Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Dictionary
Uploaded by
Ann Shen ThianCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Dictionary
Uploaded by
Ann Shen ThianCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Dictionary
The Letter A:
Absolute zero: lowest possible temperature at which gas would have a zero volume.
Absorption spectrum: spectrum of electromagnetic radiation absorbed by matter when radiation of all
frequencies is passed through it.
Acceleration: change in velocity divided by time interval over which it occurred.
Accuracy: closeness of a measurement to the standard value of that quantity.
Achromatic lens: lens for which all light colors have the same focal length.
Action-reaction forces: pair of forces involved in an interaction that are equal in magnitude and opposition
in direction.
Activity: number of decays per second of a radioactive substance.
Adhesion: force of attraction between two unlike materials.
Air resistance: force of air on objects moving through it.
Alpha decay: process in which a nucleus emits an alpha particle.
Alpha particle: positively- charged particles consisting of two protons and two neutrons emitted by
radioactive materials.
Ammeter: device to measure electrical current
Ampere: unit of electric current; one ampere is the flow of one coulomb of charge per second.
Amplitude: in any periodic motion, the maximum displacement from equilibrium.
Angle of incidence: angle between direction of motion of waves and a line perpendicular to surface the
waves are striking.
Angle of reflection: angle between direction of motion of waves and a line perpendicular to surface the
waves are reflected from.
Angle of refraction: angle between direction of motion of waves and a line perpendicular to surface the
waves have been refracted from.
Angular momentum: quantity of rotational motion. For a rotating object, product of moment of inertia and
angular velocity.
Annihilation: process in which a particle and its antiparticle are converted into energy.
Antenna: device used to receive or transmit electromagnetic waves.
Antineutrino: subatomic particle with no charge or mass emitted in beta decay.
Antinode: point of maximum displacement of two superimposed waves.
Archimedes principle: object immersed in a fluid has an upward force equal to the weight of the fluid
displaced by the object.
Artificial radioactivity: radioactive isotope not found in nature. atomic mass unit: unit of mass equal to
1/12 the atomic mass of carbon- 12 nucleus.
Atomic number: number of protons in the nucleus of the atom.
Average acceleration: acceleration measured over a finite time interval
Average velocity: velocity measured over a finite time interval.
The Letter B:
Back-EMF: potential difference a cross a conductor caused by change in magnetic flux.
Band theory: theory explaining electrical conduction in solids.
Baryon: subatomic particle composed of three quarks. Interacts with the strong nuclear force.
Battery: device that converts chemical to electrical energy consisting of two dissimilar conductors and an
electrolyte.
Beat : slow oscillation in amplitude of a complex wave
Bernoullis principle: when a fixed quantity of fluid flows, the pressure is decreased when the flow velocity
increases.
Beta decay: radioactive decay process in which an electron or positron and neutrino is emitted from a
nucleus.
Beta particle: high speed electron emitted by a radioactive nucleus in beta decay. Binding energy: negative
of the amount of energy needed to separate a nucleus into individual nucleons.
Boiling point: temperature at which a substance, under normal atmospheric pressure, changes from a liquid
to a vapor state.
Breeder reactor: nuclear reactor that converts nonfissionable nuclei to fissionable nuclei while producing
energy.
Bubble chamber: instrument containing superheated liquid in which the path of ionizing particles is made
visible as trails of tiny bubbles.
Buoyant force: upward force on an object immersed in fluid.
The Letter C:
Calorimeter: device that isolates objects to measure temperature changes do to heat flow.
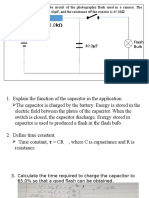
Candela: unit of luminous intensity. Capacitance: ratio of charge stored per increase in potential difference.
Capacitor: electrical device used to store charge and energy in the electrical field.
Capillary action: rise of liquid in narrow tube due to surface tension.
Carnot efficiency:
temperatures.
ideal efficiency of heat engine or refrigerator working between two constant
Centripetal force: force that causes centripetal acceleration.
Chain reaction: nuclear reaction in which neutrons are produced that can cause further reactions.
Charged : object that has an unbalance of positive and negative electrical charges.
Charging by conduction: a process of charging by touching neutral object to a charged object.
Charging by induction: process of charging by bringing neutral object near charged object, then removing
part of resulting separated charge.
Chromatic aberration: variation in focal length of lens with wavelength of light.
Circular motion: motion with constant radius of curvature caused by acceleration being perpendicular to
velocity.
Closed-pipe resonator: cylindrical tube with one end closed and a sound source at other end.
Coefficient of friction: ratio of frictional force and the normal force between two forces.
Coefficient of linear expansion: change in length divided by original length and by temperature change.
Coherent waves: waves in which all are in step; are in phase.
Cohesive force: attractive force between similar substances.
Complementary color: two colors that, when added , produce white light. Two pigments, that when
combined, produce black.
Compound machine: machine consisting of two or more simple machines.
Compton effect: interaction of photons, usually X rays, with electrons in matter resulting in increased
wavelength of X rays and kinetic energy of electrons.
Concave lens: lens thinner in center than edges; a diverging lens.
Concave mirror: converging mirror, one with center of curvature on reflecting side of mirror.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Machine Design Final CoachingDocument17 pagesMachine Design Final CoachingRina Liba0% (1)
- Chapter 6 Pumps and CompressorDocument48 pagesChapter 6 Pumps and CompressorIndiran SelvanNo ratings yet
- The History of The Atom - Theories and ModelsDocument1 pageThe History of The Atom - Theories and Modelsabbychee100% (1)
- Manual Liofilizador BiobaseDocument14 pagesManual Liofilizador BiobaseAlejandro Palomino100% (3)
- APA Format: Mechanics, 35 (3), 105-110Document2 pagesAPA Format: Mechanics, 35 (3), 105-110Ann Shen ThianNo ratings yet
- Experiment M4Document17 pagesExperiment M4Ann Shen ThianNo ratings yet
- TorqueDocument1 pageTorqueAnn Shen ThianNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document10 pagesPresentation 1Ann Shen ThianNo ratings yet
- Chapter15 Direct Current CircuitssssssssDocument19 pagesChapter15 Direct Current CircuitssssssssAnn Shen ThianNo ratings yet
- Physics Theories: Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument4 pagesPhysics Theories: Kinetic Theory of GasesAnn Shen ThianNo ratings yet
- Physics LawsDocument6 pagesPhysics LawsAnn Shen ThianNo ratings yet
- Hot Water Cold WaterDocument12 pagesHot Water Cold WaterAhmed MasoudNo ratings yet
- 2019 2352 AuthorDocument25 pages2019 2352 AuthorSharmila BNo ratings yet
- M.S. Abd-ElhadyDocument8 pagesM.S. Abd-ElhadyNasser93No ratings yet
- Saej 1004 V 002Document6 pagesSaej 1004 V 002Marcos Verissimo Juca de PaulaNo ratings yet
- Class X LP LightDocument1 pageClass X LP LightNiklesh SelvaNo ratings yet
- Topic: Concrete at Early AgeDocument33 pagesTopic: Concrete at Early AgechristianNo ratings yet
- sm5 116Document2 pagessm5 116Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Guia Calibracion TofdDocument47 pagesGuia Calibracion Tofdinspeccion_179116669100% (2)
- Wave Propagation Approach For NDE Using Surface Bonded PiezoceramicsDocument8 pagesWave Propagation Approach For NDE Using Surface Bonded PiezoceramicsBobby GrahamNo ratings yet
- MESAN IOM Manual USA 20140324 PDFDocument20 pagesMESAN IOM Manual USA 20140324 PDFDhananjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Equipos Mini Splits Comfortstar CSC1024CDDocument4 pagesEquipos Mini Splits Comfortstar CSC1024CDAguilar Joel100% (1)
- Thermochemical Properties Estimation For Biodiesel Related MixturesDocument11 pagesThermochemical Properties Estimation For Biodiesel Related Mixturesalberth_carantónNo ratings yet
- Axial Piston Fixed Motor A10FM Axial Piston Plug-In Motor A10FE Series 52Document38 pagesAxial Piston Fixed Motor A10FM Axial Piston Plug-In Motor A10FE Series 52Orlando AriasNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Gas Equation Derivation - RMS Velocity Formula PDFDocument8 pagesKinetic Gas Equation Derivation - RMS Velocity Formula PDFManish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Batch Crystallizer Manual FDocument12 pagesBatch Crystallizer Manual FShoaib PathanNo ratings yet
- RockPhysicsModellingPorousRocksMultiplePoreTypes CriticalPorosity Zhang 2019Document13 pagesRockPhysicsModellingPorousRocksMultiplePoreTypes CriticalPorosity Zhang 2019Maria Fernanda Landa ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document4 pagesTutorial 6ArvinNo ratings yet
- Handouts On DOMDocument10 pagesHandouts On DOMGitanj ShethNo ratings yet
- S10332300-3003 - 0 Process MeasurmentDocument27 pagesS10332300-3003 - 0 Process Measurmentappril26No ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Co2FeAl Heusler Alloy NanoparticleDocument5 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Co2FeAl Heusler Alloy Nanoparticlekarthik kaonNo ratings yet
- What Is The Ozone Layer and Where Is It Located?Document6 pagesWhat Is The Ozone Layer and Where Is It Located?JoseNo ratings yet
- FS 530-11 CI Single Convolution Air Actuator: Purchase Order Data Technical DataDocument1 pageFS 530-11 CI Single Convolution Air Actuator: Purchase Order Data Technical DataMichael AkhramovichNo ratings yet
- MEC-307 Design of Machine Element 6 Semester (3 Year) : Name: Chirag Shetty Urn No: 2020-B-26101996Document18 pagesMEC-307 Design of Machine Element 6 Semester (3 Year) : Name: Chirag Shetty Urn No: 2020-B-26101996Siddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- MGS Capacity CalculatorDocument13 pagesMGS Capacity CalculatorRodolfo MendezNo ratings yet
- Origins of Ferromagnetism in Transition Metal Doped DiamondDocument4 pagesOrigins of Ferromagnetism in Transition Metal Doped DiamondAlcidess R QuispeNo ratings yet
- Pump Jack, PumpsDocument8 pagesPump Jack, PumpsТатьяна НестеренкоNo ratings yet