Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Questionaire: 1. Briefly, Summarize What AIDS/HIV Is
Uploaded by
dante0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesHIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, which causes HIV infection and AIDS. AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV infection where the immune system is severely damaged. HIV attacks and destroys CD4 cells, making it difficult for the body to fight infections and certain cancers. Without treatment, HIV can destroy the immune system. HIV can be transmitted through blood or semen and from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding. Antiretroviral therapy uses a combination of medications to treat HIV infection, preventing HIV from multiplying and reducing levels in the body to protect the immune system and prevent progression to AIDS. Symptoms of HIV infection may include flu-like symptoms soon after infection or more severe symptoms like weight
Original Description:
test weast coast
Original Title
tras
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, which causes HIV infection and AIDS. AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV infection where the immune system is severely damaged. HIV attacks and destroys CD4 cells, making it difficult for the body to fight infections and certain cancers. Without treatment, HIV can destroy the immune system. HIV can be transmitted through blood or semen and from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding. Antiretroviral therapy uses a combination of medications to treat HIV infection, preventing HIV from multiplying and reducing levels in the body to protect the immune system and prevent progression to AIDS. Symptoms of HIV infection may include flu-like symptoms soon after infection or more severe symptoms like weight
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesQuestionaire: 1. Briefly, Summarize What AIDS/HIV Is
Uploaded by
danteHIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, which causes HIV infection and AIDS. AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV infection where the immune system is severely damaged. HIV attacks and destroys CD4 cells, making it difficult for the body to fight infections and certain cancers. Without treatment, HIV can destroy the immune system. HIV can be transmitted through blood or semen and from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding. Antiretroviral therapy uses a combination of medications to treat HIV infection, preventing HIV from multiplying and reducing levels in the body to protect the immune system and prevent progression to AIDS. Symptoms of HIV infection may include flu-like symptoms soon after infection or more severe symptoms like weight
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Questionaire
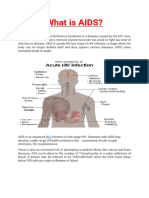
1. Briefly, summarize what AIDS/HIV is.
R: - HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, which is
the virus that causes HIV infection. The abbreviation HIV
can refer to the virus or to HIV infection.
- AIDS stands for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV infection.
2. What does HIV do?
R: HIV attacks and destroys the infection-fighting CD4 cells
of the immune system. Loss of CD4 cells makes it difficult for
the body to fight infections and certain cancers. Without
treatment, HIV can gradually destroy the immune system and
advance to AIDS.
3. Define the following words: blood semen
R: -Blood: the fluid that circulates in the heart, arteries,
capillaries, and veins of a vertebrate animal carrying
nourishment and oxygen to and bringing away waste products
from all parts of the body
- Semen: the sticky, whitish liquid containing sperm that
is produced by a male's sex organs
4. What is mother to child transmission?
R: The spread of HIV from a woman infected with HIV to her
child during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding
5. how can HIV be treated
R: The use of HIV medicines to treat HIV infection is called
antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART involves taking a
combination of HIV medicines (called an HIV regimen) every
day. (HIV medicines are often called antiretrovirals or ARVs.)
ART prevents HIV from multiplying and reduces the level of
HIV in the body. Having less HIV in the body protects the
immune system and prevents HIV infection from advancing to
AIDS.
ART cant cure HIV, but it can help people infected with HIV
live longer, healthier lives. ART also reduces the risk of HIV
transmission.
6. What are the symptoms
R: Soon after infection with HIV, some people have flu-like
symptoms, such as fever, headache, or rash. The symptoms
may come and go for a month or two after infection.
After this earliest stage of HIV infection, HIV continues to
multiply but at very low levels. More severe symptoms of HIV
infection, such as chronic diarrhea, rapid weight loss, and other
signs of opportunistic infections, generally dont appear for
many years.
7. How is AIDS diagnosed?
R: The following criteria are used to determine if a person
infected with HIV has AIDS:
The persons immune system is severely damaged as indicated
by a CD4 count of less than 200 cells/mm3. A CD4 count
measures the number of CD4 cells in a sample of blood. The
CD4 count of a healthy person ranges from 500 to 1,600
cells/mm3.
AND/OR
The person has one or more opportunistic infections
You might also like
- Aids and Hiv Power Point PresentationDocument26 pagesAids and Hiv Power Point PresentationJohn Masefield100% (1)
- Hiv Aids: Presented By: Chavez - Galang - Kaur - Noguera 2DcnDocument24 pagesHiv Aids: Presented By: Chavez - Galang - Kaur - Noguera 2DcnKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Hiv and Endemic DiseasesDocument76 pagesHiv and Endemic Diseasessimon.boatengNo ratings yet
- What Is HIV? ExpandedDocument4 pagesWhat Is HIV? ExpandedAlyannaBesares100% (1)
- Sti, Hiv and Aids: Genelyn A. DiazDocument37 pagesSti, Hiv and Aids: Genelyn A. DiazGenelyn DiazNo ratings yet
- Causes, Incidence, and Risk Factors: HIV DiseaseDocument8 pagesCauses, Incidence, and Risk Factors: HIV DiseaseAminath SamaNo ratings yet
- HIV and AIDS - PDF 2Document26 pagesHIV and AIDS - PDF 2Cheska JunturaNo ratings yet
- Ong, Jan Derrick C. Mutuc, Anne Ysabel T. 3CphDocument31 pagesOng, Jan Derrick C. Mutuc, Anne Ysabel T. 3Cphtrixie_mutucNo ratings yet
- What Is HivDocument28 pagesWhat Is HivIrene Soriano BayubayNo ratings yet
- Prevent HIV TransmissionDocument6 pagesPrevent HIV TransmissionHazel EstayanNo ratings yet
- What Is HIVDocument4 pagesWhat Is HIVTati MaryatiNo ratings yet
- Stage 1: Acute HIV InfectionDocument16 pagesStage 1: Acute HIV Infectionsalsa bilaNo ratings yet
- Causes, Incidence, and Risk Factors: Acquired Immune Deficiency SyndromeDocument7 pagesCauses, Incidence, and Risk Factors: Acquired Immune Deficiency SyndromePriyanka RaniNo ratings yet
- AidsDocument22 pagesAidsVicky Singh100% (2)
- BIO Investigatory PROJECTDocument7 pagesBIO Investigatory PROJECTDaphne SimiNo ratings yet
- Introduction: What Is Hiv and Aids?Document6 pagesIntroduction: What Is Hiv and Aids?Hasib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment AidsDocument11 pagesAssignment AidsYousaf ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Document 12Document4 pagesDocument 12Bhavya PNo ratings yet
- HIV NotesDocument38 pagesHIV NotesMie CorsNo ratings yet
- Lesson Objective: To Explore The Causes and Effects of HIV/AIDSDocument15 pagesLesson Objective: To Explore The Causes and Effects of HIV/AIDSLane StrahanNo ratings yet
- Patient Education PDFDocument12 pagesPatient Education PDFAgustinaNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids The BasicsDocument3 pagesHiv Aids The BasicsHyrum KamandeNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25 Oct 2023Document16 pagesAdobe Scan 25 Oct 2023trishikaginodiaNo ratings yet
- Sameer BeelwalDocument13 pagesSameer Beelwalsameerbeelwal42No ratings yet
- HIV AwarenessDocument35 pagesHIV AwarenessCadine DavisNo ratings yet
- Causes: HIV DiseaseDocument7 pagesCauses: HIV Diseasecsy123No ratings yet
- Biology Project Reports On HIV ADocument5 pagesBiology Project Reports On HIV AManish PatidarNo ratings yet
- HIV Notes: HIV Particles (Grey) Covering A White Blood CellDocument13 pagesHIV Notes: HIV Particles (Grey) Covering A White Blood CellMasha FloreaNo ratings yet
- Definition of AIDS and HIV InfectionDocument7 pagesDefinition of AIDS and HIV InfectionLily SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hiv and Aids PlacinoDocument19 pagesHiv and Aids PlacinoSienaNo ratings yet
- Hiv and Aids PlacinoDocument58 pagesHiv and Aids PlacinoSienaNo ratings yet
- Hiv AidsDocument12 pagesHiv AidsPatriqueNo ratings yet
- Artikel B. InggrisDocument9 pagesArtikel B. Inggrisbb dias0% (1)
- What Is AIDS?Document7 pagesWhat Is AIDS?Bhavya PNo ratings yet
- HIV ResearchDocument1 pageHIV ResearchGiuseppe Riccardo LongoNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesClass 12 Biology Investigatory Projectcomlab223No ratings yet
- Aids:: (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome)Document6 pagesAids:: (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome)Farwa DarNo ratings yet
- Hiv/AidsDocument32 pagesHiv/AidsFred C. MirandaNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids Lecture in Head NursingDocument6 pagesHiv Aids Lecture in Head NursingCelyn Nicole Fernandez RollanNo ratings yet
- H.I.V (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)Document12 pagesH.I.V (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)Adriane TomakinNo ratings yet
- Trabalho de Inglês Org 122824Document13 pagesTrabalho de Inglês Org 122824benildopereiraagostinhoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 June 7Document1 pageActivity 1 June 7Joemar FurigayNo ratings yet
- What Is Hiv?: 3 Yearstrusted Source 1.2 MillionDocument11 pagesWhat Is Hiv?: 3 Yearstrusted Source 1.2 Millionhilja shipenaNo ratings yet
- HIVDocument8 pagesHIVMahmoud SelimNo ratings yet
- Early Effects of HIV: Opportunistic Infections and AIDS-defining IllnessesDocument6 pagesEarly Effects of HIV: Opportunistic Infections and AIDS-defining IllnessesRosdianahNo ratings yet
- Smart Virus & Smarter TubeDocument56 pagesSmart Virus & Smarter TubechitravaniNo ratings yet
- IM. ID Topic 5. Chibueze AfugbuomDocument3 pagesIM. ID Topic 5. Chibueze AfugbuomChibueze AfugbuomNo ratings yet
- What Is HIVDocument14 pagesWhat Is HIVmariam miladNo ratings yet
- HIV Health TalkDocument63 pagesHIV Health TalkLiza GustyaningNo ratings yet
- Estimated HIV/AIDS Prevalence Among Young Adults (15-49) by Country As of 2008. UNAIDS 2008 ReportDocument16 pagesEstimated HIV/AIDS Prevalence Among Young Adults (15-49) by Country As of 2008. UNAIDS 2008 Reportlianghoo94No ratings yet
- Hiv ElisaDocument3 pagesHiv ElisaRasikNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts About HIVDocument2 pagesFast Facts About HIVMr AbdmanNo ratings yet
- Early Effects of HIV: Opportunistic Infections and AIDS-defining IllnessesDocument3 pagesEarly Effects of HIV: Opportunistic Infections and AIDS-defining IllnessesNida KhaerillahNo ratings yet
- Hiva Ids InformationDocument7 pagesHiva Ids InformationRohits2605No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Ambernath BiologyDocument39 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Ambernath BiologyROHIT SIHRANo ratings yet
- What Is Hiv?: Aids and HivsDocument8 pagesWhat Is Hiv?: Aids and Hivscarlous brathwateNo ratings yet
- HIV and Its TreatmentDocument24 pagesHIV and Its Treatmentaathira_kNo ratings yet
- By: Axel Jusuf (1461050177)Document9 pagesBy: Axel Jusuf (1461050177)AxelJusufNo ratings yet