Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lagrange Polynomials 1-D
Uploaded by
Gourav SrustiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lagrange Polynomials 1-D
Uploaded by
Gourav SrustiCopyright:
Available Formats
M.
Vable
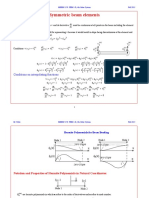
MEEM 5170: Lagrange Polynomials 1-D
Fall 2015
Lagrange Polynomials 1-D
u2
u1
x
x1 Node 1
Node 2
x2
x1 Node 1
x2
linear element
Linear Element: u x C 1 + C 2 x
u x1 = C1 + C2 x1 = u
i 1 u i L i x j
uj
Node 3
x xj
i j
u x2 = C1 + C2 x2 = u
x x2
x 1 x 2
L1 x ----------------
2
ux
i 1 u i L i x
1
0
i j
Li x j
Li x j=1 ------------------ xi xj
2
u L x
i 1 i i
Quadratic Element: u x = C 1 + C 2 x + C 3 x 2
n
Node 2
u3
quadratic element
x x2
x x1
u x u 1 ---------------- u 2 ---------------- u 1 L1 x u 2 L2 x
x 1 x 2
x 2 x 1
u xj
u2
u1
ij
x x1
x 2 x 1
L2 x ----------------
M. Vable
MEEM 5170: Lagrange Polynomials 1-D
Node 1
Node 2
Node 1
Node 2
Fall 2015
Node 3
L1(x)
L1(x)
x
1
L2(x)
x
1
L2(x)
x x2 x x3
x 1 x 2 x 1 x 3
L1 x ---------------- ----------------
x x1 x x3
x 2 x 1 x 2 x 3
L2 x = ---------------- ----------------
L3(x)
(a)
x x1 x x2
x 3 x 1 x 3 x 2
L3 x ---------------- ----------------
(b)
Continuity of displacement
Discontinuity of derivative
u2
u1
1
2
element 1
u3
u2
u1
u3
element 1
element 2
Natural Coordinates
Non-dimensional coordinates are called natural coordinates in finite element method.
u4
u5
4
element 2
M. Vable
MEEM 5170: Lagrange Polynomials 1-D
= xL
01
Node 1
1 1
Node 2
Node 1
Node 2
Natural coordinates used for approximating the geometry as well as the generalized displacements.
Curved rod: x =
= 2x L
or
Fall 2015
i 1 x i L i
y =
i 1 y i Li
Isoparametric elements are elements in which geometric transformation and the generalized displacements are approximated by
the same interpolation functions.
Natural coordinates used in numerical integration.
Linear
Quadratic
L1 1
L1 = 1 1 2
L2 =
L2 = 4 1
L3 = 1 2
M. Vable
C1
MEEM 5170: Lagrange Polynomials 1-D
Obtain the quadratic Lagrange polynomial using the natural coordinate shown below.
Node 1
Node 2
= 1
Node 3
= 1
Fall 2015
You might also like
- MEEM 5170: 4th Order Beam Bending FEMDocument7 pagesMEEM 5170: 4th Order Beam Bending FEMGourav SrustiNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument1 pageTerm PaperGourav SrustiNo ratings yet
- Ritz MethodDocument4 pagesRitz MethodGourav SrustiNo ratings yet
- FEM 1d 2nd Order SystemDocument13 pagesFEM 1d 2nd Order SystemGourav SrustiNo ratings yet
- Conforming and Non-Conforming ElementsDocument4 pagesConforming and Non-Conforming ElementsGourav Srusti0% (1)
- Homework#2p1 v3Document3 pagesHomework#2p1 v3Gourav SrustiNo ratings yet
- LectureNotes 02Document6 pagesLectureNotes 02Gourav SrustiNo ratings yet
- LectureNotes FirsthalfDocument49 pagesLectureNotes FirsthalfGourav SrustiNo ratings yet
- CH5Document50 pagesCH5Adel Abdel-ghaffarNo ratings yet
- Degrees of FreddomDocument5 pagesDegrees of FreddomGourav SrustiNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Element For Second Order System in 2-DDocument8 pagesRectangular Element For Second Order System in 2-DGourav SrustiNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)