Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Year 11 Physics World Communicates Topic Test
Uploaded by
Richa Ng0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
867 views5 pagesYear 11 preliminary hsc Physics World Communicates topic test
Original Title
Year 11 Physics World Communicates topic test
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentYear 11 preliminary hsc Physics World Communicates topic test
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
867 views5 pagesYear 11 Physics World Communicates Topic Test
Uploaded by
Richa NgYear 11 preliminary hsc Physics World Communicates topic test
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Topic Test
1. Which of the following is « wansverse 6 Which choice comectiy shows the
‘matter wave? resultant pulse when the two pulses in
(A) Hight waves ‘question 5 interact?
(B) microwaves
(©) sound waves “
(D) water waves
2 Which choice corectly defines the ®
amplitude ofa matter wave?
(A) the distance between successive
serve ples ©
@) He dunce tenant sjeent
cre or tugs,
(©) te dace ate topo est
to the bottom of a trough oO
(©) the distance fom 20 fr.
displacement to 2 position of
‘maximum displacement 7. What property identifies a wave as an
electromagnetic wave?
3. What isthe fRequeney of 2 wave which (A) its wavelength
thas a wavelength of 2.5 m and «velocity (B) its frequency
of 30s" (©) its velocity
(a) Oost (D) hothr it is teansverse or
@) 201 Tongitudinal
(© 25H
(D) 125 He 8. Which etecromaynesic waves camy the
greatest amount of exergy?
4. Which choice correctly describes how the (A) those with highest frequency
particles ofthe medium caerying «sound (B) those with longest wavelength
‘wave move? (C) those with the largest amplitude
(A) oscillate up and down (D) hose wit the fastest velocity
(B) sella let and right
(©) oscillate in the same direction as 9. Which electromagnetic waves will pass
‘energy is rensferred ‘through the atmosphere unafosted?
(D) scl at right angles to the gamma rys
section of energy transfer B) microwaves
5. Twowavesapproach each otheras shown: (©) radio waves
— (D) ulta-viote light
10, Which electromagnetic waves reflect off
the ionosphere?
(A) intired rays
a (8) longewave radio waves
(©) shorewaveradio waves
Whit coice describes how these pues ©) X-rays
interact with each other?
(A) constructive imerference 11, What produces radio waves?
{B) destructive interference (A). lectical caments
(©) pulse cancellation (B) hotobject:
(©) Superposition (C)_ oscillating electrons
(D) vibrating mocei
st
14
16,
1.
Idetify the two types of electromagnetic
radiation we can detoct with our sense.
(A) UV radiation and inured
radiation
(B) Visible light and UV radiation
(©) visible light and infa-ed méiation
(D)_ visible fight and sound
“Theintensty of ight filling ona seen is
48 units, The seeen is 1.5 m fom the
light source, Wha wil be the intensity on
the sereen at distance of 60 m?
(A). Suits
B) 6 units
(©) Suits
©) unis
A.UHE television signal has a frequency
(of 300 Me, What ists wavelength?
@ 01m
@) Lom
© 10m
(©) 9x 10%m
‘What property of waves mikes optical
fibres efficent at tansmiting data?
(A) critical angle
(B) reflection
(©) retraction
(D) total itoral reflection
‘What name is given tp a collection of
optical fibres used 19 communicate data?
A) core
(cladding
(©) grade index fibre
©) lit pipe
\Woat isa reason digital communications
jis more reliable than analog
‘communications?
(A) interference is more easily removed
‘rom digital signals
(B) digital signalstravel atte speed of
light
(©) digital signats use binary code
(D) digital data i transmitted at mach
higher frequencies
‘What isthe best way of communicating
with satellites?
A) long wavelength radio waves
(B) medium wavelength racio waves
(©) microwaves
(©) optical asers
Bs.
21
‘What isthe Law of Reflection?
«“
®
©
”
angle f=angle r
distance of object infront of itor
= distance of image behind miro
‘What remains constant during reffation?
wy
@
©
oo)
the wavelength of the wave
the foquency ofthe wave
the speed ofthe wave
the dizetion of travel ofthe wave
A wave incident a 90° to a Boundary wil
“
®
©
o
‘ot be reacted
refrac butts speed will not change
refiat but its diction of travel
‘wil not change
refloct fom the surface
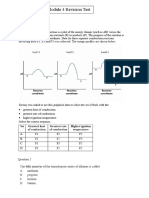
Consider the dagram below:
Consider the diagram for questions 23 and 24,
23, Which path will the refacted ay in the Whichangle represents the critical angle forthe
pai ake? ‘las?
wa ia
@ B @ 8
Oc © c
© D © D
24 ‘The mark value of each of the folowing
questions or arts of questions is shown in
brackets.
28 Conant wansversc mater waves and
clectromagneti waves. (6)
28, Compare tansverse and longitu
25. A sah of sls bs a reactive index of rater waves.)
1.3, What willbe te speed of git inthis
slau? 30. dani cach ofthe labled parts ofthe
2310 os! wave below.)
@) 3xi0as"
(© 39x10'ms" A RB C DE
() Unable to calculate without the
reffacve index of the medium
outside the pias,
26. Consider the diagram below:
aie Fe
$1, may bin pe of woe
A below. (4)
32. The speed of light is 3x 10" ms". Blue
light has a wavelength of about $50 nm
Which anges are angles of efiastion? {um= 10") Calelte te fequeney ot
(a). bealy thisight.@)
@) banda
(© dande 33, Conder the following digram which
©) donly reprseats 0.14 seconds of ine. (5)
27. Consider te diagram below:
Determine:
(@) the wavelength ofthe wave
(@) thoamplinde of the wave
34
3s.
3
37
3.
2.
40,
41
‘itacemar
(©) tho period ofthe wave
G) the frequency ofthe wave
(©) the velocity ofthe wave
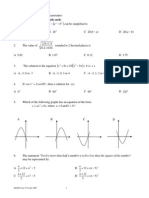
‘The graphs show two positions ofa wave
0002's apart, Calculate the wavelengt,
fequney. prod nd pdf wave,
Se |
Distinguish between constructive and
estrctve interference (8)
St 6 open of elostommgntic
waves.
In general, what is the source of
clectromagneti radiations. 2)
enti the property which distinguishes
‘one type of electromagnetic radiation
from another, (1)
Predict why some bands of
clectomagnetic radiation (eg.
microwaves and radio waves) overep.(4)
‘Show, withthe use ofa dagram, how the
inverse square law for Tight intensity is
erived. (6)
‘The laser light fling on a satelite dish
‘has an intensity of TIF the Hight $8
reflected to a recéiver equidistant to the
souree without amplification, cleat the
intensity ofthe signal atthe receiver. 2)
2
8.
44,
45
46.
4
48,
4.
Compare AM and FM radio waves. (3)
Expltin_ way FM radio wave
transmissions ate lest susoepible to
Imterference. (4)
dentify the factors which allow some ems
to be used for communications, while
‘other em are not able to Bo sed, (8)
Explain the diference between an optical
fibre an Light pipe, 2)
[Explain why cladding is necessary on
optical fibres, and identify its essential
Property. 3)
Calculate the velocity ofa laser beam in
an optical fibre of reftectve index 1.25.
o
Explain why digital eommonications is
‘more liable than analog,
‘communications. (8)
Consider the diagram below:
ir 50"
lass
CCaleulate the reactive index of ihe glass.
®
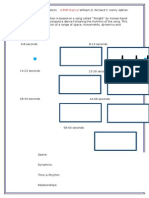
Complete each diagram to show what
“happens tothe ays of light.
(@) Plane mirror
(© Comex minor, gene of curate
si
A
(© Concave mirror, ceaxe of curvature
shown,
(©) Rectangular, glass prism.
(6 Triangular, glass prism.
The following four diagrams represent
vwaveltonts either before or aftr
Teftaction at «boundary Between ai and
lass. The shaded sections represents the
‘las. Complete the diagrams by drawing
inthe missing incident or refracted
wavetionts. (8)
52, _Aboum oflghtis incident at 50” from ar
fonlo a rectangular slab of plastic of
refractive index 1.20. After ‘revelling
through the plas, the beam passes intoa
slab of plas of reffacive index 1.45.
Calculate the angie at which the beam
emerges from the glass back into the ar.
o
‘53, Draw adiagramto show theertca angle
fara slab of pass. Show the incident end
refracted rays andthe angles of incidence
tnd refraction, Label the normal and the
critical angles)
54, Explain how total intemal reflection
reduces energy lss in single and graded
index optical fires (4)
[Note shat the Syllabus only requires youto know
‘about one of the allowing:
55, Explain how data i recorded on CDs or
DVDs. (5)
156. Outline the energy changes which oceur
‘when you send an eral vi satelite ink
toa fend overseas. (3)
57. Explain how GPS ean be used to locate a
fost explores (5)
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- 2003 James Ruse Chemistry Prelim. Half YearliesDocument15 pages2003 James Ruse Chemistry Prelim. Half YearliesRicha NgNo ratings yet
- Phys Data Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesPhys Data Sheet PDFRicha NgNo ratings yet
- NSB 4U Maths Task 1 2009Document39 pagesNSB 4U Maths Task 1 2009Richa NgNo ratings yet
- UMAT Preperation GuideDocument15 pagesUMAT Preperation GuideRicha NgNo ratings yet
- Yr 11 Chemistry Module 4 Revision TestDocument3 pagesYr 11 Chemistry Module 4 Revision TestRicha NgNo ratings yet
- Infp Profile Healer IdealistDocument22 pagesInfp Profile Healer IdealistJBNo ratings yet
- Japanese Cultural AssignmentDocument2 pagesJapanese Cultural AssignmentRicha NgNo ratings yet
- Summary Questions Preliminary Physics World Communicates (Part A)Document1 pageSummary Questions Preliminary Physics World Communicates (Part A)Richa NgNo ratings yet
- Fight Club NotesDocument7 pagesFight Club NotesRicha NgNo ratings yet
- Conquering Chemistry Module 3 Worksheet 2Document2 pagesConquering Chemistry Module 3 Worksheet 2Richa NgNo ratings yet
- Physics HSC SyllabusDocument85 pagesPhysics HSC Syllabusmeghana_skNo ratings yet
- Conquering Chemistry Module 3 Worksheet 1Document4 pagesConquering Chemistry Module 3 Worksheet 1Richa Ng100% (1)
- Debate: That We Have Made A Better WorldDocument3 pagesDebate: That We Have Made A Better WorldRicha NgNo ratings yet
- Physics HSC SyllabusDocument85 pagesPhysics HSC Syllabusmeghana_skNo ratings yet
- KPOP Dance CompositionDocument1 pageKPOP Dance CompositionRicha NgNo ratings yet
- Brain HSC ENGLISH Advanced Modules Paper July 2014Document14 pagesBrain HSC ENGLISH Advanced Modules Paper July 2014Richa NgNo ratings yet
- Linear Function - Maths in FocusDocument47 pagesLinear Function - Maths in FocusRicha Ng100% (1)
- Jack The Ripper Suspect "George Chapman"Document5 pagesJack The Ripper Suspect "George Chapman"Richa NgNo ratings yet
- Transformation Short StoryDocument2 pagesTransformation Short StoryRicha NgNo ratings yet
- Being Different Short StoryDocument2 pagesBeing Different Short StoryRicha NgNo ratings yet
- CH 6 TrigonometryDocument100 pagesCH 6 TrigonometryMin Chong100% (2)
- How To Write An Annotated BibliographyDocument2 pagesHow To Write An Annotated BibliographyRicha Ng100% (1)
- Baulkham Hills 2010 English Trial Paper 1Document9 pagesBaulkham Hills 2010 English Trial Paper 1Richa NgNo ratings yet
- ST George Girls 2012 English Trial Paper 1Document10 pagesST George Girls 2012 English Trial Paper 1Richa NgNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2008 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument16 pagesJames Ruse 2008 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsRicha Ng50% (2)
- Being DifferentDocument80 pagesBeing DifferentRicha NgNo ratings yet
- Shakespeare's use of dramatic techniques to highlight racism, inequality and power in OthelloDocument2 pagesShakespeare's use of dramatic techniques to highlight racism, inequality and power in OthelloRicha Ng100% (1)
- James Ruse 2009 English Trial Paper 1Document11 pagesJames Ruse 2009 English Trial Paper 1Richa NgNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)