Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Projection of Lines and Solids
Uploaded by
Vinoth MalaikaniCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Projection of Lines and Solids
Uploaded by
Vinoth MalaikaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Projection
Of
Lines and Solids
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
PROJECTION OF LINES
PROJECTION OF LINES
A straight line can be defined as the shortest distance between any two given point. Path traced
out by a point on a curved path is a curved line or path traced out by a point on a straight path is
called a straight line. It can also be said that the straight line is the locus of a point on a straight
path.
Location of a Line:
Location of a line with reference to the H.P. to V.P. which can be classified in any different
positions.
Line parallel to H.P. and inclined to V.P. .
Line parallel to V.P. and inclined to H.P. .
Line parallel to H.P. and V.P.
Line perpendicular to H.P. and parallel to V.P.
Line inclined to H.P. and parallel to V.P.
Line inclined to V.P. and parallel to H.P.
Line inclined to both H.P. and V.P.
1. Line parallel to H.P. and inclined to V.P.
Fig no.1
Line parallel to H.P. and inclined to V.P.
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 1
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
2. Line parallel to V.P. and inclined to H.P. .
Fig No.2
Line parallel to V.P. and inclined to H.P. .
3. Line parallel to H.P. and V.P.
Fig No.3
Line parallel to H.P. and V.P.
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 2
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
4. Line perpendicular to H.P. and parallel to V.P.
Fig No. 4
Line perpendicular to H.P. and parallel to V.P.
5. Line inclined to H.P. and parallel to V.P.
Fig No.5
Line inclined to H.P. and parallel to V.P.
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 3
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
6.
Projection of Lines and Solids
Line inclined to V.P. and parallel to H.P.
Fig No.6
Line inclined to V.P. and parallel to H.P.
7.
Line inclined to both H.P. and V.P.
Fig No.7
Line inclined to both H.P. and V.P.
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 4
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
PROBLEMS:
Problem 1.
A line AB 25 mm long is parallel to V.P. and perpendicular to H.P. point A is 35 mm above H.P.
and 20 mm infront of V.P. point B is 10 mm above H.P. Draw the projections of the line AB.
Fig No. a
Problem 2.
A line CD 20 mm long is parallel to V.P. and perpendicular to H.P. Point C is 35 mm above H.P.
and 10 mm infront of V.P. Draw its projections.
Fig No. b
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 5
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 3.
A line AB 25 mm long is perpendicular to V.P. and parallel to H.P. Its end A is 10 mm infront of
V.P. and the line is 20 mm above H.P. Draw the projections of the line.
Fig. c
Problem 4.
A line CD 30 mm long is perpendicular to V.P. and parallel to H.P. Its end C is 5 mm infront of
V.P. and the line is 10 mm above H.P. Draw the projections of the line.
Fig. No d
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 6
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 5.
A line CD 30 mm long is parallel to both the planes. The line is 40 mm above H.P. and 25 mm
infront of V.P. Draw its projections.
Fig.No. e
Problem 6.
A line PQ 40 mm long is parallel to V.P. and inclined at an angle of the 300 to H.P. The end P is
15 mm above H.P. and 20 mm infront of V.P. Draw the projections of the line.
Fig.No. f
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 7
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 7.
A line PQ, 60 mm long, is parallel to H.P. and inclined at 450 to V.P. Its end P is 20 mm above
H.P. and 15 mm infront of V.P. Draw the projection of the line.
Solution.
Draw xy line. Mark a point p, 15 mm below xy. Draw a line pq 60 mm long and inclined at 450
to xy . Then pq is the top view of the PQ.
Fig.No. g
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 8
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 8.
A line AB, 60 mm long, is parallel to V.P. and inclined at 300 to H.P. Its end A is 15 mm above
H.P. and 25 mm infront of V.P. Draw the projections of the line.
Solution.
Draw xy line. Mark a point a 15 mm above xy. Draw a line ab 60 mm long and inclined at 300
to xy. Then ab is the front view of the line AB.
Fig.No.h
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 9
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 9.
A line PQ, 65 mm long, is inclined at 450 to V. P. and parallel to H.P. Its end P is 10 mm front
V.P. and 20 mm from H.P. Draw the projection of the line.
Solution.
Take the end P 10 mm infront of V.P. and 20 mm above H.P. that is in first quadrant.
Draw xy line. Mark a point p, 10 mm below xy and p 20 mm above xy on the same vertical line.
Through p, draw a line pq 65 mm long and inclined at 450 to xy. The pq is the top view of the
line PQ.
Fig.No.i
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 10
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 10.
The length of the front view of a line CD, parallel to H.P. and inclined at 450 to V.P. is 45
mm. Its end C is mm infront of V.P. and 14 mm above H.P. Draw the projection of the
line and find its length.
Solution.
Draw the xy line. Mark a point c 20 mm below xy and c 14 mm above xy on the same
vertical line. Through c , draw a line cd 45 mm long and parallel to xy. Then cd is the
front view of the CD.
FigNo. j
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 11
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 11.
A line AB, 40 mm long, is parallel to H.P. and inclined at 300 to V.P. Its end A is 15 mm
below H.P. and 25 mm behind V.P. Draw the projections of the line.
Solution.
Draw xy line. Mark a point a, 25 mm above xy. Draw a line ab 60 mm long and inclined
at 300 to xy. Then ab is the plan of the line AB.
FigNo.k
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 12
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 12.
A line AB, 40 mm long is parallel to V.P. and inclined at 300 to H.P. Its end A is 10 mm
below H.P. and 15 mm behind V.P. Draw the projection of the line.
Solution.
Draw xy line. Mark a point a, 15 mm below xy. Draw a line ab, 60 mm long and
inclined at 300 to xy. Then ab is the elevation of the AB.
Fig.No.m
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 13
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 13.
A line AB, 70 mm long, is inclined at 300 to H.P. and 450 to V.P. Its end Ais 25 mm above H.P.
and 15 mm infront of V.P. Draw its projection.
Solution.
Draw xy line. Mark point a, 15 mm below xy and a, 25 mm above xy on the same projector.
Through a, draw a line ab1 70 mm long and inclined at 450 to xy. Through a draw a line ab 70
mm long and inclined to 300 to xy.
Through b, draw a line lm parallel to xy. It is locus of b. Similarly, through a, a and b1, draw
line no, pq and rs respectively parallel to xy.
Now, project down b at b on pq. Taking centre a and radius ab, draw an arc cutting rs at b2. Join
ab2. Then ab2 is the top view of the line AB.
Project up b1 at b1 on no. Taking centre a and radius ab1, draw an arc cutting lm at b2. Then
ab2 is the front view of the line AB.
Fig.No.n
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 14
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 14.
A line AB, 70 mm long, is inclined at 450 to H.P. and 300 to V.P. Its end A on H.P. and
25 mm above H.P. Draw its projections.
Solution.
Draw xy line. Mark a point a on xy and a 25 mm above it.
Through a draw a line ab1, 70 mm long, inclined at 300 to xy. Through a, draw a line ab2 70
mm long and inclined at 450 to xy.
Through b, draw a line lm parallel to xy. It is the locus of b. Similarly, through a and b1, draw
lines no and pq respectively parallel to xy.
Now, project up b1 at b1 on no. Taking centre b1, draw an arc to meet lm at b2. Joint ab2.
Then ab2 is the front view of the line AB.
Fig.No.o
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 15
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
PROJECTIONS OF SOLIDS
Introduction.
A solid is a three dimensional object having length, breadth and height and bounded by
Surfaces which may be plane or curved or combination of both.
Classification of solids
Prism It is a polyhedron which has two equal and parallel polygonal end faces joined by side
faces which are parallelograms or rectangles.
Fig .1.2
Triangular Prism, Rectangular Prism, Pentagonal Prism & Hexagonal Prism.
Fig.1.3
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 16
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
PYRAMID
Triangular Pyramid and Square Pyramid 9.5
Fig.1.4
Pentagonal Pyramid
Fig.1.5
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 17
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Hexagonal Pyramid
Fig. 1.6
Cylinder
Fig.1.7
Cone
Fig.1.8
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 18
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Sphere
Fig.1.9
Position of Solid:
Axis perpendicular to H.P. and Parallel to V.P.
Fig.1.10
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 19
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Axis perpendicular to V.P. and Parallel to H.P.
Fig.1.11
Axis parallel to both H.P. and V.P.
Fig.1.12
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 20
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Axis Perpendicular to V.P. and Parallel to H.P.
Problem 1.
A hexagonal prism, base 25 mm side and axis 50 mm long, is lying on the ground on one of its
rectangular faces. Its axis is perpendicular to V.P. and nearer end is 20 mm behind V.P. Draw its
projections. (Third Quadrant)
Solution.
Draw the hexagonal of 25 mm side in the front elevation, keeping one of its sides on the ground
line GL. Project up the plan, keeping the nearer end 20 mm above xy.
Fig.No.13
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 21
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 2.
A hexagonal pyramid, base 25 mm side, axis 70 mm long, is resting on one of the corners of the
base on H.P. having the axis perpendicular to V.P. The two sides of the base joining that corner
are equally inclined to H.P. Draw its projections when the vertex is nearer to V.P. (First
Quadrant).
Solution.
Draw a hexagonal abcdef of 25 mm side, in the front view, having a corner c on xy and the
sides cb and cd equally inclined to xy.
Fig.No.1.14
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 22
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 3.
A cylinder, 30 mm diameter and 60 mm long, has its one end in V.P. Its axis is 35 mm above the
ground, Draw its projections. (Third Quadrant)
Solution.
Draw a circle of 30 mm diameter below xy, its centre o being 35 mm above GL. Divide it into
four equal parts, thus completing the front view of the cylinder. Project up the plan 60 mm long
on xy.
Fig.No.1.15
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 23
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 4.
Draw the projections of a cone diameter of base 30 mm and height of axis 50 mm resting in H.P.
on it base axis parallel to V.P. (First Quadrant)
Fig.No.1.16
Problem 5.
A pentagonal pyramid of base 30 mm and height 50 mm is resting on one of its base
corners in V.P. Draw the projection when the axis is inclined at 450 to V.P. and parallel to
H.P. (First angle projection).
Fig.No.1.17
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 24
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 6.
A pentagonal pyramid of side 30 mm and axis 70 mm long is resting on one of its corners
in H.P. and axis inclined at 450 to H.P. Draw the projections. (First angle projection).
Fig.No.1.18
Problem 7.
A hexagonal pyramid of base side 30 mm, height 70 mm is having one of its triangular
Surfaces inclined at 650 to H.P. Draw the projections of the solid. (First angle projection).
Fig.No.1.19
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 25
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Problem 8.
A hexagonal pyramid base side 30 mm height 70 mm is having one of its triangular
Surfaces in V.P. Draw the projections of the solid. (First angle projection).
Fig.No.1.20
Problem 9.
A hexagonal pyramid base of side 25 mm and axis 70 mm long is resting on H.P on one
Of its triangular faces. The side of the base contained by that face is inclined at 450 to
V.P. Draw its projection when the vertex is nearer to V.P. (First angle projection).
Fig.No.1.21
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 26
Engineering Drawing and Graphics
Projection of Lines and Solids
Exercise problems:
Problem 1.
Draw the projection of a cylinder of 20 mm diameter and 50 mm long having its one ends in V.P.
Its axis is 24 mm above ground. (Third angle projection).
Problem 2.
A hexagonal prism base of 20 mm side and axis 60 mm long is lying on the H.P. on one of its
rectangular faces. Its axis is perpendicular to V.P. and nearer end is 10 mm in front of V.P. Draw
the projections of prism. (First angle projection)
Problem 3.
A pentagonal pyramid of base edge 30 mm and height 50 mm is resting on one of its
corners in H.P. Draw the projection when the axis is inclined at 450 to H.P. and parallel to
V.P. (First angle projection)
The Automobile Society (India)
Page 27
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Journal PaperDocument10 pagesJournal PaperVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Design FormatDocument1 pageDesign FormatVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- TNPSC Answer Key 1Document3 pagesTNPSC Answer Key 1Vinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- GE8261-Engineering Practices Lab - MECH PDFDocument74 pagesGE8261-Engineering Practices Lab - MECH PDFMohamed BasheerNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Tractors OverviewDocument100 pagesTractors OverviewVinoth Malaikani100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- CT2 PDFDocument116 pagesCT2 PDFVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Unit Iii Hydromatic Drive: Fluid Coupling ConverterDocument44 pagesUnit Iii Hydromatic Drive: Fluid Coupling ConverterGuruLakshmiNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Lecture 9 Farm Tractor PDFDocument4 pagesLecture 9 Farm Tractor PDFsujan paudel100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Certificate No. IIDocument3 pagesCertificate No. IIbirrajNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- CentroidsDocument118 pagesCentroidsMaxneil QuijanoNo ratings yet
- !!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!ose Je! Ose Je! Ose Je! Ose Je!.... ! ! ! !Document93 pages!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!ose Je! Ose Je! Ose Je! Ose Je!.... ! ! ! !Narveena Servai VadiveluNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Automotive MaterialsDocument45 pagesAutomotive MaterialsVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- 7 Force AnalysisDocument19 pages7 Force AnalysisEn Eskay100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Basics of Vehicle Aerodynamics: University of Rome La Sapienza" 2002Document31 pagesBasics of Vehicle Aerodynamics: University of Rome La Sapienza" 2002Vinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Control Systems in Automobile PDFDocument36 pagesControl Systems in Automobile PDFVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Review of Aerodynamic Drag Reduction Devices For Heavy Trucks and BusesDocument65 pagesReview of Aerodynamic Drag Reduction Devices For Heavy Trucks and BusesVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Composite SystemsDocument14 pagesComposite Systemsvinoth9657tycoonNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument7 pagesEngineering MaterialsVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Nceda 2016Document2 pagesNceda 2016Vinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Turbines - Hydraulic MachinesDocument26 pagesTurbines - Hydraulic MachinesVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Tracking SystemDocument22 pagesVehicle Tracking SystemVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- How Does Nature Make Saltwater DrinkableDocument5 pagesHow Does Nature Make Saltwater DrinkableVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Aston Martin IndiaDocument10 pagesAston Martin IndiaVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Weight RestrictionDocument3 pagesWeight Restrictionhareesh13hNo ratings yet
- AT6503 VDC Question BankDocument8 pagesAT6503 VDC Question BankVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Faculty Development Program PDFDocument65 pagesFaculty Development Program PDFrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Direct Solar EnergyDocument68 pagesChapter 3 Direct Solar EnergyMARUMO_LEVYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Ansers PDFDocument50 pagesChapter 6 Ansers PDFSana AshfaqNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- 02 Particle Kinematics x2Document11 pages02 Particle Kinematics x2maitesecoNo ratings yet
- Mock Board Question PDFDocument9 pagesMock Board Question PDFHanna Grace HonradeNo ratings yet
- Points, Lines, PlanesDocument18 pagesPoints, Lines, PlanesjabirNo ratings yet
- Pi Day - ExtensionDocument2 pagesPi Day - Extensionapi-521462216No ratings yet
- Homework - Mechanics: Free Fall Analysed With Multiflash PhotographsDocument3 pagesHomework - Mechanics: Free Fall Analysed With Multiflash PhotographsSanjana0% (1)
- pp11n Mo1 FwsDocument8 pagespp11n Mo1 FwssaramafareNo ratings yet
- Math-9 LAS Q3 Week-1Document7 pagesMath-9 LAS Q3 Week-1Bern BeybieNo ratings yet
- Absolutely Convex SetDocument2 pagesAbsolutely Convex SetCarlo Edoardo CapponiNo ratings yet
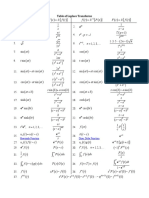
- Laplace Table PDFDocument2 pagesLaplace Table PDFCrafterNo ratings yet
- Calculus 3 Lecture NotesDocument96 pagesCalculus 3 Lecture NotesEXAMMATENo ratings yet
- 02-Angle Pair Relationships PDFDocument4 pages02-Angle Pair Relationships PDFAJ LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Euclidean Plane and Its Relatives - Anton Pretunin PDFDocument166 pagesEuclidean Plane and Its Relatives - Anton Pretunin PDFRaeNo ratings yet
- Axisymmetric SolidsDocument24 pagesAxisymmetric SolidsSunil VermaNo ratings yet
- Motion Formula SheetDocument2 pagesMotion Formula SheetimkushofficialNo ratings yet
- Chapt 6 - Complex Numbers PDFDocument33 pagesChapt 6 - Complex Numbers PDFLutwama Gideon100% (1)
- Time TravekDocument2 pagesTime TravekRavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Distance ChangingDocument22 pagesDistance ChangingJohn MarsNo ratings yet
- CCCCCC C C CDocument16 pagesCCCCCC C C CAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- Acceeration MechanismDocument33 pagesAcceeration MechanismDavid nelsonNo ratings yet
- How To Draw EllipseDocument3 pagesHow To Draw EllipseRakib Hossain100% (1)
- Cartesian Components of VectorsDocument23 pagesCartesian Components of VectorsHaresh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- S.3 Holiday Work (Technical Drawing) Attempt All QuestionsDocument3 pagesS.3 Holiday Work (Technical Drawing) Attempt All QuestionsAthiyo MartinNo ratings yet
- Typology of Tactile Architectural Drawings Accessible For Blind and Partially Sighted PeopleDocument30 pagesTypology of Tactile Architectural Drawings Accessible For Blind and Partially Sighted PeoplesuhailaNo ratings yet
- Vectors & Calculus PDFDocument80 pagesVectors & Calculus PDFTanmay SagarNo ratings yet
- DOM QP ScribdDocument5 pagesDOM QP ScribdvsanthanamNo ratings yet
- Kaylee - Spencer Et Al. Maya Imagery, Architecture - Space and Spatial Analysis in Art History 2015 Ori PDFDocument442 pagesKaylee - Spencer Et Al. Maya Imagery, Architecture - Space and Spatial Analysis in Art History 2015 Ori PDFljudmil100% (1)
- Trigonometry Study Material Exercise Hints Explanations PDFDocument14 pagesTrigonometry Study Material Exercise Hints Explanations PDFManish SoyalNo ratings yet
- Isye 4256 Supplemental Material: Fall, 1999Document14 pagesIsye 4256 Supplemental Material: Fall, 1999Ram Prasad YadavNo ratings yet
- 329 Chapter 8. Euclidean GeometryDocument1 page329 Chapter 8. Euclidean GeometryreacharunkNo ratings yet