Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wireless Systems and Standards: Yimin Zhang, Ph.D. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Villanova University
Uploaded by
Sumanth MopideviOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wireless Systems and Standards: Yimin Zhang, Ph.D. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Villanova University
Uploaded by
Sumanth MopideviCopyright:
Available Formats
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Chapter 11
Wireless Systems and Standards
Yimin Zhang, Ph.D.
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering
Villanova University
http://yiminzhang.com/ECE8708
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Evolution Overview
Wireless
Japan
US
Europe
Europe
TACS
NMT450
AMPS
1st
Cordless
US
Japan
CT03
NMT900 NETZ-C
RADIOCOM
2nd
D-AMPS/IS-54
PDC
PCS 1900
CDMA/IS-95
GSM 900
GSM 1900
DECT
GSM 1800
Paging
PACS
PHS
3G
IMT-2000
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Terminology
AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System): North American cellular
phone standard, operates in 800 MHz and 900 MHz bands. About
85% of AMPS subscribers are in the U.S.
GSM (Groupe Speciale Mobile): Digital cellular standard in Europe.
DCS 1800 (Digital Communication Service): an extension of GSM
standard, operates at 1800 MHz.
DECT (Digital European Cordless Telecommunications): a cordless
system supporting voice and data.
NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone): one of the first cellular systems,
operates in 450 MHz and 900 MHz bands. Used in Scandinavian
countries (Norway, Sweden, Finland).
TACS (Total Access Communications System): derivative of AMPS
developed in U.K. 91% of TACS subscribers come from Europe.
TACS/NTT: Japanese digital transmission scheme, operates in
800 MHz and 1500 MHz bands; based on TDMA/FDD.
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Generations of Mobile Systems
1st Generation (1G): Analog Transmission
2nd Generation (2G): Digital Transmission
AMPS
TACS (ETACS)
NMT
GSM
CT2, CT3 (Cordless Telephone)
DECT
CDMA
3rd Generation (3G): Unification of technologies
FPLMTS (Future Public Land Mobile Telecommunication Systems)
UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecom System)
cdma2000, WCDMA (Wideband CDMA)
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
First Generation - History
AMPS: Advance Mobile Phone System
-
1978 First cellular experimental analog
systems - AT&T AMPS system
(Chicago, IL); channel spacing is 30
KHz
1983 First commercial analog system
at Chicago, IL; total 40 MHz spectrum
in 800 MHz band
1989 Additional 10 MHz (extended
spectrum) band
- 1991 Motorola developed AMPS-like
system N-AMPS (narrowband AMPS);
channel spacing is 10 KHz
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
First Generation - History
ETACS: European Total Access
Communication System, or
TACS
-
Developed in Mid-1980s; virtually
identical to AMPS
The channel spacing is 25 KHz
The mobile identification number
(MIN) accommodates country
codes.
N-AMPS developed by Motorola
(3*capacity, still analog) in 1991
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation USDC/ CDMA/GSM
IS-54 dual mode digital cellular in 1990, also known as USDC
(United States Digital Cellular), D-AMPS (Digital AMPS), and NADC
(North American Digital Cellular)
TDMA/FDD
Support 3 full-duplex users on each AMPS channel
IS-136 in 1994 (against competition from PCS1900)
Design objectives:
Higher Capacity
Backward compatibility
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation USDC/CDMA/GSM
Qualcomm CDMA proposal in 1989 and IS-95 in 1992
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication)
Design objectives:
- Standardized Pan-European mobile system
- Equivalent traffic capacity to pre-existing 25kHz European
analog cellular bandwidth (200kHz/8)
- Wireless counterpart for ISDN
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation Share
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
10
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
11
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
User 1
Slot 1
Slot 4
User 2
Slot 2
Slot 5
User 3
Slot 3
Slot 6
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
12
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
FACCH:
FACCH:Fast
FastAssociated
Associated
Control
ControlChannel
Channel
--important
importantcontrol
controlof
of
specialized
specializedtraffic
trafficdata
data(e.g.,
(e.g.,
handoff)
handoff)
--within
withindata
datatraffic
trafficchannel
channel
Data: total 260 bits
Sync: 28 bits
SACCH: 12 bits - Slow Associated Control Channel
- provides a signaling channel in parallel with the digital speech
- carries various control and supervisory messages between the
subscriber unit and the base station
- used by the mobile unit to report the results of signal strength
measurement of neighboring base station
CDVCC: 12 bits Coded Digital Verification Color Code
- 8 bit information + 4bit coding
- MS must receive, decode, and retransmit the same CDVCC
Guard: 6 bits - guard bits to compensate for timing differences
Ramp: 6 bits - ramp bits to allow for power ramp up of RF signal
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
13
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Data: total 260 bits
Sync: 28 bits
SACCH: 12 bits - Slow Associated Control Channel
FACCH: Fast Associated Control Channel
- within data traffic channel
CDVCC: 12 bits Coded Digital Verification Color Code
- 8 bit information + 4bit coding
- MS must receive, decode, and retransmit the same CDVCC
Reserved: 12 bits
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
14
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation USDC
Channel coding:
uncoded information: 77 class-1 bits and 82 class-2 bits.
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
15
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation USDC
Interleaving
Use two speech frames x and y.
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
16
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation USDC
Modulation
48.6 kbps over 30 kHz band
1.62 bps/Hz spectral efficiency
/4-DQPSK is used.
Roll-off factor: 0.35
Equalization
symbol rate : 24.3 ksps
maximum rms delay is 4.12s without equalization
Probability that rms delay exceeds 4s is 25% of the location in 4 cities
DFE equalizer: 4 feedforward taps (1/2 symbol spacing), 1 feedback
tap
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
17
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation USDC
IS-136 Final USDC standard
provide new features and services to be competitive with IS-95 and
GSM.
- short message capability
- private, user group
- sleep mode
- control channel changes from 10 kbps FSK to 48.6 kbps DQPSK
- IS-54 and IS-136 terminals are not compatible
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
18
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
-
Before GSM, European countries used different cellular standards
throughout Europe.
GSM is now the worlds most popular standard for 2nd generation
wireless communications in the world.
First introduced in 1991.
Several non-European countries in South America, Asia, Australia
adopted GSM.
GSM uses removable Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) to store
information of the subscribers identification information, network and
countries where the subscriber is entitled to service, private keys.
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
19
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
20
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
G S M S y s te m
m o b ile
M o b ile S ta tio n
M o b ile E q u ip m e n t
S u b s c rib e r Id e n tity M o d u l (S IM )
F ix e d
R a d io N e tw o rk
< B a s e S ta tio n S u b s y s te m > (B S S )
B a s e T ra n s c e iv e r S ta tio n (B T S )
B a s e S ta tio n C o n tro lle r (B S C )
M o b ile S w itc h in g N e tw o rk
< S w itc h in g a n d M a n a g e m e n t S u b s y s te m > (S M S S )
M o b ile S w itc h in g C e n te r (M S C )
G a te w a y M o b ile S w itc h in g C e n te r (G M S C )
In te rn a tio n a l S w itc h in g C e n te r (IS C )
H o m e L o c a tio n R e g is te r (H L R )
V is ito r L o c a tio n R e g is te r (V L R )
M a n a g e m e n t N e tw o rk
< O p e ra tio n a n d M a in te n a n c e S u b s y s te m > (O M S S )
O p e ra tio n a n d M a in te n a n c e C e n te r (O M C )
E q u ip m e n t Id e n tity R e g is te r (E IR )
A u th e n tic a tio n C e n te r (A U C )
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
21
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
BTS: Provide the radio channel for signaling and user data traffic in this cell
BSC: Control of BTSs; Frequency administration
MSC : The major tasks of an MSC are routing incoming and outgoing calls and
the assignment of user channels on the A-interface.
HLR : An HLR can be regarded as a large database that administers the data of
literally hundreds of thousands of subscribers.
VLR : A VLR contains subscriber data, but only part of the data in the HLR and
only while the particular subscriber roams in the area for which theVLR is
responsible.
ISC Connections to other mobile or international networks are mostly routed
over the International Switching Center (ISC) of the respective country.
OMCAdministration and commercial operation; Security management;
Network configuration, performance management
AUCConfidential data and keys are stored or generated in AUC
EIRStores the serial numbers of the terminals
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
22
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
-
GSM originally used two 25 MHz cellular bands.
GSM uses FDD and a combination of TDMA and FHMA schemes to
provide multiple access to mobile users.
Forward and reverse frequency bands are divided into 200 kHz wide
channels, called ARFCN (Absolute Radio Frequency Channel
Numbers).
Each channel is time shared between as many as 8 subscribers using
TDMA.
Guard band of 100 kHz at each end; total 125 channels (about 1000
users).
ARFCN+TS constitutes physical channel.
Data rate: 270.833 kbps per channel, 33.854 kbps per user
Modulation: GMSK modulation with BT=0.3
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
23
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
24
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
25
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
26
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
27
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH)
Broadcast Channel
(BCH)
<Downlink>
Synchronization Channel (SCH)
Signaling
Frequency Correction Channel (FCH)
Common Control
Channel
(CCCH)
<Down- or Uplink>
Random Access Channel (RACH) <Uplink>
Access Grant Channel (AGCH) <Downlink>
Paging Channel (PCH) <Downlink>
Standalone Dedicated Control Channel (SDCCH)
Dedicated Control
Channel
(DCCH)
<Bidirectional>
Traffic
Traffic Channel
(TCH)
<Bidirectional>
Associated Control
Channel
(ACCH)
Slow Associated Control Channel (SACCH)
Fast Associated Control Channel (FACCH)
Full-rate Channel (Bm)
Half-rate Channel (Lm)
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
28
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
29
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
30
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation GSM
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
31
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Second Generation CDMA
-
Qualcomm developed CDMA/AMPS dual mode phone in 1994.
As of 2001, there are over 80 million CDMA subscribers worldwide.
Each IS-95 channel occupies 1.25 MHz on each one way link.
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
32
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
CDMA
24x16 array
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
33
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
CDMA
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
34
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
35
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Migration Path 2G, 2.5G, 3G
2000
Japan
PDC
Europe
GSM
2001
2002
2003
W-CDMA
GPRS
EDGE
HSCSD
America
AMPS/D-AMPS
IS-95A
2G System
3G System
D-AMPS+
IS-95B
CDMA2000
Easy upgrade
Upgrade requiring new modulation
Upgrade requiring entire new radio system
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
36
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Evolution
2G Handsets
This is the current digital mobile phone
technology most of us are using.
Features includes:
Phone calls
Voice mail
Receive and send SMS
Speed: 9.6 kilobits/sec
Time to download a 4 min MP3 song: 50 min
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
37
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Evolution Cont.
2.5G Handsets
The best technology now widely available
Features includes:
Phone calls/fax - always on
Voice mail
Send/receive large email messages
Internet browsing
GPS
Instant news update
Speed: >10 - 144kilobits/sec
Time to download a 4 min MP3 song: 7 - 12min
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
38
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Evolution Cont.
3G Handsets
Combines a mobile phone, laptop PC and television.
Features includes:
Phone calls/fax - always on
Global roaming
Send/receive large email
High speed internet
GPS
Videoconferencing
Live streaming
Speed: >144 - 2 megabits/sec
Time to download a 4 min MP3 song: 15sec - 1.6min
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
39
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Generations of Mobile Systems
1st Generation (1G): Analog Transmission
2nd Generation (2G): Digital Transmission
AMPS
TACS (ETACS)
NMT
GSM
CT2, CT3 (Cordless Telephone)
DECT
CDMA
3rd Generation (3G): Unification of technologies
FPLMTS (Future Public Land Mobile Telecommunication Systems)
UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecom System)
cdma2000, WCDMA (Wideband CDMA)
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
40
ECE 8708 Wireless Communications : Wireless Systems and Standards
Homework Assignment 6
9.12
11.1 (find by yourself for DECT)
11.13
11.6 (optional + 20)
Deadline 4/20/05
Before next class begins
Yimin Zhang, Villanova University
41
You might also like
- Kurose Chapter7 Multimedia Networking PDFDocument102 pagesKurose Chapter7 Multimedia Networking PDFjuninhom_10No ratings yet
- IPv6 SubnettingDocument3 pagesIPv6 SubnettingSaturnoNo ratings yet
- 100 REAL TIME COMPUTER NETWORKING Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFDocument14 pages100 REAL TIME COMPUTER NETWORKING Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFSufian IqbalNo ratings yet
- Multiple BSSID Element: AuthorsDocument16 pagesMultiple BSSID Element: AuthorsNanjil NanbanNo ratings yet
- 10gigabit XFP Optical ReceiverDocument6 pages10gigabit XFP Optical ReceivermichelNo ratings yet
- Technical, Commercial and Regulatory Challenges of QoS: An Internet Service Model PerspectiveFrom EverandTechnical, Commercial and Regulatory Challenges of QoS: An Internet Service Model PerspectiveNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Telecommunications Part AFrom EverandInnovations in Telecommunications Part AJamal ManassahNo ratings yet
- Intro To IxNetwork Feb 2012Document207 pagesIntro To IxNetwork Feb 2012Brent Taira100% (1)
- Ipv 6Document24 pagesIpv 6Mohamed Khalid R. JubaraNo ratings yet
- GPS Sync Design GuideDocument3 pagesGPS Sync Design Guidek2wojciechowskiNo ratings yet
- CCNA3 Case StudyDocument15 pagesCCNA3 Case StudyIris Ivy Ting DizonNo ratings yet
- Raspberry PiDocument32 pagesRaspberry PiGukeshNo ratings yet
- CAMBIUM EPMPCnPIlotCnMaestro Seminar ShortOct2015-3Document93 pagesCAMBIUM EPMPCnPIlotCnMaestro Seminar ShortOct2015-3sellabiNo ratings yet
- 365 Ais - Database.model - file.PertemuanFileContent LOGMAT 8Document32 pages365 Ais - Database.model - file.PertemuanFileContent LOGMAT 8Asep MiftahudinNo ratings yet
- LTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencyFrom EverandLTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencySeppo HämäläinenNo ratings yet
- Micran enDocument39 pagesMicran endbrbyuNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 - OSI Model and Application LayerDocument39 pagesCCNA 1 - OSI Model and Application LayerJohn BlackwoodNo ratings yet
- Railway Track Security SystmDocument28 pagesRailway Track Security SystmNikhil Hosur0% (1)
- BluetoothDocument39 pagesBluetoothਗੁਰਪਰੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੂਰਾਪੁਰੀNo ratings yet
- DHomesb Chapter 1 - CCNA DiscoveryDocument6 pagesDHomesb Chapter 1 - CCNA DiscoveryAbdullah Al HawajNo ratings yet
- CCNA 4 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Practice Final Exam Answers Full PDFDocument28 pagesCCNA 4 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Practice Final Exam Answers Full PDFJoseph JesusNo ratings yet
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionFrom EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNo ratings yet
- ITNE3006 Design Network Infrastructure: AssignmentDocument12 pagesITNE3006 Design Network Infrastructure: Assignmentqwerty100% (1)
- Presented By: B.Divya SD - Jasmeen MD - Hafeez External Guide: Dr.Y.Ragavender RaoDocument22 pagesPresented By: B.Divya SD - Jasmeen MD - Hafeez External Guide: Dr.Y.Ragavender RaoRaghavender MNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document108 pagesCH 1Janhavi VishwanathNo ratings yet
- Lan, Wan, ManDocument20 pagesLan, Wan, ManCatherine JoyNo ratings yet
- MPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesFrom EverandMPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- 05 TCP IP BasicsDocument9 pages05 TCP IP BasicsjaxvertNo ratings yet
- IT Essentials ITE v6.0 Chapter 7 Exam Answers 100 2016Document5 pagesIT Essentials ITE v6.0 Chapter 7 Exam Answers 100 2016Tholakele TholaNo ratings yet
- Project Synopsis On LAN ConnectionDocument15 pagesProject Synopsis On LAN ConnectionডৰাজবংশীNo ratings yet
- Making Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessFrom EverandMaking Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessNo ratings yet
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkFrom EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Optical Wireless CommunicationsDocument19 pagesOptical Wireless CommunicationsPratik SinghNo ratings yet
- IOT NetworkingDocument61 pagesIOT Networkinglalit24006No ratings yet
- ACLDocument69 pagesACLr00t32No ratings yet
- IEEE 802.11ahDocument5 pagesIEEE 802.11ahteste_downloadNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Fundamentals of Ethernet LANsDocument16 pagesPart 1 Fundamentals of Ethernet LANsNOVA MAROCNo ratings yet
- WLANDocument13 pagesWLAN150ashok150No ratings yet
- Sigtran Connectuon by CiscoDocument75 pagesSigtran Connectuon by CiscoKomunitasGerakanCintaJagapuraNo ratings yet
- DHCP and Arp: ICND1 v1.0 - 4-1Document20 pagesDHCP and Arp: ICND1 v1.0 - 4-1Viet Thang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument16 pagesProject ReportMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- Data Communications IntroductionDocument204 pagesData Communications Introductionjeretraca100% (1)
- 29 Cyberoam Best PracticesDocument2 pages29 Cyberoam Best PracticesShishir Tripathi0% (1)
- Voice Over Internet ProtocolDocument23 pagesVoice Over Internet Protocolkarthiksrinivas100% (3)
- Application of IOT Devices For Smart Car Parking SystemDocument11 pagesApplication of IOT Devices For Smart Car Parking SystemabdelrahmanelfakiNo ratings yet
- 151x Ccna 1 Ejw CH 9 AnswersDocument12 pages151x Ccna 1 Ejw CH 9 Answersapi-3842231100% (3)
- AOS - Alcatel-Lucent Operating SystemDocument4 pagesAOS - Alcatel-Lucent Operating SystemKito TomNo ratings yet
- CS 515 Mobile and Wireless Networking: Ibrahim Korpeoglu Computer Engineering Department Bilkent University, AnkaraDocument82 pagesCS 515 Mobile and Wireless Networking: Ibrahim Korpeoglu Computer Engineering Department Bilkent University, AnkaraEngAbdAsalamSaberNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 07 / LECTURE - 01 / Data Link LayerDocument8 pagesCHAPTER - 07 / LECTURE - 01 / Data Link LayerNagaraj VaratharajNo ratings yet
- CCNA v4 Accessing The Wan CH 1 100%Document3 pagesCCNA v4 Accessing The Wan CH 1 100%richmone73No ratings yet
- D4 - SBA-Student (To Preparation)Document5 pagesD4 - SBA-Student (To Preparation)Tou HerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ZigBee TechnologyDocument48 pagesIntroduction To ZigBee Technologylordi9ordinaryNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radio Network Design in the VHF and UHF Bands: A Practical ApproachFrom EverandMobile Radio Network Design in the VHF and UHF Bands: A Practical ApproachNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Final ReportDocument34 pagesIndustrial Training Final ReportAnjab HossainNo ratings yet
- Network Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandNetwork Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Embedded & Real Time Systems Notes: by Mr. Suman Kalyan OduriDocument20 pagesEmbedded & Real Time Systems Notes: by Mr. Suman Kalyan OdurisindhuuuNo ratings yet
- n thi tuyển sinh lớp 10 môn tiếng AnhDocument29 pagesn thi tuyển sinh lớp 10 môn tiếng AnhnguyenanhmaiNo ratings yet
- VS TLN 27547 2208 3Document12 pagesVS TLN 27547 2208 3Deni ArdianNo ratings yet
- Sepam Range High Impedance Differential ProtectionDocument12 pagesSepam Range High Impedance Differential ProtectionosmpotNo ratings yet
- HW1 Mastering PhysicsDocument16 pagesHW1 Mastering Physicszmontgom183% (6)
- 合并PDFDocument3 pages合并PDFBozhaoNo ratings yet
- Water Resource: Dr. Tausif AltamashDocument16 pagesWater Resource: Dr. Tausif AltamashAfzal khanNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Community CHN2 090120Document62 pagesConcepts of Community CHN2 090120Pucha MorinNo ratings yet
- People vs. PerezDocument4 pagesPeople vs. PerezjiggerNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Quality Monitoring in A Developing Area Using Water Quality Index and Principal Component Analysis: A Case Study of Visakhapatnam IndiaDocument8 pagesGround Water Quality Monitoring in A Developing Area Using Water Quality Index and Principal Component Analysis: A Case Study of Visakhapatnam IndiaMallikarjuna Rao DuvvadaNo ratings yet
- Sf2 - 2023 - Grade 1 - AguinaldoDocument2 pagesSf2 - 2023 - Grade 1 - AguinaldoDesiree C. BaricuatroNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Robots Industry Group 1Document13 pagesCollaborative Robots Industry Group 1SoorajKrishnanNo ratings yet
- Stop Talking Start Doing Action Book Sample ChapterDocument21 pagesStop Talking Start Doing Action Book Sample ChapterCapstone Publishing100% (1)
- Delicious Indian DishesDocument2 pagesDelicious Indian DishesRam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Benefits of Electrical Load ScheduleDocument7 pagesPreparation and Benefits of Electrical Load ScheduleMila GamidoNo ratings yet
- Kno3 2 Finished PDFDocument1 pageKno3 2 Finished PDFBennyNo ratings yet
- 2 - 1D Conduction Eq.Document88 pages2 - 1D Conduction Eq.AhmedNo ratings yet
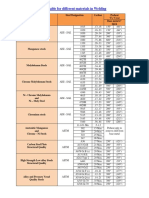
- Preheat Temperature Table For Different Materials in WeldingDocument1 pagePreheat Temperature Table For Different Materials in WeldingRakesh Soni0% (1)
- D - 14k - 3 - Delta Checklist ISO 14001-2015 - 20150917 - Short - EnglDocument9 pagesD - 14k - 3 - Delta Checklist ISO 14001-2015 - 20150917 - Short - EnglPRASAD SHETTYNo ratings yet
- Roof Work HIRARCDocument4 pagesRoof Work HIRARCSarah Liyana86% (7)
- Ajef Doc 001 - PQPDocument54 pagesAjef Doc 001 - PQPJonald DagsaNo ratings yet
- 0568Document77 pages0568selvakrishna0% (1)
- Unit 7 ListeningDocument41 pagesUnit 7 ListeningHo NgocthuNo ratings yet
- Fast & Fluid Management: Manual TM280Document17 pagesFast & Fluid Management: Manual TM280Pasha SiregarNo ratings yet
- OK 67.70 ESAB 309moDocument1 pageOK 67.70 ESAB 309moSadashiva sahooNo ratings yet
- St. Vincent de Ferrer College of Camarin, Inc.: Introduction: 14 Learner-Centered PrinciplesDocument4 pagesSt. Vincent de Ferrer College of Camarin, Inc.: Introduction: 14 Learner-Centered PrinciplesMichelle Gutierrez SibayanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Limitting Values For Exposure Grade Pages From en 206Document1 pageConcrete Limitting Values For Exposure Grade Pages From en 206Ahmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNo ratings yet
- UFFL Company Case StudyDocument6 pagesUFFL Company Case StudyDell CaasieNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Process Alarm Management: M. S. Mannan, H. H. WestDocument5 pages1.6 Process Alarm Management: M. S. Mannan, H. H. WestkangsungjinNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion ReviewDocument4 pagesCircular Motion ReviewrasajatiNo ratings yet
- Ordinance of Davao City."Document12 pagesOrdinance of Davao City."Jan kristel100% (1)