Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A+ Cert Chapter 1 Misc
Uploaded by
123456Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A+ Cert Chapter 1 Misc
Uploaded by
123456Copyright:
Available Formats
A+ Cert Chapter 1 Misc
Study online at quizlet.com/_st8cf
1.
Parallel: Data travels parallel in different paths.
2.
SCSI: SCSI (Small Computer Systems Interface)
SCSI or "scuzzy" stands for Small Computer Systems Interface. It is a method of connecting storage devices to computers. At the time the
name was created, most of the computers were small. SCSI adapters allow for daisy chaining, creating a chain up to at most 16 devices.
What makes SCSI so powerful is that not only is it easy to plug in, but the interface and the communication itself is very intelligent. This
allows for a lot of communication over the SCSI bus. To end a chain of SCSI devices, the last device has to be a "Terminator". The
Terminator sits as the last device on the chain and tells SCSI communication where the signal ends. Without it, data would gather and
become static. Most new SCSI interfaces have terminators built into the device itself.
3.
AGP 2x,4x, 8x: Accelerated Graphics Port-Graphical processor for computers. Was created to increase bandwidth for gaming and high
intensity programs. The AGP had its own dedicated slot in most computers. Was replaced when PCLe was changed to the standard
expansion slot which provided better speeds. AGP 1.0 (3.3v) gave x1 speeds of 266Mb/s and x2 speeds of 266Mb/s. AGP 2.0 (1.5v) gave x1
speeds of 1.07Gb/s. AGP 3.0 (0.8v) gave x8 speeds of 2.1Gb/s.
4.
AM2: The Socket AM2 was released in 2006. Like the Socket 940, it features 940 pins and a pin grid array. Unlike the Socket 940, it only
5.
AM2+: The Socket AM2+ was released in 2007. It has 940 pins and is a pin grid array. The AM2+ boasts faster communication and better
supports the use of DDR2 memory. It is not backwards compatible with the Socket 940.
power management. The Socket AM2+ is backwards compatible with the Socket AM2. Likewise, there are AM2 processors that can fit onto
an AM2+ motherboard. Interchanging the processors and motherboards generally requires a BIOS upgrade.
6.
AM3: AMD socket AM3 is a PGA ZIF socket that has 941 pins. AM3 replaced its predecessors, AM2 and AM2+ in 2009. AM3 supported
7.
AM3+: Socket AM3+, used with AMD processors, is the next socket type, following AM3. It has 942 pins arranged in a PGA-ZIF package.
DDR3 RAM for faster more reliable speeds.
AM3+ has 1 more pin than AM3, which has 941 pins. The socket is backwards compatible, meaning that users could upgrade their
motherboard to AM3+, but still be able to use their AM3 processor.
8.
AMD: (Advanced Micro Devices) AMDs processors fit certain types of CPU sockets, with the most modern ones being the AMD 3 and AMD
3+ socket. The AMD Socket 940 is a 940 pin Pin Grid Array type socket. (so it was mainly designed for 64 bit server computers), and has
support for DDR RAM
9.
AMD 940: The AMD Socket 940 is a 940-pin Pin Grid Array type socket which is Zero Insertion Force (that means that the pins for the
socket are on the CPU and not the socket, and the CPU requires zero force to be inserted into the socket, it just locks in). This socket is
developed by AMD and released in 2003. This socket was used for the AMD Opteron and the AMD Athlon 64 FX (so it was mainly designed
for 64 bit server computers), and has support for DDR RAM
10.
ATX: Intel created this motherboard in 1995, and it has since became popular and standardized. Several updates have been made, including
the change from a 20 pin power connector to a 24 pin power connector. This motherboard is relatively large, so it is mainly used in
desktops. Because of its size, the ATX has spaces to upgrade.
11.
BIOS: Basic Input Output System, BIOS is software stored on a motherboard chip that preforms functions such as keyboard commands and
starting the computer. Helps cpu interact with devises and helps with start up.
12.
Blue-Ray: A more advanced and modern optical format than the commonly used CD or DVD. Blu-ray disks allow for much larger storage,
where each side can hold 25GB of data. This optical format can be used to start up your computer and install an operating system.
13.
BNC: Bayonet Neill-Concelman- this is used for high end video mostly comercial use. It is sent thought RGB and then Vertical and
Horizontal sync.
14.
CD-ROM, CD-RW: -Compact disk read only memory (700mg)
- Compact disk rewritable (4.7gb, 8.5gb double layer)
15.
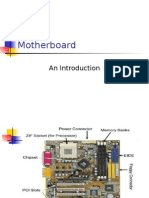
Chipset: The chipset is found on the motherboard. This handles the flow of information from things such as the CPU and memory. The
northbridge handles memory between the CPU and memory cards, while the southbridge connects to other things such as USB or ethernet.
16.
Clock Speed: How much data is passing through each second or each turn of the cycle. The expansion bus has its own clock, so it does not
need to run at the same speed as the rest of the CPU
17.
CMOS: Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor is a on board chip that is powered by its own battery. System time and date is kept by
the CMOS. The battery also keeps the BIOS powered.
The CMOS chip keeps inventory of the all the hardware and the BIOS gathers inventory info from the CMOS. It also keeps the system time.
18.
CNR: Comunications and Networking Riser- pacifically for modems and network connections. They were used so that a full PCI slot didn't
have to be taken up. The CNR has been phased out in recent years because now those functionalities are embedded within the motherboard
itself.
19.
Compact Flash: Compact flash
o SD
o Micro-SD
o Mini-SD
o xD
o SSD
20.
CPU: A central processing unit (CPU) is the hardware within a computer that carries out the instructions of a computer program by
21.
Crimper: Attaches connectors to cables.
22.
CRT: Cathode Ray Tube- XGA/1024x768, SXGA/1280x1024, UXGA/1600x1200
23.
DDR: Double Data Rate (DDR)
performing the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system.
This uses an electron gun to make images.
A very common RAM that has been upgraded throughout the years. It first started out as DDRAM, the name was given because it was
double the speed of SDRAM. Multiplying the Memory Bus Clock Rate by 16 will you give you the maximum amount of bytes you can transfer.
So a bus clock rate of 100Mhz will give you 1600Mb/s peak data rate
24.
DDR2: Double Data Rate 2 (DDR2) SDRAM
DDR2 was the next generation of DDR memory. It featured an enhanced electrical interface, buffers, and off-chip drivers. It is twice as fast
as DDR memory. The peak data rate is 3200 MB/s.
25.
DDR3: Double Data Rate 3 (DDR3) SDRAM
DDR3 is the latest generation of DDR memory. It has twice the data rate of DDR2 and it has larger chip capacities. It's peak data rate is
6400 MB/s.
26.
Digital Projecters: Lots of light so it gets very hot and the fan needs to cool downs properly.
27.
DIMM: Dual inline memory module
This is the most modern type of memory module . The "dual" means that there are copper contacts on both the front and back of the module
are separate. Also, the 64 bit data width, as opposed to 16 or 32 bits, allowed for more data to be transmitted in each clock cycle than before
28.
Display Port: VESA standard which is a royalty free channel. The data is sent in packets like ethernet and PCIe it is also compatible with
HDMI and DVI
29.
DVD-ROM, DVD-RW: -Digital video disk read only memory
-Digital video disk rewritable
30.
DVI: Digital Visual Interface.
Single Link- 3.7 Gbps (HDTV at 60fps)
Dual Link- 7.4 Gbps ( HDTV at 85fps)
DVI-A= analog
DVI-D= digital
DVI-I= both
31.
Dynamic RAM: Most common used random access memory. Data is moved to the RAM from the hard drive, then it is used by the CPU.
32.
ECC: Error Correcting Code
This type of memory, used in important contexts (such as a website server), constantly checks and corrects itself. ECC memory appears the
same as non-ECC memory on the outside.
33.
eSATA: A standard of SATA developed to plug external storage devices into your computer. SATA and eSATA cables are not
34.
Ethernet: IEEE 802.3 or Ethernet is a LAN cable that works with networking.
35.
F: A LGA type socket, featuring 1,207 pins. This socket fit in the same generation as the AMD 2 socket. This socket was designed for servers
36.
Firewire: "Firewire", otherwise know as IEEE 1394 is an external storage device connector. You can use IEEE 1394 to connect up to 63
interchangeable, however: you can't use the same cable both inside and outside of the computer.
as it had a faster Front Side Bus (FSB), and DDR2 memory.
different devices, through daisy-chaining, tree topology or a P2P network. The first version of IEEE 1394 was Alpha Mode. It ran at 100,
200/400 Mbit/s. The second version was IEEE 1394 Beta Mode. Its speeds were 800 Mbit/s.
37.
FMI: This is a 905 pin socket that was introduced in 2011. This type of socket allowed for processors with higher performance and use of
DDR3 memory. It also allowed for the movement of the PCI express controller onto the CPU itself.
38.
HDMI: High Definition Multimedia Interface- Video and audio stream all digital
39.
Hemostat clamps: Replaces tweezers for inserting and removing jumper blocks and cables
40.
Hex driver: hexagon shaped screwdriver mostly used on cases and motherboards
41.
Hot swappable drives: This devices do not require the computer to be powered off and back on to be switched out.
42.
IDE: Integrated Drive Electronics created by western digital. It became the standard for PATA (standard connection for hard drives)
43.
ITX: Created in 2012, ITX is smaller in size than it's "bigger brother" ATX. ITX form is used in smaller sized desktop computers. ITX boards
have limited expansions slots and memory slots, but they are relatively similar to ATX in terms of power and onboard features. ITX has
different types of board layouts, each getting gradually smaller in size. They are Mini-ITX, Nano-ITX, Pico-ITX and Micro-ITX.
44.
LCD: Liquid Crystal Display- A back light is always on and it can depolarize a light to make a color.
45.
LED: The backlight uses and LED to backlight it. They are ether on the edges or in an array on the back. It has more contrast
46.
LGA 775: The Intel LGA 775, or Socket T, is a CPU socket used around 2004. As an LGA socket, it has pins on the motherboard instead of
the CPU. It had 775 pins as the name implies, and was used in some of the later Pentium 4 and Intel Core 2 Duos, as well as some Xeon and
some Celeron chips. Socket T stands for Tejas core, a chip that was eventually canceled by Intel, but is a name still used to refer to this
socket.
47.
LGA 1155: Land Grid Array Socket for CPU, replacement for 1156 but not compatible with 1156 CPUs. Released in 2011 for intel Sandy
48.
LGA 1156: The Intel LGA 1156, or Socket H1, was a replacement for the LGA 775 like the LGA 1366. Similar to both, the LGA 1156 had the
Bridge and Ivy Bridge microCPUs.
pins on the motherboard instead of the CPU, and has 1,156 pins as the name implies. Released in 2009, this socket allowed for the
Northbridge to be integrated into the CPU for faster response times, as well as better efficiency when accessing memory.
49.
LGA 1366: Similar to the Intel LGA 775, the LGA 1366 is a Land Grid Array socket with the pins on the board instead of the CPU, and had
1,366 pins as the name implies. This socket was also referred to as the Socket B, and was used around 2008. One of the first Intel Core i7s
used the LGA 1366 as its motherboard interface.
50.
Loopback Plug: Checks for correct input/output from USB, serial, parallel and network cables.
51.
Lumens: 3,000 lumen work in dim room
52.
Micro-ATX: Smaller than the standard ATX with less expansion slots
53.
Micro-SD: ...
54.
mini PCI: Created primarily for mobile use at is is much smaller but still using the same standard of the PCI format. It can be used in
6,000 lumen work in mid light room
laptops to include features like WiFi, mobile broadband, and many more functions. The downfall to these adapters cards is that they are
inserted into the laptop and are hard to access after installed.
55.
Mini-SD: ...
56.
MiniDin-6: Low res and sent over two channels no audio
57.
Native Resolution: LCD displays have a set number of pixels
58.
Northbridge: Also known as "memory controller hub" Connects the CPU to memory and high-speed graphics card
59.
OLEM: Fast response time, Made from organic compounds, Wider viewing angle, Power efficient, Low cost
60.
Optical Format: It is a common type of storage media on devices. Things like CDs, DVDs, and Blu-rays discs all use these small bumps
on the disk that are then read by small lasers beams. The lasers read the bumps and know what type of data is encoded on the device.
61.
Parity Memory: A type of memory that checks itself. Its memory that has another parity bit on the module which constantly checks out the
communication in and out of that one memory module. If something gets through that it doesn't recognize then it will flag a message and
stop all communications so the error doesn't expand itself to the rest of the system.
62.
PATA cable: Big ribben cable that sends in parallel
63.
PCI: This is an expansion slot that allows additional cards. For example a video card can be connected to a PCI slot.
64.
PCI-X: An updated version of the PCI, stands for PCI-eXtended. Was designed for servers that needed more bandwidth. It offers four times
65.
PCIe: The PCI Express, or PCIe (Not to be confused for PCI-X) is a new PCI standard which is used on most modern PCs. Instead of using
the clock speed in order to handle higher network and storage. This is not to be confused with PCI-e(PCI-express).
the standard 32-bit or 64-bt busses, the PCIe uses a unidirectional serial system Each port has it's own full-duplex lane, which allows a
PCIe card to send data back and fourth between it and the North Bridge. PCIe cards come in x1, x2, x4, x16, and x32 lanes ("x" means by in
this case, so "x32" reads as "by 32"). So far, there are four known versions, each improving the throughput of the last. There is PCIe v1.x,
which is 250 MB/s throughput, PCIe v2.x, which is 500 MB/s, PCIe v3.0, which is fairly new and uncommon and transfers at 1 GB/s, and
PCIe v4.0, which is still to be released transfers at 2 GB/s throughput.
66.
Penlight: Illuminates dark cases
67.
Philips and Straight-Blade Screwdriver: Philips is the plus shaped screwdriver and Straight-Blade is the minus shaped screw driver.
68.
Plasma Display: This has tinny cells holding a noble gas and mercury and it hits a phosphor which creates and image. This allows for
very deep black and high response times. But it uses a lot of plasma and radio interference.
69.
Punch Down Tool: Used for installing UTP (ethernet) cables into a wall jack.
70.
RAID: -Redundant Array of Independent (sometimes "inexpensive") Disks
-Not all RAID has redundancy
-Can be software (lower performance)/hardware
RAID 0 - Striping (improves performance through parallelism of read and write operations)
RAID 1- Mirroring (comprises mirroring (without parity or striping). Data is written identically to two (or more) drives,)
RAID 5 - Striping with Parity (comprises block-level striping with distributed parity)
RAID 10 (RAID 1+0/ Nested RAID) - Stripe of Mirrors
71.
RAMBUS: Rambus Inc. , partnered with intel, created the RDRAM which was a much faster memory. Not all systems used this memory
because of how expensive it was, so new types of memory were created after this.
72.
RCA: Used for audio and video, It is commonly used for composite video( yellow cable) . It can also send Component video (rgb colored
cables)
73.
Refresh Rate: Measured in Hz. How fast it can fill the screen in a second. When it drops below 72Hz you can see flickering in CRTs but it
can be fine if you have 60Hz on a LCD.
74.
RJ: RJ 45- This is the same standard as ethernet can it is a lot more modern then RJ11.
RJ 11- This is used for phone line connections and it is smaller than the RJ 45.
75.
SATA: (Serial ATA) A computer bus that connects components on a motherboard. Uses two individual connections between points, one in
each direction for communication with each direction traveling at its own speed. Replaced PATA
76.
SATA cable: Cirial connection that is a lot smaller
77.
SD: (Secure Digital) It is a type of memory card used for storing data in devices. The card is one of the smaller memory card formats. To give
the cards some orientation, the top-rght corner of each SD card is slanted. Even though the cards are extremely small, as of late 2004, they
can hold up to 8GB of data
78.
SDRAM: Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory, is a kind of DRAM that is synchronized with the system clock. This kind of
memory isn't commonly found on modern systems, where you'll more commonly see DDR type memory. SDRAM is labeled with the same
speed as the memory clock bus. For example, if the clock runs at 133MHz, then the SDRAM would be marked PC133.
79.
Serial: Data travels one after another.
80.
SO-DIMM: This is the Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module that was made for use in mobile devices like laptops. The point of this
version of ram was to make the original desktop ram package smaller to fit into a mobile device. They are 68mm x 32mm and come in 72
pin, 100 pin, 144 pin, 200 pin, and 204 pin variations. There are also variations to accommodate to a motherboards needs, so different
types of modules are made for DDR, DDR2, and DDR3.
81.
Southbridge: Manages connections (I/O Controller Hub - USB, ATA, SATA, Ethernet) and it is slower than the Northbridg.
82.
SSD: The Solid State Drive is the counter-part to the Hard Drive, unlike the Hard Drive the Solid State Drive (or SSD) has no moving parts
and is entirely memory. This makes the SSD much faster then it's counter-part Hard Drive, although it is currently much more expensive
than the Hard Drive so it is not feasible for mass consumers currently.
83.
Toner Probes: Used to determine the patch panel port that matches a particular network wall socket.
84.
Torx driver: star-shaped screwdriver which is used on compact models.
85.
USB: Universal Serial Bus, has been around since 1997, and has many different connectors. These include USB Type-A, Type-B, Micro-B,
and Mini-B. Micro-B.
USB 1.1-1.5 to 10 megabits
USB 2.0- 480 megabits
USB 3.0- 4.8 gigabits
86.
VGA: Video Graphics Array- DE-15 connector and always colored blue. It outputs in analog signal.
87.
xD: ...
88.
Zero Insertion Force: that means that the pins for the socket are on the CPU and not the socket, and the CPU requires zero force to be
inserted into the socket, it just locks in.
You might also like
- Intro To It Hardware1Document32 pagesIntro To It Hardware1tprastyanaNo ratings yet
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- 1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorDocument12 pages1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorTuesept Anne Vargas UrgenteNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: The CPUDocument10 pagesMotherboard: The CPU000pssNo ratings yet
- Parts of A System UnitDocument41 pagesParts of A System UnitDebie Catanyag-TorioNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware: Intel AMD Dual CoreDocument6 pagesComputer Hardware: Intel AMD Dual CoreanishklNo ratings yet
- Aim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)Document15 pagesAim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)VanessaNo ratings yet
- The Motherboard: Basics of Computer HardwareDocument34 pagesThe Motherboard: Basics of Computer Hardwareprashanth2222No ratings yet
- Motherboard TerminologyDocument8 pagesMotherboard TerminologyshockkrewNo ratings yet
- IEEE 1394 PortDocument4 pagesIEEE 1394 PortPRincess ScarLetNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument4 pagesParts of A MotherboardPamieDyNo ratings yet
- Four Types of MotherboardsDocument12 pagesFour Types of MotherboardsNard EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard and Other PartsDocument32 pagesMotherboard and Other PartsJom's Mijares100% (1)
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsDocument98 pagesFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and Peripheralsjuliet brusola100% (1)
- 1 - Firewire HeaderDocument4 pages1 - Firewire HeaderVishnu TejaNo ratings yet
- BIOS InstallationDocument5 pagesBIOS InstallationArif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components... CSEDocument28 pagesMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan100% (1)
- Motherboard ConnectorsDocument5 pagesMotherboard Connectorsmohitpar128No ratings yet
- Components of System UnitDocument8 pagesComponents of System UnitIvan Louie Cruto100% (1)
- Computer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsDocument29 pagesComputer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsRajendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsDocument78 pagesFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsVencent BuellNo ratings yet
- Chs 11 LessonDocument8 pagesChs 11 LessonMaverick Borres Romo ChoiiNo ratings yet
- Components of System UnitDocument8 pagesComponents of System Unitroger_embalsado331988% (16)
- Computer Acronyms and AbbreviationsDocument5 pagesComputer Acronyms and AbbreviationsJeian Ashley A. MaasinNo ratings yet
- CHN EXPDocument32 pagesCHN EXPAnanduNo ratings yet
- A+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationDocument40 pagesA+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationLindasharon AwourNo ratings yet
- Selecting Criteria of A MotherboardDocument3 pagesSelecting Criteria of A MotherboardDa NishNo ratings yet
- Motherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryDocument8 pagesMotherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryJhay Consolacion WalkerNo ratings yet
- Component of A System Unit - Desktop PCDocument8 pagesComponent of A System Unit - Desktop PCRoger EmbalsadoNo ratings yet
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument14 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- Description of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Document4 pagesDescription of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Nain khanNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware-Related AcronymsDocument3 pagesComputer Hardware-Related Acronymsghoul ciprianoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Parts (Explained)Document1 pageMotherboard Parts (Explained)maryNo ratings yet
- Computer Parts and CablesDocument32 pagesComputer Parts and CablesMelissa Jane MoradoNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument8 pagesReportapi-3734554100% (1)
- PC Por DentroDocument2 pagesPC Por DentroDemoclydes CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - IO BusesDocument70 pagesLecture 8 - IO BusesHydie CruzNo ratings yet
- Chs Assignment 1Document7 pagesChs Assignment 1Kiruba KaranNo ratings yet
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument31 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionNhil Cabillon QuietaNo ratings yet
- Hard Ware Note BookDocument22 pagesHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- How Motherboard WorksDocument12 pagesHow Motherboard Worksrez hablo100% (1)
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument9 pagesParts of A Motherboardapi-251392462No ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument56 pagesComputer HardwareKenneth BautistaNo ratings yet
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemDocument13 pagesBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemSaymon Casilang SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Lab2 - Hardware-2Document24 pagesLab2 - Hardware-2Mohammed AlobaidyNo ratings yet
- Motherboard HandoutDocument5 pagesMotherboard HandoutJudea SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Computer ComponentsDocument32 pagesComputer ComponentsJSPAMoreNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction To The Personal Computer SystemDocument35 pages1.0 Introduction To The Personal Computer SystemAdron LimNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument18 pagesMotherboardPalash Jain100% (1)
- Dav Institute of Engineering & Technology, JalandharDocument35 pagesDav Institute of Engineering & Technology, JalandharKaran GuptaNo ratings yet
- Components of A MotherboardDocument114 pagesComponents of A Motherboarddeejhay14100% (1)
- Cassy AssignmentDocument8 pagesCassy AssignmentrickNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Document4 pagesParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathNo ratings yet
- Lesson 02 - Main Parts of ComputerDocument22 pagesLesson 02 - Main Parts of ComputerDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Storage Area NetworkDocument109 pagesStorage Area Networksunil kumarNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument30 pagesSeminarShweta Vishwakarma100% (1)
- Parts of System Unit & MotherboardDocument6 pagesParts of System Unit & MotherboardNonoy Enopena100% (2)
- The MotherboardDocument3 pagesThe Motherboardbryan ramosNo ratings yet
- Add-On Modules 2021Document754 pagesAdd-On Modules 2021Felipe UPNo ratings yet
- Controlling The Projector Using A Personal Computer: DLP™ Projector WD8200UDocument17 pagesControlling The Projector Using A Personal Computer: DLP™ Projector WD8200Uzulfikar rochimNo ratings yet
- Pricelist Computer AccessoriesDocument17 pagesPricelist Computer AccessoriesAyyasamr0% (2)
- TV - Panasonic Th-50pf20er PDFDocument153 pagesTV - Panasonic Th-50pf20er PDFserrano.flia.coNo ratings yet
- SAMSUNG TFT-LCD 933HD (LS19CFE) - TroubleshootingDocument28 pagesSAMSUNG TFT-LCD 933HD (LS19CFE) - TroubleshootingJoão Lopes100% (1)
- Getting Started With Raspberry PiDocument1 pageGetting Started With Raspberry PiSteve AttwoodNo ratings yet
- Manual Ln37b530 LCD TVDocument101 pagesManual Ln37b530 LCD TVlealvarfeNo ratings yet
- User's Manual: MML1941-PCRDocument48 pagesUser's Manual: MML1941-PCRDecko RizhaNo ratings yet
- C2G AV LegrandDocument25 pagesC2G AV LegrandMarco DorantesNo ratings yet
- DataVideo SE-900 ManualDocument81 pagesDataVideo SE-900 Manualwilmeral1No ratings yet
- ImageDP4 Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesImageDP4 Datasheet PDFWilmer Solano RomaníNo ratings yet
- Samsung HPS5053Document146 pagesSamsung HPS5053paache12100% (1)
- KTL201S-Xx SPVA Service ManualDocument41 pagesKTL201S-Xx SPVA Service ManualCamilo Ernesto Rodriguez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- DS100Document48 pagesDS100Bil BilerestNo ratings yet
- LG Lb22e 32lm6200-Ta (SM) PDFDocument79 pagesLG Lb22e 32lm6200-Ta (SM) PDFshamsudin yassinNo ratings yet
- Manual TV-Monitor LG 22MA33DDocument42 pagesManual TV-Monitor LG 22MA33DDragos DragoshNo ratings yet
- Optiplex 3010 Technical GuidebookDocument38 pagesOptiplex 3010 Technical GuidebookmateepNo ratings yet
- HDMI Specification 1.4aDocument430 pagesHDMI Specification 1.4a杨光炜No ratings yet
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Document1 pageTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)sanketNo ratings yet
- DM - Linea CompletaDocument4 pagesDM - Linea CompletaFernando RapisardiNo ratings yet
- Manual Ga-880gm-Ud2h (Us2h) v1.4 eDocument104 pagesManual Ga-880gm-Ud2h (Us2h) v1.4 eAlaxinSkywalkerNo ratings yet
- An 01 en Motherboard Foxconn G41MXDocument75 pagesAn 01 en Motherboard Foxconn G41MXghettosoNo ratings yet
- Wise Surgical Display: ™ 26 HDTVDocument42 pagesWise Surgical Display: ™ 26 HDTVJaime MonterrosaNo ratings yet
- Monitor Stryker 26 PLGDocument28 pagesMonitor Stryker 26 PLGBrandon MendozaNo ratings yet
- Msi b450 Tomahawk 7c02 002r 109380 - enDocument1 pageMsi b450 Tomahawk 7c02 002r 109380 - enReedBluesNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Manual 26el833gDocument60 pagesToshiba Manual 26el833gkafroNo ratings yet
- Edge Artix 7 Dev Board User Manual PDFDocument34 pagesEdge Artix 7 Dev Board User Manual PDFsubashNo ratings yet
- Controller m70 4u e Datasheet20160815Document5 pagesController m70 4u e Datasheet20160815Agencia DigitalNo ratings yet
- Keyboard, Mouse, MonitorDocument5 pagesKeyboard, Mouse, MonitorLournie ErodistanNo ratings yet
- DVD Home Theater System: Owner'S ManualDocument44 pagesDVD Home Theater System: Owner'S ManualjoaoNo ratings yet
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsFrom EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- CompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)From EverandCompTIA A+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide, Eleventh Edition (Exams 220-1101 & 220-1102)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (229)
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]From EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Cyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandCyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsHoubing H. SongNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- Raspberry Pi Retro Gaming: Build Consoles and Arcade Cabinets to Play Your Favorite Classic GamesFrom EverandRaspberry Pi Retro Gaming: Build Consoles and Arcade Cabinets to Play Your Favorite Classic GamesNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: A Concise IntroductionFrom EverandComputer Science: A Concise IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XFrom EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra User Guide For Beginners: The Complete User Manual For Getting Started And Mastering The Galaxy S22 Ultra Android PhoneFrom EverandSamsung Galaxy S22 Ultra User Guide For Beginners: The Complete User Manual For Getting Started And Mastering The Galaxy S22 Ultra Android PhoneNo ratings yet
- Raspberry PI: Learn Rasberry Pi Programming the Easy Way, A Beginner Friendly User GuideFrom EverandRaspberry PI: Learn Rasberry Pi Programming the Easy Way, A Beginner Friendly User GuideNo ratings yet
- Cancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionFrom EverandCancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Hacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxFrom EverandHacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxNo ratings yet
- Mastering IoT For Industrial Environments: Unlock the IoT Landscape for Industrial Environments with Industry 4.0, Covering Architecture, Protocols like MQTT, and Advancements with ESP-IDFFrom EverandMastering IoT For Industrial Environments: Unlock the IoT Landscape for Industrial Environments with Industry 4.0, Covering Architecture, Protocols like MQTT, and Advancements with ESP-IDFNo ratings yet
- The User's Directory of Computer NetworksFrom EverandThe User's Directory of Computer NetworksTracy LaqueyNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide To IPhone 14 Pro Max Mastering: The Comprehensive User Guide And Illustrated Owner's Manual With Tips And Advanced Tricks For New BeFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide To IPhone 14 Pro Max Mastering: The Comprehensive User Guide And Illustrated Owner's Manual With Tips And Advanced Tricks For New BeNo ratings yet


























































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1715193157?v=1)