Office Risk Assessment Sample
Uploaded by
GanchocuteOffice Risk Assessment Sample
Uploaded by
Ganchocute- Office Risk Assessment
Common questions
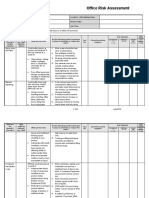
Powered by AIRegular assessments and feedback facilitate the identification and mitigation of new or existing workplace hazards. This ongoing process allows organizations to update safety measures in response to accidents or changes in the work environment. Engaging staff in discussions about these assessments encourages proactive risk management and reinforces a culture of safety and health .
To ensure worker health in an office environment, management should help staff understand their duties and responsibilities clearly. There should be provisions for staff to speak confidentially to a supervisor or manager if they feel unwell or uneasy about workplace issues. Additionally, effective management and communication of change can also support worker health and improve their sense of job control .
Conducting a fire risk assessment is crucial to prevent fatal injuries from smoke inhalation or burns in the event of a fire. Important measures include establishing and regularly testing evacuation plans, ensuring fire alarms function properly, conducting annual fire drills, and checking to ensure escape routes and fire exit doors are unobstructed. These precautions ensure that employees can evacuate safely during emergencies .
To ensure safety, good housekeeping must be practiced to keep fire escape areas free of obstructions. Regular maintenance checks of building lifts should be conducted to ensure their safe operation. These practices ensure exits remain accessible during emergencies and reduce the risk of injury to employees .
The risks faced by staff using work equipment include electrical shocks or burns from faulty electrical equipment and injury from moving parts of improperly balanced equipment. Mitigation strategies include checking all new equipment before use, training staff in equipment use, encouraging staff to report defective plugs or cables, and promptly taking defective equipment out of service. These actions significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents involving work equipment .
Measures to ensure lone worker safety include requiring staff to leave details of their visits and contact numbers at the office, checking in after visiting clients if not returning to the office, and having those responsible for closing the office at night check all areas before leaving. These procedures ensure that lone workers remain in contact and their whereabouts are known during their working hours .
To minimize the risk of slips and trips in an office environment, general good housekeeping should be carried out. All areas, including stairs, need to be well-lit. Trailing leads or cables should be moved or properly protected. Staff must keep work areas clear, ensuring that no boxes are left in walkways and that deliveries are stored immediately. Additionally, staff should mop up or report spillages promptly .
To manage risks associated with computer and workstation use, workstations should be assessed and adjusted to reduce risks of posture problems, pain, and injuries. Staff should receive proper training and information on ergonomic practices. Regular breaks and planned activity changes are necessary to prevent overuse. Employers should also cover the cost of eye tests for display screen equipment users and provide basic spectacles specific for visual display unit use if required .
To mitigate health risks from cleaning chemicals, offices can replace products marked as 'irritant' with milder alternatives. Providing staff with mops, brushes, and protective gloves, and instructing them on safe usage of cleaning products will also help. Adequate storage of cleaning materials further reduces the potential for hazardous exposure .
In an office setting, managers should ensure that vulnerable workers have access to safe escape routes and consider any pre-existing conditions that may be exacerbated by office activities. Work processes may need to be adapted for expectant mothers, and awareness should be raised among all staff regarding the unique needs or potential inexperience of younger colleagues. Additionally, an agreed action plan should be developed with the input of vulnerable workers to address any specific needs they may have .