Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ES 62 Notes
ES 62 Notes
Uploaded by
Jules Nikko Dela Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 page62 notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document62 notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageES 62 Notes
ES 62 Notes
Uploaded by
Jules Nikko Dela Cruz62 notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
ES 62 Notes
CHAPTER 1
Kinematics of a Particle
Mechanics is a branch a physical sciences
that is concerned with the state of rest or
motion of bodies subjected to the action of
forces.
Statics is concerned with the equilibrium of
a body that is either at rest or moves with
constant velocity.
Dynamics deals with the accelerated
motion of body.
Kinematics treats only with the geometric
aspect of the motion.
Kinetics is the analysis of forces causing the
motion.
Galileo Galilei was one of the first major
contributors of the principles of dynamics.
The most significant contribution was made
by Isaac Newton who is notes for his
formulation of the 3 fundamental laws of
motion and the law of gravitational
attraction.
The position coordinate is used to specify
the location of the particle at any given
instant.
The displacement of the particle is defines
as the change in its position.
A particle has a mass but negligible in size
and shape.
Rectilinear kinematics refers to straight-line
motion.
Speed refers to the magnitude of the
velocity.
Curvilinear motion can cause change in
both magnitude and direction of the
position, velocity, and acceleration vectors.
The velocity vector is always directed
tangent to the path.
In general , the acceleration vector is not
tangent to the path , but rather , it is tangent
to the hodograph.
If the motion is described using rectangular
coordinates, then the components along
each of the axes do not change direction,
only their magnitude and sense will change.
By considering the components motions ,
the change in magnitude and direction of
the particles position and velocity are
automatically taken into account.
When air resistance is neglected, the only
force acting on the projectile is its weight
,which causes the projectile to have a
constant downward acceleration.
When the path along which a particle
travels is known , then it s often convenient
to describe the motion using n and t
coordinate axes which act normal and
tangent to the path, respectively, and at the
instant considered have their origin located
at the particle.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ECE 51 - Lab Activity 1 PDFDocument5 pagesECE 51 - Lab Activity 1 PDFJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 6Document3 pagesActivity 4 6Jules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Who Got Funded RecentlyW1Document1 pageWho Got Funded RecentlyW1Jules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Request For Cash Advance: Grand TotalDocument1 pageRequest For Cash Advance: Grand TotalJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- DLL G6 Q3 WEEK 2 (Mam Inkay Peralta)Document71 pagesDLL G6 Q3 WEEK 2 (Mam Inkay Peralta)Jules Nikko Dela Cruz100% (6)
- Grade 5 DLL Science 5 q4 Week 1Document5 pagesGrade 5 DLL Science 5 q4 Week 1Jules Nikko Dela Cruz100% (1)
- REPORTME1Document150 pagesREPORTME1Jules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A1Document4 pagesA1Jules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines and Drives An Introduction To Principles and CharacteristicsDocument267 pagesElectrical Machines and Drives An Introduction To Principles and CharacteristicsJules Nikko Dela Cruz67% (3)
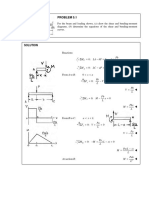
- Problem 5.1: SolutionDocument10 pagesProblem 5.1: SolutionJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- LAB 2 Newton-Raphson MethodDocument3 pagesLAB 2 Newton-Raphson MethodJules Nikko Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Kitchen Utensils Quantity Unit Items Description Unit Price Total PriceDocument2 pagesKitchen Utensils Quantity Unit Items Description Unit Price Total PriceJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- September: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayDocument2 pagesSeptember: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Project IN: Physical EducationDocument10 pagesProject IN: Physical EducationJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Es64 Group 9 TemplateDocument1 pageEs64 Group 9 TemplateJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet