Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C3 Series Circuits
Uploaded by
ChathunikaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C3 Series Circuits
Uploaded by
ChathunikaCopyright:
Available Formats
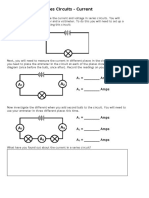
Series Circuits - Current
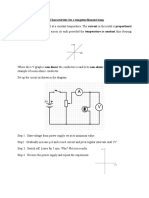
In this lesson you will investigate the current and voltage in series circuits. You will
measure these using an ammeter and a voltmeter. To do this you will need to set up a
series circuit. Start by constructing this circuit:
Next, you will need to measure the current in different places in the circuit. To do this,
you need to place the ammeter in the circuit at each of the places shown on this
diagram (once before the bulb, once after). Record the readings on your ammeter.
A1 = ________ Amps
A2 = ________ Amps
Now investigate the different when you add second bulb to the circuit. You will need to
use your ammeter in three different places this time.
A1 = ________ Amps
A2 = ________ Amps
A3 = ________ Amps
What have you found out about the current in a series circuit?
What has happened to the current in the circuit with the added bulb?
What will happen to the current if we add another cell to the circuit?
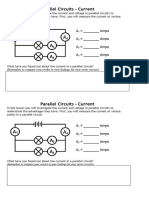
Series Circuits - Voltage
Now you will look at voltage. Voltage is the measure of potential difference. It tells us
how much push is left in a circuit at any point. To measure this, we find the difference
in push between two parts of a circuit using a voltmeter. Because the voltmeter
compares the push in two different places, it must be placed in parallel across the
circuit it does not form part of the circuit itself. This diagram shows how a voltmeter
can be connected across a single bulb in a circuit:
Next, you will need to measure the voltage in different places in the circuit. To do this,
you need to place the voltmeter in the circuit at each of the places shown on this
diagram (once before the bulb, once after). Record the readings on your voltmeter.
V1 = ________ Volts
V2 = ________ Volts
V3 = ________ Volts
What have you found out about the voltage in a series circuit?
You might also like
- 23 Seriesand Parallel CircDocument7 pages23 Seriesand Parallel CircAshley O'Neal50% (2)
- Solar Cell ExperimentDocument11 pagesSolar Cell ExperimentMuhammad Balyan80% (5)
- Circuits investigation combined (копия)Document5 pagesCircuits investigation combined (копия)Никита БабкинNo ratings yet
- C4 Parallel Circuits - CurrentDocument2 pagesC4 Parallel Circuits - CurrentChathunika100% (1)
- Practical SheetsDocument3 pagesPractical SheetsJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Basic CircuitsDocument9 pagesBasic CircuitsMSM7865No ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Circuits Lab - ACt 3Document3 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits Lab - ACt 3NAPHTALI WILLIAMS GONo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Current in Simple DC CircuitDocument6 pagesLab 4 - Current in Simple DC CircuitAbdoul BinJim100% (1)
- Lab Manual-Electrical Instrumentaion and MeasrementDocument28 pagesLab Manual-Electrical Instrumentaion and MeasrementEngr Haseena Jabbar0% (1)
- 1.2.3 Electic CircuitDocument8 pages1.2.3 Electic CircuitNavya ChirutaNo ratings yet
- EMMI Lab PDFDocument31 pagesEMMI Lab PDFSarithareddy AvuluriNo ratings yet
- Circuit StuffDocument6 pagesCircuit StuffStanley ChuNo ratings yet
- Appendix A ElectricKitPrimerDocument4 pagesAppendix A ElectricKitPrimerabdullah abdulNo ratings yet
- Exp 6Document8 pagesExp 6HR HabibNo ratings yet
- DC Machine & TransformerDocument33 pagesDC Machine & TransformerShashank YadavNo ratings yet
- 8c1 Electricity Booklet EditedDocument6 pages8c1 Electricity Booklet EditedJobanpreet RangiNo ratings yet
- DC - CircuitsDocument5 pagesDC - Circuitscoconut borneoNo ratings yet
- Stage 9 Topic 9.2 PhET ActivitiesDocument24 pagesStage 9 Topic 9.2 PhET ActivitiesMinh - 7B2 NGUYỄN HOÀNGNo ratings yet
- Online Lab 4 - DC CircuitsDocument8 pagesOnline Lab 4 - DC CircuitsSardar Rehan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electricity and The Electron: Which Way Does Electricity Flow?Document76 pagesElectricity and The Electron: Which Way Does Electricity Flow?Edgar PeridaNo ratings yet
- Astable MultivibratorDocument3 pagesAstable MultivibratorTushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- 0 Lab6 Astable MultivibratorDocument3 pages0 Lab6 Astable Multivibratorchandu3072002No ratings yet
- Physic Lab Report 1Document7 pagesPhysic Lab Report 1api-455964056No ratings yet
- Ohms Law and Basic Circuit TheoryDocument7 pagesOhms Law and Basic Circuit TheoryMinji LeeNo ratings yet
- Connecting Voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter in A Circuit SunilSaharanDocument2 pagesConnecting Voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter in A Circuit SunilSaharanPankaj Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Series CircuitsDocument26 pagesSeries CircuitsJoel GecaineNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Electric Current, Battery and Bulb: Activity 1-1Document29 pagesWorksheet: Electric Current, Battery and Bulb: Activity 1-1Neil CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Circuit Connection (Series and Parallel)Document4 pagesCircuit Connection (Series and Parallel)iyaryu496No ratings yet
- 1 2 3 A Sim ElectricalcircuitsDocument9 pages1 2 3 A Sim Electricalcircuitsapi-256421289No ratings yet
- Instituto Politécnico Nacional: Practice: 1 "Use of Ohmmeter, Voltmeter and Ammeter in Measurements D.C"Document11 pagesInstituto Politécnico Nacional: Practice: 1 "Use of Ohmmeter, Voltmeter and Ammeter in Measurements D.C"José Emmanuel Martínez CerónNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine PDFDocument40 pagesElectrical Machine PDFAanjenay PandeyNo ratings yet
- EIM 4th SemDocument5 pagesEIM 4th SemVishal Pandey M LE 06No ratings yet
- Lab 12Document6 pagesLab 12api-458764744No ratings yet
- Lab2 Fall2017-1Document9 pagesLab2 Fall2017-1Tony VoNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's Rules and Applying Them: Assignment ViewDocument23 pagesKirchhoff's Rules and Applying Them: Assignment ViewukhyeonNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Lab 1Document5 pagesMechatronics Lab 1daisyhendersonNo ratings yet
- Testing of Continuity in Switches and LoadDocument7 pagesTesting of Continuity in Switches and LoadVikas UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- 0708 ElectricityDocument33 pages0708 ElectricitywalyatNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument7 pagesLab 3 - Series and Parallel CircuitsHảo PhùngNo ratings yet
- EM2 Lab 1Document6 pagesEM2 Lab 1Amit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Basic Measurements: Experiment 1Document8 pagesBasic Measurements: Experiment 1arunkumar_gtsNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument2 pagesOhms LawMurad M. Murad100% (1)
- 1 2 3 A SIM ElectricalCircuits 2Document9 pages1 2 3 A SIM ElectricalCircuits 2HarvirChimaNo ratings yet
- Physics 272 - Lab 8 Circuit Elements: Resistors: Learning GoalsDocument19 pagesPhysics 272 - Lab 8 Circuit Elements: Resistors: Learning GoalsMichael CurryNo ratings yet
- Electrical Workshop Practice: Laboratory ManualDocument30 pagesElectrical Workshop Practice: Laboratory ManualJigar SoniNo ratings yet
- DC Component AnalysisDocument9 pagesDC Component Analysisvivianzhu120No ratings yet
- EE 442 Laboratory Experiment 2 Introduction To The Measurement of Voltage, Current, Resistance and Voltmeter LoadingDocument12 pagesEE 442 Laboratory Experiment 2 Introduction To The Measurement of Voltage, Current, Resistance and Voltmeter LoadingAdrien MunyanezaNo ratings yet
- ECE422L Activity No. 03 Series, Parallel and Series-Parallel Circuits MarasiganAA, UmaliGCDDocument13 pagesECE422L Activity No. 03 Series, Parallel and Series-Parallel Circuits MarasiganAA, UmaliGCDAlexis MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Lab Manual (1.0)Document9 pagesSolar Energy Lab Manual (1.0)RLcircuit0% (1)
- Charge and CurrentDocument13 pagesCharge and CurrentAnonymous N3VvjVSTATNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits Lab Ohms Law CETT 1403Document5 pagesDC Circuits Lab Ohms Law CETT 1403juanm01No ratings yet
- Mi Exp 2Document3 pagesMi Exp 2Dr. Tapas Kumar MajiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Series and Parallel Circuits by Praewa 1108 4Document13 pagesLab Report Series and Parallel Circuits by Praewa 1108 4api-439639600No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument283 pagesElectricityOmar M AlsalmanNo ratings yet
- TLEd 201 - Module 3 Lesson 2Document6 pagesTLEd 201 - Module 3 Lesson 2charmen rogandoNo ratings yet
- Aim of The Experiment: Apparatus RequiredDocument3 pagesAim of The Experiment: Apparatus RequiredGIRISH KUMAR SHARMANo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Year 10 Astronomy Questions For Term 1 ExaminationDocument1 pageYear 10 Astronomy Questions For Term 1 ExaminationChathunikaNo ratings yet
- A Language For MeasurementsDocument3 pagesA Language For MeasurementsChathunikaNo ratings yet
- I-V For Tungstan FilamentDocument2 pagesI-V For Tungstan FilamentChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Electromotive Force E.m.f, Internal Resistance and Terminal P.DDocument1 pageElectromotive Force E.m.f, Internal Resistance and Terminal P.DChathunikaNo ratings yet
- SPA5000 Student Essays: Notes For Students BackgroundDocument2 pagesSPA5000 Student Essays: Notes For Students BackgroundChathunikaNo ratings yet
- S2!3!01 - Distance Time Graphs - SimulationDocument8 pagesS2!3!01 - Distance Time Graphs - SimulationChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 - Formatting Page ContentDocument3 pagesLesson Plan 3 - Formatting Page ContentChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Python Lesson 3Document3 pagesPython Lesson 3ChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Practical InvestigationDocument4 pagesLesson 5: Practical InvestigationChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Introduction To Information TechnologyDocument3 pagesLesson 3: Introduction To Information TechnologyChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Essential Skills For Croom Management Micro - SkillsDocument30 pagesEssential Skills For Croom Management Micro - SkillsChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Tobeabletodrawa Circuit Diagram For A Parallel Circuit To Describe How Parallel Circuits Differ To Series CircuitsDocument10 pagesTobeabletodrawa Circuit Diagram For A Parallel Circuit To Describe How Parallel Circuits Differ To Series CircuitsChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Practical Activity 1) Series Circuit. A) One BulbDocument2 pagesPractical Activity 1) Series Circuit. A) One BulbChathunikaNo ratings yet
- What Are SI Units?: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolDocument1 pageWhat Are SI Units?: Physical Quantity Unit SymbolChathunikaNo ratings yet
- A Language For MeasurementsDocument3 pagesA Language For MeasurementsChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Particle Physics SummaryDocument2 pagesParticle Physics SummaryChathunikaNo ratings yet