substation Feasibility StudyDocument16 pages132kV Substation Feasibility StudyTafadzwa MurwiraNo ratings yet
- K&J Magnetics - Demagnetization CurvesDocument4 pagesK&J Magnetics - Demagnetization CurvessubbannachrsNo ratings yet
- NDTDocument2 pagesNDTRoop Sathya kumarNo ratings yet
- +chapter 6 Binomial CoefficientsDocument34 pages+chapter 6 Binomial CoefficientsArash RastiNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Current Transformer Accuracy Limit FactorDocument14 pagesCalculation of The Current Transformer Accuracy Limit FactorWeiKiat Goh67% (3)
- Deld12070 CC18 GT 371 C CDocument1 pageDeld12070 CC18 GT 371 C CDEBASIS BARMANNo ratings yet
- Vintage Tavern - PrintInspectionDocument4 pagesVintage Tavern - PrintInspectionBryce AirgoodNo ratings yet
- Lec 8-10Document5 pagesLec 8-10osamamahmood333No ratings yet
- 1 Name of Work:-Improvement of Epum Road (Northern Side) Connecting With Imphal-Saikul Road I/c Pucca DrainDocument1 page1 Name of Work:-Improvement of Epum Road (Northern Side) Connecting With Imphal-Saikul Road I/c Pucca DrainHemam PrasantaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Acetylation Method On Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Based Sago "Hampas"Document18 pagesEffect of Acetylation Method On Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Based Sago "Hampas"myrraNo ratings yet
- Art and Geography: Patterns in The HimalayaDocument30 pagesArt and Geography: Patterns in The HimalayaBen WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Leaflet CycleManager Ep CycleManager ErDocument7 pagesLeaflet CycleManager Ep CycleManager ErValeska ArdilesNo ratings yet
- Food - Forage - Potential - and - Carrying - Capacity - Rusa Kemampo - MedKonDocument9 pagesFood - Forage - Potential - and - Carrying - Capacity - Rusa Kemampo - MedKonRotten AnarchistNo ratings yet
- Fantasy AGE - Spell SheetDocument2 pagesFantasy AGE - Spell SheetpacalypseNo ratings yet
- Feature Writing EnglishDocument2 pagesFeature Writing EnglishAldren BababooeyNo ratings yet
- Smart Watch User Manual: Please Read The Manual Before UseDocument9 pagesSmart Watch User Manual: Please Read The Manual Before Useeliaszarmi100% (3)