PROBLEM 1
a.
Variable cost per unit = Total variable costs/ Total units produced
VCPU for x = $420,000/20,000
= $21
VCPU for y = $555,000/30,000
=$18.5
b.
In my view low level management of MT are involved directly in business and it has idea about
what are required to operate for business it calculates budget by plan and schedule of each
department and sums up at final so, based on assumption but budget x is practical so it has
c.
high costs and low sales forecast.
Middle level management are setting total budget and breaking them and allocating them to
each department. Also as an investor senior level determines high sales target minimizing the
d.
cost
Middle level management are the investor and low level management are the staff who are
directly involved in day to day business activities, they have idea about handling business. are
incomplete without one another. So both party should come on agreement to maximize the
profit minimizing expenses.
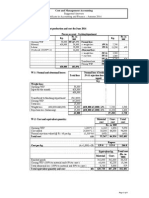
PROBLEM 2
a.
Sales Budget for 1st quarter for WJ Company
No of units
Price per
July
35,000
$85
August
20,000
$85
September
15,000
$85
Total
70,000
$85
October
8,000
$85
November
6,000
$85
unit
Total Sales
$2,975,000
$1,700,000
$1,275,000
$5,950,000
$680,000
$510,000
Total
70,000
October
8,000
November
6,000
Revenue
b.
Sales in
Production Budget for 1st quarter for WJ Company
July
35,000
August
20,000
September
15,000
�Unit
Add:
16,000
12,000
6,400
34,400
4,800
sale)
Total Units
51,000
32,000
21,400
104,400
12,800
required
Less:
28,000
16,000
12,000
56,000
6,400
23,000
16,000
9,400
48,400
6,400
Desired
Inventory
(80% of
following
months
Opening
Inventory
Total
Number of
Units to
produce
c.
Direct Material Budget for 1st quarter for WJ Company
Total Number of Units
July
23,000
August
16,000
September
9,400
Total
48,400
October
6,400
to produce
Polyester used per unit
(in meters)
Total Polyester used
115,000
80,000
47,000
242,000
32,000
(in meters)
�Add: Desired Ending
8,000
4,700
3,200
15,900
(17,000)
(8,000)
(4,700)
(29,700)
the month of July)
Total polyester need to
106,000
76,700
45,500
228,200
purchase (in meters)
Cost of Polyester per
$8
$8
$8
$8
$8
meter
Total Cost of Polyester
Lining materials used
848,000
3
613,600
3
364,000
3
182560
3
per unit (in meters)
Total Polyester used
69,000
48,000
28,200
145,200
19,200
(in meters)
Add: Desired Ending
4,800
2,820
3,200
1,920
(10,200)
(4,800)
(2,820)
(17,820)
63,600
46,020
27,300
136,920
meters)
Cost of lining (per
$2
$2
$2
$2
meter)
Total Cost of linen
127,200
92,040
54,600
273,920
Inventory (10% of
following months
production need)
Less: Opening
Inventory (Given for
Inventory (10% of
following months
production need)
Less: Opening
Inventory (Given for
the month of July)
Total lining materials
need to purchase (in
d.
Direct Labor Budget 1st quarter for WJ Company
July
23,000
August
16,000
September
9,400
Total
48,400
October
6,400
$2
$2
$2
$2
$2
unit
Total no. of
46,000
32,000
18,800
96,800
12,800
hours
Labor
$15
$15
$15
$15
$15
690,000
480,000
282,000
1,452,000
192,000
Total
Number
of
Units
to
produce
Direct labor
cost
per
per
hour
Direct Labor
�cost
e.
Overhead Budget for 1st quarter for WJ Company
Fixed Overheads
Fixed
July
August
September
Total
Overhead
Fixed shop
3,000
3,000
3,000
9,000
e overhead
Fixed
4,000
4,000
4,000
12,000
supervision
Depreciation
Tax
Others
Total Fixed
60,000
5,000
10,000
82,000
60,000
5,000
10,000
82,000
60,000
5,000
10,000
82,000
180,000
15,000
30,000
246,000
maintenanc
Overhead
Variable Overheads
Variable
July
August
September
Total
Overhead
Factory
$46,000
$32,000
$18,800
$96,800
$34,500
$24,000
$14,100
$72,600
$23,000
$16,000
$9,400
$48,400
$92,000
$64,000
$37,600
$193,600
$195,000
$136,000
$79,900
$410,000
supplies ($1 x
hours)
Energy
Supplies
($0.75
hours)
Shop
Maintenance
($
0.5
hours)
Other
Variable ($2x
hours)
Total Variable
�Overhead
Total
$277,500
$218,000
$161,900
$656,000
Manufacturin
g overhead
f.
Selling
Selling general and administration expenses
and
July
August
September
Total
18,000
22,000
10,000
105,000
26,250
52,500
18,000
22,000
10,000
60,000
15,000
30,000
18,000
22,000
10,000
45,000
11,250
22,500
54,000
66,000
30,000
210,000
52,500
57,500
General
expenses
Fixed Salaries
Depreciation
Other
Commission
Shipping
Other
PROBLEM 3
a.
Standard direct material cost per tractor tyre
= standard material quantity x price of standard material
= 15 kgs x $3.50
= $52.50
b. Some advantages of implementing a standard cost system are listed as:
1. It requires less resource and easily be implemented
2. It formulates production policy by determining price, which helps making
estimation for product planning and processing.
3. It helps to find relation between price and usage to overcome wastage.
c.
1- Purchasing Power - find purchasing power by determined price
2- Mixing department supervisor supervise the mixing department
3- Moulding department supervisor supervise moulding department and
maintain standard
4- Cost accountant look after accounting part according to standard cost
5- Product engineer designing product
d.
Material price variance = (AP x AQ) (SP x AQ)
�=AQ (AP SP)
Where,
AP= Actual Price
= $3.44
AQ= Actual Quantity
=75,000
SP= Standard Price =$3.5
= 75,000(3.44-3.5)
=$4500 favorable
Direct labor rate variance = AH (AR-SR)
Where,
AH= Actual Hour
=3220
AR= Actual Rate
=9.65
SR= Standard Rate =10
= 3220 (9.65- 10)
= ($1127) unfavorable
Labor Efficiency variance = SR (AH-SH)
Where,
SR= Standard Rate =10
AH= Actual Hour
=3220
SH= Standard Hour
= 0.75 x 4500
=10(3220-3375)
= ($1,550) unfavorable
Submitted by:
=3,375
�Anil Shahi
Student id: s285516
Subject: Accounting for Managers (PRBA007)
Charles Darwin Melbourne Campus