Professional Documents
Culture Documents
052 Functional Groups PDF
052 Functional Groups PDF
Uploaded by
ThuvarakaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
052 Functional Groups PDF
052 Functional Groups PDF
Uploaded by
ThuvarakaCopyright:
Available Formats
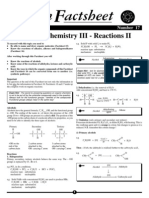
Chem Factsheet
April 2003
Number 52
Reactions of Functional Groups - A Summary
To succeed in this topic you need to:
Be able to recall and write out the functional groups represented
in this Factsheet;
Have a thorough knowledge of the organic reactions and their
conditions (described in the Organic Chemistry Factsheets to
date 27, 31, 32, 33, 34 and 39);
Recognise the summarised versions of the equations in this
Factsheet and be able to write them out in full under exam
conditions.
Reactions of alkenes
After working through this Factsheet you will:
Have revised the organic chemistry reactions that candidates
are required to learn for AS and A2 Chemistry modules.
Have a reference paper as you start to work through questions
on organic pathways and synthesis.
Diol
CO2 + H2O
Alkane
H2
electrophilic
heat,
addition
Ni catalyst
Di-halogenoalkane
halogen
hydrogen
halide
electrophilic
addition
Halogenoalkane
electrophilic
addition
oxidation
electrophilic addition
Reactions of alcohols
bromo-alkane
nucleophilic substitution
chloro-alkane
These spider diagrams represent the reactions in a summarised version, in
a visual fashion that suits many learners. They should be used in
conjunction with Factsheets 27, 31, 32, 33, 34 and 39, which show the
reactions in a more detailed format.
NaBr(s) +
H2SO 4(conc.)
to make HBr
nucleophilic
substitution
A good way of using this Factsheet to revise effectively would be as
follows:
1. Pick a group to revise (e.g. alkanes).
2. Pick a member of that group at random (e.g. propane).
3. Use the spider diagram to help you write out balanced chemical
reactions, with conditions, for the organic chemical you have chosen.
iodo-alkane
nucleophilic
substitution
P(s) + I2(s)
to make PI 3
dry PCl5
halogenation
Propane and oxygen (combustion)
C3H8 + 5O2
heat
Alcohol
3CO2 + 4H2O
dehydration
Propane and chlorine (free radical substitution)
C3H8 + Cl2
uv light
C3H7Cl + HCl
conc. H2SO4
In an exam, candidates are required to apply their knowledge of organic
reactions to a wide variety of compounds, so the more of these you do, the
better!
Carbon Dioxide
+ Water
heat to
170 o C
oxidation
primary
alcohols
Cr2O72(aq)
O2
heat
halogen
Alkanes
UV Light
Cr2O72(aq)
aldehyde
Halogeno
alkane
further oxidation
Cr2O72(aq)
free radical
substitution
H+(aq)
carboxylic
acid
secondary
alcohols
H+(aq)
alkene
Reactions of alkanes
combustion
heat
Alkenes
alkaline
KMnO4(aq)
This Factsheet is designed to be used as a revision aid as candidates set
about the sometimes daunting task of learning all of the organic reactions
required by the A2 Chemistry course.
(e.g.)
O2
H+(aq)
ketone
Chem Factsheet
Reactions of Functional Groups - A Summary
Ester Reactions
Fig. 3 Halogenoalkane reactions
Alcohol
Nitrile
nucleophilic
substitution
KCN in
water/ethanol
Carboxylic acid
+
Alcohol
nucleophilic
substitution
NaOH(aq)
heat under
reflux
heat under
reflux
Carboxylic acid
+
Alcohol
H 2O
Ester
acid
conditions
alkaline
conditions
Halogenoalkane
KOH in
ethanol
NH3 in
ethanol
H 2O
heat under
reflux
heat
Amines
Acyl Chloride Reactions
Alkene
nucleophilic
elimination
nucleophilic
substitution
Grignard Reagents
Carboxylic
acid
Ester
nucleophilic
substitution
nucleophilic
substitution
H 2O
Preparation
alcohol
Mg turnings
Grignard Reagent
"R-MgHal"
Halogenoalkane
Dry ether solvent
Boil under reflux
Acyl
Chloride
addition
primary
amine
Reactions
Primary
Alcohol
N-substituted
Amide
nucleophilic
addition / hydrolysis
nucleophilic
substitution
ketone
+ H2O(l)
H+(aq)
nucleophilic
addition / hydrolysis
nucleophilic
addition / hydrolysis
nucleophilic
addition / hydrolysis
2,4-DNP
Derivative
nucleophilic
addition then
elimination
Polyester
nucleophilic substitution /
polymerisation
boil under reflux
conc. H2SO4
Na2CO3
or NaHCO 3
Diacid
+
H+(aq)
Diol
Carboxylic
Acid
aqueous
Sodium Salt +
CO2 + H2O
neutralisation
reduction
LiAlH4
then
H+(aq)
LiAlH4 in
dry ether
dry
HCN
PCl5
Acyl Chloride
nucleophilic
substitution
reduction
LiAlH4
in ether
silver
nitrate in
ammonia
warm
solution
Fehlings
solution
H2SO4
Positive Silver
Mirror Test
redox
Alcohol
alcohol
Primary
Alcohol
NaBH4 in
ethanol
Aldehydes
2,4-DNP in
ethanol
Carboxylic Acid Reactions
nucleophilic
substitution
reduction
nucleophilic addition
trace of
KOH
Tertiary
Alcohol
Primary
Alcohol
Hydroxy-nitrile
compound
H+(aq)
Carboxylic
Acid
Ester
nucleophilic
substitution
Reactions of Aldehydes
aldehyde (not methanal)
+ H2O(l)
Grignard Reagent
"R-MgHal"
CO2 (g)
+ H2O(l)
Secondary
Alcohol
H+(aq)
H 2O
Amide
nucleophilic
substitution
methanal,
CH2=O(g) then use
+ H2O(l) dilute acid
for hydrolysis
Alkane
NH3
warm
Positive Fehlings
Test
redox
Chem Factsheet
Reactions of Functional Groups - A Summary
Reactions of Aldehydes
Reactions of Amino Acids
Secondary
Alcohol
Hydroxy-nitrile
compound
reduction
HCN
reduction
NaBH4 in
ethanol
alkali
Amino Acids
neutralisation
Secondary
Alcohol
nucleophilic addition
trace of
KOH
acid
Salt
Salt
neutralisation
Reactions of Phenol
LiAlH4
in ether
2,4,6tribromophenol
Phenate ion
Ketones
neutralisation
electrophilic substitution
-
OH (aq)
2,4-DNP in
H2SO4
Br 2(aq)
Phenol
2,4-DNP
Derivative
acyl chloride,
in NaOH(aq)
nucleophilic addition then
elimination
Ester
Reactions of Amines
nucleophilic substitution
Salts
Substituted
Amides
nucleophilic addition /
neutralisation
nucleophilic
substitution
Reactions of Benzene
Bromobenzene
acid
electrophilic substitution
acyl chloride
Amines
Br2
primary amines + acyl chlorides
if monomers contain 2 amine
groups and 2 acyl chloride groups
Benzene
50o C conc
H2SO4
Polyamides
nucleophilic substitution
polymerisation
hydrolysis
alkali
acid
Nitriles
heat under
reflux
heat under
reflux
Br2
Nitrobenzene
Alkylbenzene
electrophilic substitution
Sn,
conc. HCL,
NaOH
Carboxylic
acid
Fe cat. dry
HNO3
electrophilic substitution
Reactions of Nitrites
Carboxylic
acid salt
Fe cat.
dry
KMnO 4
in alkali
heat under
reflux
hydrolysis
Phenylamine
LiAlH4
in ether
reduction
Benzocarboxylic
acid
oxidation
HNO2
+
HCl
Amine
reduction
Benzenediazonium
ions
Reactions of Amides
Nitrile
dehydration
P4 O10
warm
Amides
Br2(l) +
NaOH(aq)
warm
Amine +
CO2
Acknowledgements: This Factsheet was researched and written by Kieron Heath
Curriculum Press, Unit 305B, The Big Peg, 120 Vyse Street, Birmingham, B18 6NF
ChemistryFactsheets may be copied free of charge by teaching staff or students, provided that
their school is a registered subscriber. No part of these Factsheets may be reproduced, stored
in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any other form or by any other means, without the
prior permission of the publisher. ISSN 1351-5136
hydrolysis
You might also like
- Sterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ACS Sample QuestionsDocument20 pagesOrganic Chemistry ACS Sample QuestionsNajmusawwa Aulia RahmahNo ratings yet
- Summary of Organic TestDocument2 pagesSummary of Organic TestritmrazNo ratings yet
- Hem Actsheet: Redox Equilibria IV - Redox TitrationsDocument3 pagesHem Actsheet: Redox Equilibria IV - Redox TitrationsAya ZhNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Copper: Number 83 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukDocument5 pagesThe Chemistry of Copper: Number 83 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.uks7076728g100% (1)
- Book Answers Edexcel As Chemistry PDFDocument99 pagesBook Answers Edexcel As Chemistry PDFahmed100% (1)
- 32 Organ PDFDocument3 pages32 Organ PDFThuvarakaNo ratings yet
- Chem Factsheet 17Document3 pagesChem Factsheet 17drdre12100% (1)
- Hem Actsheet: Organic Chemistry 4: Carbonyl CompoundsDocument3 pagesHem Actsheet: Organic Chemistry 4: Carbonyl CompoundsDaniel C. WalshNo ratings yet
- Reacciones Caracteristicas Por Grupos FuncionalesDocument3 pagesReacciones Caracteristicas Por Grupos FuncionalesAdelitza StrubingerNo ratings yet
- 16 Organ PDFDocument3 pages16 Organ PDFAya ZhNo ratings yet
- 34 Org N CompoundsDocument2 pages34 Org N CompoundsBotagoz Kaukenova100% (1)
- 11oxida PDFDocument3 pages11oxida PDFThuvarakaNo ratings yet
- C IndexDocument17 pagesC IndexalvinkoyNo ratings yet
- Chem FactsheetDocument4 pagesChem FactsheetChandan Aggarwal100% (1)
- 94 Enthalpies of SolutionDocument4 pages94 Enthalpies of SolutionJude PeelNo ratings yet
- 67 Why Students Lose Marks 1 Redox PDFDocument3 pages67 Why Students Lose Marks 1 Redox PDFThuvarakaNo ratings yet
- 69 Trends in Physicalpropsrevised PDFDocument3 pages69 Trends in Physicalpropsrevised PDFThuvarakaNo ratings yet
- Hem Actsheet: Answering Questions On Electrochemical CellsDocument2 pagesHem Actsheet: Answering Questions On Electrochemical CellsAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Enthalpies of SolutionDocument4 pagesEnthalpies of SolutionNana_Banana_940% (1)
- 054 Infrared Spectro PDFDocument3 pages054 Infrared Spectro PDFThuvarakaNo ratings yet
- 70 Trends in PTable2 Chem Revised PDFDocument4 pages70 Trends in PTable2 Chem Revised PDFsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- 133 AcylationDocument4 pages133 AcylationAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- 048 Lab Chemistry - Organic PDFDocument3 pages048 Lab Chemistry - Organic PDFSakib AhsanNo ratings yet
- Applied Organic ChemistryDocument2 pagesApplied Organic ChemistrycliffmusicgirlNo ratings yet
- Answering Questions On Redox Titrations I: Number 57 WWW - Curriculumpress.co - UkDocument3 pagesAnswering Questions On Redox Titrations I: Number 57 WWW - Curriculumpress.co - UkWeb BooksNo ratings yet
- 23titra PDFDocument2 pages23titra PDFThuvarakaNo ratings yet
- Why Students Lose Marks - Reaction Mechanisms: Number 131 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukDocument4 pagesWhy Students Lose Marks - Reaction Mechanisms: Number 131 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukAmelia AkandeNo ratings yet
- 20 - Periodic Table - Group 4Document3 pages20 - Periodic Table - Group 4winnielong100% (1)
- Chemistry Revision Package For SH1 IP 2011Document18 pagesChemistry Revision Package For SH1 IP 2011le_nhat_11No ratings yet
- Edexcel - IAS - Organic Chemistry - 1Document21 pagesEdexcel - IAS - Organic Chemistry - 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Standard Electrode Potentials & CellsDocument3 pagesStandard Electrode Potentials & Cellsmy nameNo ratings yet
- Born Haber ProcessDocument4 pagesBorn Haber ProcessNana_Banana_94No ratings yet
- Kinetics I - Rates of Reaction: Hem ActsheetDocument4 pagesKinetics I - Rates of Reaction: Hem ActsheetApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy ChangesSMPLFDDocument55 pagesEnthalpy ChangesSMPLFDtopherchandraNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry NotesDocument16 pagesA-Level Chemistry NotesMurad100% (1)
- 22kpaDocument4 pages22kpaNidhi SisodiaNo ratings yet
- 046 Transition Metals 2 No Answer Chen Fact SheetDocument2 pages046 Transition Metals 2 No Answer Chen Fact SheetlicciNo ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry Revision Guide For A2 LevelDocument15 pagesCIE Chemistry Revision Guide For A2 LevelBakhita MaryamNo ratings yet
- Hem Actsheet: Organic Chemistry 2: Halogeno-Compounds and Grignard ReagentsDocument2 pagesHem Actsheet: Organic Chemistry 2: Halogeno-Compounds and Grignard Reagentskishan_katwaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry GRE SampleDocument0 pagesChemistry GRE Sampleyoostan100% (2)
- Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit - 2 - Topic 1Document49 pagesEdexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit - 2 - Topic 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry: Number 97 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukDocument5 pagesOxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry: Number 97 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukKirsty McCulloughNo ratings yet
- Edexcel As Chemistry Practice Unit Test1Document17 pagesEdexcel As Chemistry Practice Unit Test1Mohammed Hussain100% (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNo ratings yet
- The Determination of Carboxylic Functional Groups: Monographs in Organic Functional Group AnalysisFrom EverandThe Determination of Carboxylic Functional Groups: Monographs in Organic Functional Group AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- O Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9From EverandO Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Unit 6 Reaction of Functional Groups - A SummaryDocument3 pagesUnit 6 Reaction of Functional Groups - A SummaryklahaNo ratings yet
- 16 Hydroxy CompoundsDocument57 pages16 Hydroxy CompoundsMinh Thy Nguyen LeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Carbonyl CompoundsDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Carbonyl CompoundsJacqueen0330No ratings yet
- Organic chem examination review - 複本Document22 pagesOrganic chem examination review - 複本Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Chemistry Previous Year Questions With Solutions On HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesJEE Main Chemistry Previous Year Questions With Solutions On HydrocarbonsAnsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Alcohols IIDocument38 pagesAlcohols IIRafael G. Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- F334 - What's in A Medicine?Document11 pagesF334 - What's in A Medicine?Becky Tenney100% (1)
- 1f. Aqa Chy3f W QP Jan08Document16 pages1f. Aqa Chy3f W QP Jan08LouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- 17h Ch3hp Jun 13 WreDocument7 pages17h Ch3hp Jun 13 WreLouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- 13h Aqa Chem W SQP 3hDocument20 pages13h Aqa Chem W SQP 3hLouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- 1h Aqa Chy3h W QP Jan08Document16 pages1h Aqa Chy3h W QP Jan08LouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry OlympiadsDocument10 pagesChemistry OlympiadsLouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- 2004 RD 1 Answers tcm18-190747Document8 pages2004 RD 1 Answers tcm18-190747LouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- 13f Aqa Chem W Sms 3fDocument10 pages13f Aqa Chem W Sms 3fLouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- 2000 RD 1 Answers tcm18-190755Document7 pages2000 RD 1 Answers tcm18-190755LouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- 2002 RD 1 Questions tcm18-190750Document10 pages2002 RD 1 Questions tcm18-190750LouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- 13h Aqa Chem W Sms 3hDocument12 pages13h Aqa Chem W Sms 3hLouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- 2000 RD 1 Answers tcm18-190755Document7 pages2000 RD 1 Answers tcm18-190755LouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- 2000 - RD - 1 - Questions - tcm18-190754Document9 pages2000 - RD - 1 - Questions - tcm18-190754LouiseflemingNo ratings yet
- CalgonDocument22 pagesCalgonFayyad GhayyadNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAS Bonding 1Document14 pagesEdexcel IAS Bonding 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Chempro Chap-12 HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesChempro Chap-12 HydrocarbonsBerry101No ratings yet
- Hartley F.R. (Ed.) - The Chemistry of The Metal-Carbon Bond. V.4. The Use of Organometallic Compounds in Organic SynthesisDocument1,355 pagesHartley F.R. (Ed.) - The Chemistry of The Metal-Carbon Bond. V.4. The Use of Organometallic Compounds in Organic Synthesisjulianpellegrini860100% (1)
- Selective Transport and Storage of IronDocument11 pagesSelective Transport and Storage of IronAbhishek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Group 5Document3 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris Group 5Nafilatul ArfaNo ratings yet
- Benzene and It's DerivativesDocument28 pagesBenzene and It's DerivativesIrshad Khan Naushad KhanNo ratings yet
- HCH111 Quiz 2, Answers, 2019Document2 pagesHCH111 Quiz 2, Answers, 2019Bonita NengweNo ratings yet
- D and F-Block Elements and Coordination Chemistry: 6.1 The D-Block Metals Have Multiple Oxidation StatesDocument8 pagesD and F-Block Elements and Coordination Chemistry: 6.1 The D-Block Metals Have Multiple Oxidation StatesBlueAbeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry PracticalDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry PracticalAbdulmujeeb simpaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes & Ketones: (Alkanals & Alkanones)Document21 pagesAldehydes & Ketones: (Alkanals & Alkanones)Firgin DeisyellaNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram New DM PlantDocument1 pageBlock Diagram New DM PlantDevraj RoyNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds QuestionsDocument82 pagesCoordination Compounds QuestionsShyam SubediNo ratings yet
- Ch24 TestbankDocument40 pagesCh24 TestbankIannah Malvar100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/51Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/51yas ahmedNo ratings yet
- DRAFT Exp 3 Preparing Buffer SolutionsDocument94 pagesDRAFT Exp 3 Preparing Buffer SolutionsConcepcion R. AquinoNo ratings yet
- CH 018Document23 pagesCH 018phdf5s2p5gNo ratings yet
- CBSE-X Chapterwise (Previous Years) Qs - Science - SOL-min PDFDocument60 pagesCBSE-X Chapterwise (Previous Years) Qs - Science - SOL-min PDFmathanagopal balasundram100% (1)
- Homework One Naming CompoundsDocument3 pagesHomework One Naming CompoundsGlen fongNo ratings yet
- CinnamylDocument3 pagesCinnamyljennyihateNo ratings yet
- Oc Mock 03Document3 pagesOc Mock 03invooo prabamadhan100% (1)
- Quantitative: Analytical Chemistry (Qualitative and Chemistry)Document13 pagesQuantitative: Analytical Chemistry (Qualitative and Chemistry)Rizza OlivaNo ratings yet
- Chemical PolarityDocument6 pagesChemical PolarityRUZCHEMISTRYNo ratings yet
- Appendix A Critical Constants and Acentric Factors: Compiled FromDocument3 pagesAppendix A Critical Constants and Acentric Factors: Compiled FromSonia LecunaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis, Structure and Spectroscopic Characterization of Ni (II), Co (II), Cu (II) and ZN (II) Complexes With Saccharinate and PyrazoleDocument9 pagesSynthesis, Structure and Spectroscopic Characterization of Ni (II), Co (II), Cu (II) and ZN (II) Complexes With Saccharinate and PyrazoleLucía BolañosNo ratings yet
- Common Foundation Organic Q in A LevelDocument21 pagesCommon Foundation Organic Q in A Level黄维燕No ratings yet
- Humayra Hannan - Beginning BalancingDocument5 pagesHumayra Hannan - Beginning BalancingDivya SinghNo ratings yet
- Empirical Versus Molecular FormulasDocument5 pagesEmpirical Versus Molecular FormulasJaz SantosNo ratings yet
- Revision ChemDocument32 pagesRevision ChemNada AlbuainainNo ratings yet
- BIF401 Final Term Papers Fall 2018Document5 pagesBIF401 Final Term Papers Fall 2018HRrehmanNo ratings yet
- AromaticityDocument6 pagesAromaticityFatma ElsaidNo ratings yet