Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structural Statics Chapter 2
Uploaded by
Prashim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Structural statics chapter 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesStructural Statics Chapter 2
Uploaded by
PrashimCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
MAE3315
Homework No.2 (SOLUTION)
Problem 2-1
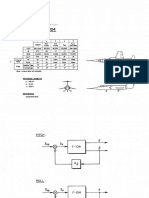
A state of stress is given at a point on the vertical fin of an aircraft as
Gira aoe aaa:
[ESE al
Find :
a) The normal and shear stress components on the plane ABCD.
b) The corresponding stress components if the original plane is rotated 45° about the 2-
ln
Solution:
First, we need the projection of {n} on {x} and {y}.
and 1, = Sin(9)= Sin(45)=
‘Therefore, the vector {n} becomes,
v2
be {isa}
On the other hand, {¢}=[o]-{n},
ChE hte
i
Finally, 0, =7-7,
of +S? = lif
= Vl -o.
Where,
sore (34) (ty
I= .fe? +2 = (3) (3) = 578 +98 = 26Ksi
S = (26) -(24F
S=10Ksi
With,
34/2 uy2
inetd
ee
‘This means that the direction of the Shear Stress is negative in our convention. Therefore,
‘S=-10ksi. There is another way to solve for the Shear Stress,
To calculate the components of the vector {7},
ale = Cos(@) = Cos(45)=
v2 ”
—Sin(9) = -Sin(45) =
2
sin
Asa result, the vector {t} becomes,
i
|
-Vy2
fue
And then, S'=7-#,
Ac
AS Fp) gs
S= Fone tts,
i)
lev E-lle.]
EH - =) ie
Tey} [-mn mn m?—n? | |r,
@] ie bv} al v2\iiv2) | f30
o, =| (val Wv2P — ~2ftr/2{ir/2) |} 10 |e
al —bv2firv2) (va)iv2) Qvv2) -frv2) | L4
o,] fu2 v2 17 p30
oy |=| 1/2 1/2 -1}-] 10 |Ksé
tyy| [-1/2 2 0} L4
o, | f24
oy |=] 16 [ksi
Tey} [10
Same results as part a, as expected!
P Ps
|
|
|
Problem 2-2
‘A stress state at a point P on a plane is given as below.
1-3 5
-3 2 2|-x10? Psi
ee 3]
Consider a plane, 4x+3y+6z=12 through the point P.
a) Find the normal component of the traction o, and its tangential component S acting at
that point P on this plane,
b) Find the direction cosines of o, and S.
©) Find the magnitude of the traction vector ¢ and its angle with the normal vector n
Solution:
a)
First, we need to find the directional cosines of that plane 4x +3y +62 =12.. From this
equation is easy to compute that: a=3, b=4, and o=2.
fe ea eee ete Oe ye
Teo rel aay wey (eR ay
ag eee 3841 =m
oF veoh Hey ey Ge) ery
pu assist seit etet guniranieintd ©, Jinrranig a
OT Fea Meare Cay
0.5121)
0.3841
0.7682}
Asweknow, {}=[c]-{n},
Sera 0.5121 3.2009)
{§=|-3 2 2|Ksi) 0.3841) =40.7682)Ksi
5 2 3} 0.7682} [5.6336]
i
[fl =¥G.2009Y + (0.7682) + (6.63367 = 6.5249 Ksi
Finally, o, =7-7,
F-f=tn, +1,n, +£,2, = (3.2009)(0.5121)+ (0.7682\(0.3841) + (5.6336)(0.7682) = 6.2623Ksi
And,
b)
‘The directional cosines of 6, is naturally {n},
0.5121
0.3841
0.7682,
And the directional cosines of 7 are,
3.2009 0.5121
0.7682 + — 6.2623; 0.3841
5.6336 0.7682
1.8323,
°)
The magnitude of {t) was already calculated,
f]=6.5249 Ks
To calculate the angle, we know that,
tang =
ie
o= arctof ©) =0.2847radians=16.3"
°,
Another way to solve it,
FLL6]=[Fpl cose
@= AreCof £2623MPa_ |
6.5249 MPa
6=163"
Same answer as expected!
Problem 2-3
‘A stress element has the state of stress as shown below:
Find the principal stresses and their corresponding directions.
Note: Use the method given in the class only.
4ksi
—>
4 isi
i : Aksi
6ksi eS 6 ksi
y
eee
Aksi
Solution:
0
-4
(0, {-6-o,)-16=0
p\-6-0,)-16=0
o3 +60, -16=0
Therefore, the principal stresses are:
6, = 2Ksi
o, = OKsi
0, = -8Ksi
For 0, = 2Ksi:
(2 cele
For 0, =-8Ksi:
eo” —
azn SF
FE S58
i i
2 Ear
se Be
ee Se
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Design PointsDocument2 pagesDesign PointsPrashimNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- STEM ScholDisbursementDocument1 pageSTEM ScholDisbursementPrashimNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Internet Read File ExampleDocument1 pageInternet Read File ExampleA.B. CbmNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Quasi TurbineDocument1 pageQuasi TurbinePrashimNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- HW#2Document22 pagesHW#2PrashimNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- MATLAB TEchniquesDocument58 pagesMATLAB TEchniquesPrashim100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- LaTeX Mathematical SymbolsDocument4 pagesLaTeX Mathematical Symbolsjfreyre100% (9)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Introduction To Fracture Mechanics Introduction To Fracture MechanicsDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Fracture Mechanics Introduction To Fracture MechanicsShiba Narayan SahuNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Case 3 Az ResponseDocument1 pageCase 3 Az ResponsePrashimNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Case 3 H ResponseDocument1 pageCase 3 H ResponsePrashimNo ratings yet
- (M - S MW) S2-MqsDocument6 pages(M - S MW) S2-MqsPrashimNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Case 3 Theta ResponseDocument1 pageCase 3 Theta ResponsePrashimNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Introduction To Fracture Mechanics Introduction To Fracture MechanicsDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Fracture Mechanics Introduction To Fracture MechanicsShiba Narayan SahuNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Fracture Mechanics - WikipediaDocument13 pagesFracture Mechanics - WikipediaPrashimNo ratings yet
- CruiseDocument7 pagesCruisePrashimNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Maurice Nicoll The Mark PDFDocument4 pagesMaurice Nicoll The Mark PDFErwin KroonNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamic 2Document38 pagesGas Dynamic 2Prashim0% (1)
- Case 3 Az ResponseDocument1 pageCase 3 Az ResponsePrashimNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Maurice Nicoll The Mark PDFDocument4 pagesMaurice Nicoll The Mark PDFErwin KroonNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- 2016 Ae CDocument1 page2016 Ae CPrashimNo ratings yet
- Naca 4412Document19 pagesNaca 4412Ashfaq AhamedNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Homework 13 Handling Qualities (Due Oct 31)Document11 pagesHomework 13 Handling Qualities (Due Oct 31)PrashimNo ratings yet
- Structural Statics For EngineerDocument4 pagesStructural Statics For EngineerPrashimNo ratings yet
- 3315 hw1 14Document2 pages3315 hw1 14Deep NarulaNo ratings yet
- MAE3315-16 Supplementary Notes: No.1 Problem: SN1.1: I T H T) B T BT H ×2Document5 pagesMAE3315-16 Supplementary Notes: No.1 Problem: SN1.1: I T H T) B T BT H ×2PrashimNo ratings yet
- MAE 3303 Aerodynamics of Compressible FlowsDocument1 pageMAE 3303 Aerodynamics of Compressible FlowsttimmyturnerNo ratings yet
- FFF SolutionsDocument152 pagesFFF SolutionsMohammedAL-AthariNo ratings yet
- MAE3303 Aerodynamics of Compressible Flow: SyllabusDocument28 pagesMAE3303 Aerodynamics of Compressible Flow: SyllabusPrashimNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)