Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
SYAZWANI HUSNA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pagephotogrammetry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentphotogrammetry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageTutorial 1
Uploaded by
SYAZWANI HUSNAphotogrammetry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
fTUTORIAL 1: GLS 455
What is the difference between metric photogrammetry and interpretative
photogrammetry?
Explain the difference between a map and an aerial photograph.
Explain the following photogrammetric terms: end lap, side lap, air base,
principal point and flying height.
Differentiate between vertical, low oblique and high oblique photographs.
Define scale. Give the differences between a large scale and a small scale.
How do you express scale?
Derive scale of a vertical photograph for a variable terrain.
Derive scale of a tilted photograph at the isocenter, nadir and the principal
point. Is the scale at nadir greater/lower than the scale at the isocenter?
Give the differences between a metric camera and a non metric camera.
10
Are maps equal to photographs?
11
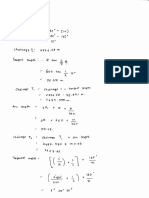
A pair of overlapping vertical photos was taken from a flying height of 990.60
m above average ground with an air base of 600 m. If the focal length of the
camera was 152.4 mm and the photo format was 230 mm x 230 mm,
calculate the percentage end lap.
(6 marks)
12
A distance ab on a vertical photograph is 51.7 mm, and the corresponding
ground distance AB is 1282 m. If the camera focal length is 88.95 mm, what
is the flying height above the terrain upon which line AB is located?
(7 marks)
You might also like
- Article Human TraffickingDocument23 pagesArticle Human TraffickingSYAZWANI HUSNANo ratings yet
- Presentation EcrmDocument3 pagesPresentation EcrmSYAZWANI HUSNA0% (1)
- 3D NDCDBDocument3 pages3D NDCDBSYAZWANI HUSNANo ratings yet
- Sample of Video Appraisal Movie Title: HOPS (April 2011) Movie SynopsisDocument3 pagesSample of Video Appraisal Movie Title: HOPS (April 2011) Movie SynopsisSYAZWANI HUSNANo ratings yet
- Survey Science Geomatics Faculty Architecture Planning Survey UITM Malaysia Shah Alam Selangor Darul EhsanDocument45 pagesSurvey Science Geomatics Faculty Architecture Planning Survey UITM Malaysia Shah Alam Selangor Darul EhsanSYAZWANI HUSNA100% (1)
- Practical Report Writting FormatDocument1 pagePractical Report Writting FormatSYAZWANI HUSNANo ratings yet
- 7e, QQT: 60o Baflrctio" qn6trDocument1 page7e, QQT: 60o Baflrctio" qn6trSYAZWANI HUSNANo ratings yet
- Versus Healthy Food Among Student in Universiti Teknologi Mara Shah Alam"Document2 pagesVersus Healthy Food Among Student in Universiti Teknologi Mara Shah Alam"SYAZWANI HUSNANo ratings yet
- Blank Solar Obsn FormDocument1 pageBlank Solar Obsn FormdrummingstickNo ratings yet
- Course Information Confidential: Universiti Teknologi MaraDocument4 pagesCourse Information Confidential: Universiti Teknologi MaraSYAZWANI HUSNANo ratings yet
- Report TheodolitesDocument18 pagesReport TheodolitesSYAZWANI HUSNA100% (1)
- DroneDocument6 pagesDroneSYAZWANI HUSNANo ratings yet
- GDM2000 & CCS Infrastructure Dr. Samad, JUPEMDocument14 pagesGDM2000 & CCS Infrastructure Dr. Samad, JUPEMSYAZWANI HUSNANo ratings yet
- GDM2000 & CCS Infrastructure Dr. Samad, JUPEMDocument14 pagesGDM2000 & CCS Infrastructure Dr. Samad, JUPEMSYAZWANI HUSNANo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)