Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ivfluidchart PDF
Uploaded by
Caleb FellowesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ivfluidchart PDF
Uploaded by
Caleb FellowesCopyright:
Available Formats
See also IV fluid guidelines at www.rch.org.au/clinicalguide/cpg.cfm?doc_id=5203, contact email: trevor.duke@rch.org.au or mike.south@rch.org.
au
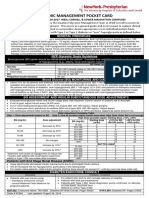
Intravenous fluids
Hourly maintenance intravenous fluid requirements
[Resuscitation bolus (Normal saline): 10-20 ml/kg]
Weight (kg)
10
12
14
16
20
30
40
50
60
70
ml/hr
16
24
32
40
44
48
52
60
70
80
90
100
100
Reminders
1. Check weight of patient
2. Check maintenance fluids infusion rate according to weight. Remember that the maintenance fluid volume will need to be reduced in many unwell children, especially
children with meningitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, some surgical problems and many children with hyponatraemia.
3. Consider why the patient needs IV fluid. If a child is prescribed anything other than a 0.9% or 0.45% NaCl solution, ask why.
4. Check the written order
5. If in doubt about fluids please ask, call a paediatric registrar, a consultant or the ICU
Lactate Ca++
Type of fluid
Comment
Na+
ClK+
Glucose
Monitor
(mmol/L)
See also Clinical Practice Guidelines Intravenous Fluids
(mmol/L)
(mmol/L)
(mmol/L)
(mmol/L)
(gram/L)
0.9% NaCl
(Normal Saline)
0.9% NaCl with 5% dextrose
(Normal saline with glucose)
0.45% NaCl with 5% dextrose
and KCl 20 mmol/l
Isotonic, contains no glucose
Use for initial volume resuscitation, e.g.
septic shock, trauma.
Use as maintenance fluid for suspected
meningitis, acute neurological conditions,
where IV fluids are used for gastroenteritis or
when the serum sodium is low.
Use for mildly to moderately unwell children,
where serum Na+ and K+ are normal.
150
150
150
150
75
75
20
Use for mildly or moderately unwell children
if serum K+ is elevated.
75
75
Isotonic, no glucose. Often used intraoperatively and post-operatively.
Used in pre-term babies and neonates in
NNU.
Sometimes used for pre-term neonates, for
treatment of hypoglycaemia and inherited
metabolic disorders. Not a maintenance
fluid. See hypoglycemic guidelines.
Hypertonic
Used only for treatment of hypoglycaemia.
Not a maintenance fluid.
See hypoglycemic guidelines
130
110
30
30
30
100
IV fluids do not provide
adequate nutrition. Give
oral or enteral feeds
whenever you can.
150-200
1g glucose = 16.7kJ
Very Hypertonic Not used on wards.
Not a maintenance fluid.
Given as a small bolus if hypoglycemic
50
(1/2 Normal saline with glucose
and no potassium)
Hartmann's solution
0.18% NaCl and 4% dextrose
(4% and 1/5th normal saline)
10% glucose in water
Monitor blood glucose and
serum sodium
15% or 20% glucose in water
Give only via a central line as
a 1-2ml/kg bolus for
hypoglycaemia. Monitor
blood glucose
25% or 50% glucose in water
Never as an infusion (Only
used in ICU and NNU at low
vol eg. 1-2mls/hr via central
line)
Other fluids
See hypoglycemic guidelines on intranet
Check carefully with drug dose book
(formulary) and intranet guidelines
50
2
Clinical signs of
dehydration and overhydration
Weigh prior to
commencement of IV
therapy, then 6-8 hours
after infusion
commenced, then at
least daily.
Electrolytes and
glucose should be
measured before
infusion and then at
least daily (up to 4-6
hourly in very unwell
children).
50
(1/2 Normal saline with glucose
and potassium)
0.45% NaCl with 5% dextrose
40
See nutrition guidelines for
recommended daily energy
intake
-
250-500
Fluid orders should be
checked and re-written
daily
You might also like
- HAAD Exam SyllabusDocument2 pagesHAAD Exam SyllabusAnuRavipati75% (4)
- DXC Select BrochureDocument18 pagesDXC Select BrochurePradyut TiwariNo ratings yet
- COE WorksheetDocument16 pagesCOE WorksheetiloveraynaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument2 pagesHypertensionheadseNo ratings yet
- Case Study HemodialysisDocument5 pagesCase Study HemodialysisCharmaine del RosarioNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument19 pagesSepsisapi-308355800No ratings yet
- 2017 05 GC Pocket CardDocument2 pages2017 05 GC Pocket Cardapi-312241089No ratings yet
- HyponatremiaDocument26 pagesHyponatremiapreethi.rayan455No ratings yet
- Isbi Practice Guidelines For Burn Care Part 2 2018 PDFDocument90 pagesIsbi Practice Guidelines For Burn Care Part 2 2018 PDFAstri SuyataNo ratings yet
- Liverpool SDL CRRTDocument62 pagesLiverpool SDL CRRTupul85No ratings yet
- Infective Endocarditis: A Multidisciplinary ApproachFrom EverandInfective Endocarditis: A Multidisciplinary ApproachArman KilicNo ratings yet
- 2017 Hypertension Webinar PDFDocument81 pages2017 Hypertension Webinar PDFMira Mariana UlfahNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Case Study 1 Fall 2014 JeremyDocument5 pagesHeart Failure Case Study 1 Fall 2014 Jeremyapi-264487290No ratings yet
- Acid Base EquationsDocument21 pagesAcid Base EquationsBen JonesNo ratings yet
- INOTROPIC SUPPORT (Autosaved)Document23 pagesINOTROPIC SUPPORT (Autosaved)Bindhu RaniNo ratings yet
- Perioperative AnaphylaxisDocument23 pagesPerioperative AnaphylaxiscrackernetNo ratings yet
- Nil by Mouth Best Practice and Patient EducationDocument3 pagesNil by Mouth Best Practice and Patient EducationGrace SimarmataNo ratings yet
- Esrd FinalDocument26 pagesEsrd FinalCreighton A. BayonganNo ratings yet
- Seizures in Children JULIO 2020Document29 pagesSeizures in Children JULIO 2020Elizabeth HendersonNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesDocument7 pagesManagement of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesdaypranitaNo ratings yet
- ENT Emergencies LectureDocument29 pagesENT Emergencies LectureThea Bertea100% (1)
- Report2014 PDFDocument332 pagesReport2014 PDFShareDialysis100% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance QuizDocument2 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalance QuizteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Adults With Suspected Epiglottitis - Supraglottitis Guidelines For The Management ofDocument2 pagesAdults With Suspected Epiglottitis - Supraglottitis Guidelines For The Management ofAlexandros MegasNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure in Children: Mihai Craiu MD PHD IomcDocument41 pagesRenal Failure in Children: Mihai Craiu MD PHD IomcIonicǎ AdrianNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrestDocument49 pagesCardiac Arrestpraveenkumar biradarNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrestDocument54 pagesCardiac ArrestIdha FitriyaniNo ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument27 pagesRenal FailureMae DacerNo ratings yet
- Technologies Designed To Help Improve Patients OutcomeDocument53 pagesTechnologies Designed To Help Improve Patients OutcomeHarby Ongbay AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- Febuxostat (Uloric), A New Treatment Option For Gout: Carmela Avena-Woods Olga Hilas Author Information Go ToDocument9 pagesFebuxostat (Uloric), A New Treatment Option For Gout: Carmela Avena-Woods Olga Hilas Author Information Go ToAnadi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument23 pagesPeritoneal Dialysismakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument17 pagesPeritoneal DialysisIan Benedict GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Programs: Lactated Ringers (Also Known As LR, Ringers Lactate, or RL)Document5 pagesNursing Programs: Lactated Ringers (Also Known As LR, Ringers Lactate, or RL)KiaBlancheTahud100% (1)
- Observation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. RoaquinDocument15 pagesObservation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. Roaquineljhayar_18No ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis: Irish Nicole Dela Cruz Gessel Ann BoguenDocument79 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: Irish Nicole Dela Cruz Gessel Ann BoguenIrish Nicole DCNo ratings yet
- Renal Transplant: 1) Steps Involved in Kidney TransplantationDocument4 pagesRenal Transplant: 1) Steps Involved in Kidney TransplantationNadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid CommonDocument1 pageIV Fluid CommonmydewyboyNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection FractionDocument19 pagesHeart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fractioncosmin balanNo ratings yet
- Strategies To Prevent Central Line Associated Bloodstream Infections in Acute Care Hospitals 2022 UpdateDocument17 pagesStrategies To Prevent Central Line Associated Bloodstream Infections in Acute Care Hospitals 2022 Updatealejandro montesNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument2 pagesAnemiaLazeh MeNo ratings yet
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Pregnancy (Dengan Foto Punya DR RositaDocument9 pagesAntiphospholipid Syndrome and Pregnancy (Dengan Foto Punya DR RositadidongNo ratings yet
- 13.knowledge and Practices of Universal Precautions Among Basic B. Sc. Nursing StudentsDocument10 pages13.knowledge and Practices of Universal Precautions Among Basic B. Sc. Nursing StudentsPutri Alin Kende RiaralyNo ratings yet
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument9 pagesDeep Vein ThrombosisGladys YaresNo ratings yet
- Icu Sop: TOPIC: Length of Stay in ICUDocument5 pagesIcu Sop: TOPIC: Length of Stay in ICURohit RajeevanNo ratings yet
- Anemia Anemia Describes The Condition in Which The Number of Red Blood Cells in The Blood Is Low. Probability & StatisticsDocument7 pagesAnemia Anemia Describes The Condition in Which The Number of Red Blood Cells in The Blood Is Low. Probability & StatisticsSahara GalayNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Case PresentationDocument32 pagesHypertension Case PresentationAnnaMaeGacutanMarantanNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy: Housemanship Training Programme Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive CareDocument55 pagesOxygen Therapy: Housemanship Training Programme Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive CaretorreslysNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Encephalopathy and ComaDocument19 pagesHepatic Encephalopathy and ComaJas Castro JoveroNo ratings yet
- Australian Diabetes Society Guidelines For Routine Glucose Control in HospitalDocument70 pagesAustralian Diabetes Society Guidelines For Routine Glucose Control in HospitalYovan PrakosaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Shock PIPODocument25 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Shock PIPOFitri NurullahNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Fluid Management in ChildrenDocument31 pagesPerioperative Fluid Management in ChildrenRashmi SahaNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure PresentationDocument65 pagesRenal Failure PresentationBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Dka Vs Hhs Edit 1Document25 pagesDka Vs Hhs Edit 1Razeen RiyasatNo ratings yet
- Kidney TransplantDocument11 pagesKidney TransplantPrincess Xzmae RamirezNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia and HypernatremiaDocument39 pagesHyponatremia and HypernatremiaManhal A AbdulkaderNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis: NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Injury, Risk For (Loss of Vascular Access) Risk Factors May IncludeDocument10 pagesHemodialysis: NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Injury, Risk For (Loss of Vascular Access) Risk Factors May IncludeChevelle Valenciano-GaanNo ratings yet
- Kidney Stones 1Document4 pagesKidney Stones 1mynksharma100% (1)
- Haad Dataflow GuideDocument16 pagesHaad Dataflow Guidehady920100% (4)
- Background: Open Fractures Compartment SyndromeDocument1 pageBackground: Open Fractures Compartment Syndromehady920No ratings yet
- Postpartum-First 6 Weeks After: ChildbirthDocument22 pagesPostpartum-First 6 Weeks After: Childbirthhady920100% (1)
- Narrative ChartDocument5 pagesNarrative Charthady920100% (1)
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument3 pagesParkinson's Diseasehady920No ratings yet
- NCLEX - Study Points 1Document2 pagesNCLEX - Study Points 1hady920No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Nausea & VomitingDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Nausea & Vomitingderic87% (47)
- Fluid Management-OnlineDocument24 pagesFluid Management-Onlinehady920No ratings yet
- PrayersDocument2 pagesPrayersshariqhkNo ratings yet
- Haad Dataflow GuideDocument16 pagesHaad Dataflow Guidehady920100% (4)
- Experience Letter Salary Sheet Experience LetterDocument1 pageExperience Letter Salary Sheet Experience LetterNajmul HasanNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument25 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalancehady920No ratings yet
- Types of SolutionDocument10 pagesTypes of Solutionhady920No ratings yet
- Go With The Flow of Chest Tube Therapy: by Arlene M. Coughlin, RN, MSN, and Carolyn Parchinsky, RN, MADocument14 pagesGo With The Flow of Chest Tube Therapy: by Arlene M. Coughlin, RN, MSN, and Carolyn Parchinsky, RN, MAhady920100% (1)
- 17-19 Late AdulthoodDocument52 pages17-19 Late AdulthoodAlen AlanoNo ratings yet
- Common Emergency DrugsDocument48 pagesCommon Emergency Drugshady920100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument67 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Pinoyalfred31191% (23)
- Care of Chest Tubes Closed Chest Drainage SystemDocument21 pagesCare of Chest Tubes Closed Chest Drainage Systemhady920100% (2)
- Chest Tubes & Water Seal DrainageDocument13 pagesChest Tubes & Water Seal Drainagehady920100% (2)
- Physical AssessmentDocument8 pagesPhysical AssessmentJ. ishtelleNo ratings yet
- Chest Tubes & Water Seal DrainageDocument13 pagesChest Tubes & Water Seal Drainagehady920100% (2)
- Physical AssessmentDocument6 pagesPhysical AssessmentLondera BainNo ratings yet
- Business Education Vaccine Info For Filling OutDocument61 pagesBusiness Education Vaccine Info For Filling OutReniljay abreoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal KBDocument7 pagesJurnal KBAnahNo ratings yet
- Health Booklet 2014Document68 pagesHealth Booklet 2014QwesxzNo ratings yet
- Nurs FPX 4050 Assessment 4 Final Care Coordination PlanDocument6 pagesNurs FPX 4050 Assessment 4 Final Care Coordination PlanEmma WatsonNo ratings yet
- RTSO Airwaves Summer 2014Document68 pagesRTSO Airwaves Summer 2014rtsocanadaNo ratings yet
- Study. RSUD Soetomo Surabaya. Vol. 26. No 3. Universitas AirlanggaDocument2 pagesStudy. RSUD Soetomo Surabaya. Vol. 26. No 3. Universitas AirlanggaKhoirunnisaSPazkaNo ratings yet
- Great Eastern Life Newsletter - CEO MessageDocument3 pagesGreat Eastern Life Newsletter - CEO MessageAnura BirdNo ratings yet
- Post-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPost-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanCyrus De AsisNo ratings yet
- The Medical Plan That You For: Rewards Living HealthyDocument25 pagesThe Medical Plan That You For: Rewards Living HealthyErik RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine Deformity Surgery by Christopher P Ames K. Daniel Riew Justin S. Smith Kuniyoshi AbumiDocument206 pagesCervical Spine Deformity Surgery by Christopher P Ames K. Daniel Riew Justin S. Smith Kuniyoshi AbumiDaniel AraujoNo ratings yet
- Sample Stakeholder Engagement PlanDocument3 pagesSample Stakeholder Engagement PlanMonique Ruste100% (2)
- Live Online Review - May 2021 Weekdays Class - Comprehensive Phase - UpdatedDocument2 pagesLive Online Review - May 2021 Weekdays Class - Comprehensive Phase - UpdatedJohnmer AvelinoNo ratings yet
- Grafik Absensi KaryawanDocument3 pagesGrafik Absensi KaryawansolichunNo ratings yet
- Pathology Competency Evaluation FormDocument2 pagesPathology Competency Evaluation FormSarahNo ratings yet
- Treating OAPS GalarzaDocument8 pagesTreating OAPS GalarzaCarlos Durán NoritzNo ratings yet
- Kesesuaian Anamnese Kefarmasian Oleh Apo 833182d5 PDFDocument5 pagesKesesuaian Anamnese Kefarmasian Oleh Apo 833182d5 PDFelvinaNo ratings yet
- Annex C Notification Form MiV NDocument5 pagesAnnex C Notification Form MiV NVincent JosephNo ratings yet
- SOMEWHERE TO TURN Meeting The Mental Health Needs of Adoptive and Guardianship Families. p26Document40 pagesSOMEWHERE TO TURN Meeting The Mental Health Needs of Adoptive and Guardianship Families. p26Abdi ChimdoNo ratings yet
- ICU Admission Discharge Triage GuidelinesDocument50 pagesICU Admission Discharge Triage GuidelinesNindya Anggi SinantaraNo ratings yet
- Acutes by LucDocument7 pagesAcutes by Lucaldodias100% (1)
- COPARDocument5 pagesCOPAREdezer CariasNo ratings yet
- Personal ProfileDocument2 pagesPersonal ProfileSeema ChapagainNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ON: TopicDocument6 pagesLesson Plan ON: TopicVishal DubeyNo ratings yet
- Nurse Call SystemDocument5 pagesNurse Call SystemJamal BanziNo ratings yet
- Aramark E-Portfolio Resume - Dena ElbroodyDocument1 pageAramark E-Portfolio Resume - Dena Elbroodyapi-346487179No ratings yet
- State Wise HospitalDocument22 pagesState Wise HospitalShahbaz AlamNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6214 Assessment 1 Technology Needs AssessmentDocument6 pagesNURS FPX 6214 Assessment 1 Technology Needs Assessmentfarwaamjad771No ratings yet
- CMS Statement of Deficiencies On Parkland After Failing Reinspection On 8/31/11 Printed On 9/9/11Document164 pagesCMS Statement of Deficiencies On Parkland After Failing Reinspection On 8/31/11 Printed On 9/9/11Marshall HayworthNo ratings yet