Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JIndianSocPedodPrevDent302183-1552415 041844
Uploaded by
NiNis Khoirun NisaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JIndianSocPedodPrevDent302183-1552415 041844
Uploaded by
NiNis Khoirun NisaCopyright:
Available Formats
[Downloadedfreefromhttp://www.jisppd.comonWednesday,October24,2012,IP:110.138.184.
158]||ClickheretodownloadfreeAndroidapplicationforthisjour
Case Report
Presurgical management of a child with
missing lower lip using a new design of fixed
lower tongue crib
Abstract
Missing of any perioral structure can result in imbalance of
muscular forces leading to loss of structure and function along
with esthetics especially in a growing individual and can result
in permanent damage. Rehabilitation of such children is a
challenge and requires an integrated multidisciplinary approach
not only to correct the defect, but also to ensure normal
development with minimal handicap. Here is a case report
of a 10-year-old child with missing lower lip due to childhood
infection and its presurgical management using a new design of
fixed lower tongue crib used to limit tongue pressure, improve
tongue position, and facilitate lower incisor retraction.
Safeena S, Najmuddin M1, Reddy K
Department of Orthodontics, Al-Badar Rural Dental College
and Hospital, Gulbarga, 1Department of Oral Medicine and
Radiology, AMEs Dental College, Raichur, India
Correspondence:
Dr. Safeena S, Department of Orthodontics,
Al-Badar Rural Dental College and Hospital, Gulbarga.
E-mail: aksafe@yahoo.com
Access this article online
Quick Response Code:
Website:
www.jisppd.com
DOI:
10.4103/0970-4388.100019
A new clinical experience for lower lip missing cases in children
are added, as these cases are rare.
PMID:
***
Key words
Fixed tongue crib, incisor retraction, missing lip, Top of page
Introduction
Equilibrium theory states that an object subjected to
unequal forces will be accelerated and thereby move
to different positions in space. Equilibrium effects
on dentition are governed by masticatory forces and
pressure from the lips, cheek, and tongue. The pressures
from the soft tissues are much lighter than the forces
of mastication, but much greater in duration. Injury to
the lip leading to scarring and contracture will lead to
the incisors being tipped lingually and if the pressure
from the lip or cheek are removed, unopposed pressure
from the tongue will lead to outward movement of the
teeth.[1] We report a case of missing lower lip due to
infection and scarring leading to proclination of lower
incisors and its early management in a child using a
fixed lower tongue crib and fixed orthodontic appliance.
Case Report
A 10-year-old male patient was referred from the
department of oral surgery with a chief complaint
of proclined lower incisors and a missing lower lip.
Patients father gave a history of infection of the lower
lip with purulent discharge when the child was 4-year
old that healed with scarring and lead to loss of the
lower lip.
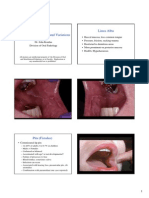
On examination, it was found that 2/3rd of the lower lip
was missing and there was scar tissue in the chin area,
fused to the lower alveolus. Upper and lower central
incisors and first molars were erupted except the lower
right central incisor. Lower incisors were severely
proclined with the tongue resting on the lower incisors
[Figure 1a]. He had missing lower right deciduous
molars and upper deciduous first molars due to caries.
The remaining deciduous teeth also showed gingival
recession and mobility [Figures 1c and d].
JOURNAL OF INDIAN SOCIETY OF PEDODONTICS AND PREVENTIVE DENTISTRY | Apr - Jun 2012 | Issue 2 | Vol 30 |
183
[Downloadedfreefromhttp://www.jisppd.comonWednesday,October24,2012,IP:110.138.184.158]||ClickheretodownloadfreeAndroidapplicationforthisjour
Safeena, et al.: Presurgical management of missing lower lip
Figure 2: (a) Fixed tongue crib and initial Niti wire for alignment.
(b)Post retraction intraoral view. (c) Occlusal view before retraction.
(d) Occlusal view post-retraction
Figure 1: (a, b) Extraoral view. (c) Lateral Cephalogram showing
severe proclination of lower incisors. (d) Extraoral left profile view
Cephalometric analysis showed a class II skeletal
pattern, hyperdivergent mandibular base with FMA 32
and lower incisor inclination to the mandibular plane
being 141 [Figure 1b] indicating severe proclination
of the lower incisors.
OPG examination revealed missing lower central
incisor and all other teeth present at different staged
of eruption.
Lingual pressure from the tongue had to be controlled
and lower incisors had to be retracted in order to
improve esthetics and function, and to facilitate a lip
reconstruction surgery.
Treatment
The lower incisors and the remaining deciduous
teeth were bonded with Begg appliance except the
lower left canine since it showed grade II mobility.
Since the tongue was resting on the lower incisors, it
was necessary to position the tongue away from the
incisors to facilitate retraction. A fixed lower tongue
crib was planned. The lower permanent molars were
banded and the tongue crib was soldered to the bands
with two metal extensions soldered on the right side.
Since the lower-left deciduous molars were lost, the
wire extensions would help support the long span of
184
archwire on the left side. Initially a 0.016 NiTi wire was
used for alignment and the retraction was done using
0.016 stainless steel wire and elastic thread.
At the end of retraction, the lower incisors were
positioned at 122 to the mandibular plane which was
141 pretreatment. After debonding the appliance and
removal of the tongue crib, the patient was referred
back to the department of oral surgery for the lip
reconstruction surgery. [Figure 2]
Discussion
Reported causes of loss of lower lip in children have
been due to neonatal oral infection (cancrum oris)
chemical, electrical burns, trauma, animal bites, cancer
and as a surgical complication, cancrum oris being the
most common cause seen especially in the African subSahara region, leading to facial deformities.[2]
Presurgically, these children need to be rehabilitated for
function and to prevent further malocclusion. Medical
management of such children for control of disease has
been reported.[3] Surgical reconstruction is required
in such children and presurgical management is also
essential.
Fixed tongue crib has been used for control of oral
habits such as tongue thrusting and thumb sucking
especially in noncompliant patients, which usually leads
to proclination of upper incisors in children. Tongue
crib is rarely given in the lower arch.[4] Here we have
devised a new design of tongue crib to be fixed to the
JOURNAL OF INDIAN SOCIETY OF PEDODONTICS AND PREVENTIVE DENTISTRY | Apr - Jun 2012 | Issue 2 | Vol 30 |
[Downloadedfreefromhttp://www.jisppd.comonWednesday,October24,2012,IP:110.138.184.158]||ClickheretodownloadfreeAndroidapplicationforthisjour
Safeena, et al.: Presurgical management of missing lower lip
lower arch which not only prevents lingual forces of
the tongue on the lower incisors, but also helps support
the long span of archwire that may become too flexible
and distort if left unsupported.
Conclusion
The new design of fixed tongue crib given in the
mandibular arch is an efficient way of controlling the
unbalancing forces from the tongue especially when the
tongue position is low lying.
orthodontic problems. 3rd ed. Missouri: Mosby 2000; p-128.
2. Nthumba P, Carter L. Visor flap for total upper and lower
lip reconstruction: A case report. J Med Case Reports 2009;
3:7312 p1-5
3. Moss JP. Soft tissue environment of teeth and jaws:
An experimental and clinical study: Part 1. Br J Orthod
1980;7:127-37.
4. Cooke MS. A lower fixed lingual tongue crib and lip toning
exercises: Report of an unusual case. Br J Orthod 1977;
4:143-8.
References
How to cite this article: Safeena S, Najmuddin M, Reddy K.
Presurgical management of a child with missing lower lip using a
new design of fixed lower tongue crib. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev
Dent 2012;30:183-5.
1. Proffit WR. Contemporary Orthodontics, The etiology of
Source of Support: Nil, Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Announcement
Android App
A free application to browse and search the journals content is now available for Android based
mobiles and devices. The application provides Table of Contents of the latest issues, which
are stored on the device for future offline browsing. Internet connection is required to access the
back issues and search facility. The application is compatible with all the versions of Android. The
application can be downloaded from https://market.android.com/details?id=comm.app.medknow.
For suggestions and comments do write back to us.
JOURNAL OF INDIAN SOCIETY OF PEDODONTICS AND PREVENTIVE DENTISTRY | Apr - Jun 2012 | Issue 2 | Vol 30 |
185
You might also like
- JIndianSocPedodPrevDent302179-1553084 041850Document4 pagesJIndianSocPedodPrevDent302179-1553084 041850NiNis Khoirun NisaNo ratings yet
- Self Etching Adhesive On Intact Enamel: Devarasa GM, Subba Reddy VV, Chaitra NLDocument6 pagesSelf Etching Adhesive On Intact Enamel: Devarasa GM, Subba Reddy VV, Chaitra NLNiNis Khoirun NisaNo ratings yet
- Price List DENTAL JAYA Dental SupplyDocument24 pagesPrice List DENTAL JAYA Dental SupplyNiNis Khoirun Nisa100% (3)
- HypnosisDocument18 pagesHypnosisNiNis Khoirun Nisa100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Fink, Carson & DeVellis - Adult Circumcision Outcomes Study PDFDocument4 pagesFink, Carson & DeVellis - Adult Circumcision Outcomes Study PDFOmar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Syndromes of Head and NeckDocument1 pageSyndromes of Head and NeckKandasamy MuruganNo ratings yet
- Resume 2Document1 pageResume 2api-436090845No ratings yet
- What Is An Office Hysteroscopy?Document4 pagesWhat Is An Office Hysteroscopy?ericNo ratings yet
- Section Editor: Steven A. Newman, MD: J Neuro-Ophthalmol, Vol. 28, No. 4, 2008Document10 pagesSection Editor: Steven A. Newman, MD: J Neuro-Ophthalmol, Vol. 28, No. 4, 2008Jessica Leika MatibagNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery Direct 6 Yrs PDFDocument31 pagesNeurosurgery Direct 6 Yrs PDFSoumitraNo ratings yet
- HEENT History TakingDocument15 pagesHEENT History TakingPépé TechopathamNo ratings yet
- Visual Requirements For Driving: by Catharine Chisholm PHD Mcoptom, University of BradfordDocument5 pagesVisual Requirements For Driving: by Catharine Chisholm PHD Mcoptom, University of Bradfordagisab100% (1)
- Developmental DefectsDocument16 pagesDevelopmental DefectsdeenmNo ratings yet
- Concussion PPT June 20101Document36 pagesConcussion PPT June 20101CiiFitriNo ratings yet
- Hospital MedicineDocument36 pagesHospital MedicineCarlos HernándezNo ratings yet
- Spec Newport e360T-LKPPDocument4 pagesSpec Newport e360T-LKPPDwi SanitaNo ratings yet
- ALGA Medical NetworkDocument56 pagesALGA Medical NetworkCarl HernandezNo ratings yet
- Know Your Hospital: Submitted by Joyita ChatterjeeDocument13 pagesKnow Your Hospital: Submitted by Joyita ChatterjeeJoyita ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Bronchiolitis in ChildrenDocument16 pagesBronchiolitis in ChildrenNym Angga Santosa100% (1)
- Interproximal Height of BoneDocument3 pagesInterproximal Height of Bonefinislux1No ratings yet
- Coeliac Disease: John S. Leeds, Andrew D. Hopper, and David S. SandersDocument14 pagesCoeliac Disease: John S. Leeds, Andrew D. Hopper, and David S. Sandersbdalcin5512No ratings yet
- CircumcisionDocument4 pagesCircumcisionapi-244757499No ratings yet
- 1 Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome - Diagnosis and ManagementDocument52 pages1 Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome - Diagnosis and ManagementThana Balan100% (1)
- Congenital Lobar EmphysemaDocument25 pagesCongenital Lobar Emphysemasheme1711No ratings yet
- 26 Lessons Learned As A NurseDocument2 pages26 Lessons Learned As A NurseAnthonyBernardoAbustanNo ratings yet
- The Natural Way To A Healthy HealingDocument111 pagesThe Natural Way To A Healthy HealingAnjanaNo ratings yet
- King Edward Memorial Hospital: Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical CollegeDocument6 pagesKing Edward Memorial Hospital: Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical CollegeSwapnali GhegadeNo ratings yet
- HEYER VizOR - Product List - en 0314 2Document7 pagesHEYER VizOR - Product List - en 0314 2kalandorka92No ratings yet
- Tapentadol ParacetamolDocument2 pagesTapentadol ParacetamolMohammad Shahbaz Alam100% (1)
- Acne Vulgaris PDFDocument8 pagesAcne Vulgaris PDFsmackooooooNo ratings yet
- Acute Nephrology For The Critical Care Physician 2015th EditionDocument280 pagesAcute Nephrology For The Critical Care Physician 2015th EditionHiago Sousa100% (1)
- Developmental Assessment of Hospitalized ChildDocument11 pagesDevelopmental Assessment of Hospitalized ChildmcowellNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics 1981 Versmold 607 13Document9 pagesPediatrics 1981 Versmold 607 13Andrés AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Patient Fall Incident ReportDocument2 pagesPatient Fall Incident ReportXYZ100% (1)