Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ME101 Materials and Stresses - Practice Questions
Uploaded by
Saqib JabbarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ME101 Materials and Stresses - Practice Questions
Uploaded by
Saqib JabbarCopyright:
Available Formats
ME 101
Materials & Stresses - Practice Questions for Exam I
1. When a 90-kg man stands on a snow-covered trail, he sinks a certain amount into the snow because
the compressive stress between his boots and the snow is larger than the snow can support without
crumbling. Assuming typical cross-country skis are 1.65 m long and 6 cm wide, calculate the
percentage reduction in stress applied to the snow when he is wearing skis instead of boots (assume a
typical snow boot has a sole that is 8 cm wide and 25 cm long).
Answer: ~80%
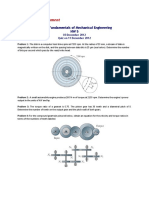
2. As a machinist presses the handles of a bolt cutter, link AB carries a 7.5 kN force (see figure below).
If the link has a 14 mm 4 mm rectangular cross section, calculate the tensile/axial/normal (these are
the same thing) stress within it.
Answer: 133.93 MPa
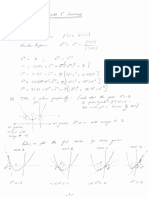
3. See the figure below.
(a) By using vector algebra, determine the magnitude of F that will cause the net effect of the three
forces to act vertically.
(b) For that value of F, determine the stress in the bolts 1-cm-diameter straight shank.
Please see next page
Answer: (a) 568.46 N, (b) 10.08 MPa
4. The tires of the 20.25 kN sedan car pictured below are 16.5 cm wide (into the plane of the paper).
Each tire contacts the ground over a distance of 10.8 cm along the vehicles length, as shown.
Calculate the compressive stress acting at the interface between each tire and the road. Pay attention to
the location of the vehicles mass center.
Hint: First determine the reaction forces at each tire using the principles of static equilibrium (theres
only one force component at each tire). Now calculate the corresponding stress over each tires contact
area with the ground.
Answer: 340.90 kPa for the front tires, 227.27 kPa for the rear tires.
5. A steel rod with a round cross-section is fixed to a vertical surface (see picture below). When the
rod is subjected to 15.5 kN of axial tension, calculate (a) the stress and strain in the rod, (b) the amount
that it stretches, and (c) its change in diameter. (d) If the force was only 5 kN, by what amount would
the rod have stretched? As it is common to do for steel alloys, assume an E of 210 GPa and of 0.3.
Answer: (a) 137.1 MPa and 0.0653%, (b) 0.196 mm, (c) -0.0023 mm, (d) only 0.0632 mm
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Hum Assignment 1Document4 pagesHum Assignment 1Saqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Cs 113 Lab 03 Spring 2015-16 Lab 2: Important: Yourlastname - Firstname - Lab01 - Questionnumber.M (Ex: Akgun - Ali - Lab01 - Q1B.M)Document2 pagesCs 113 Lab 03 Spring 2015-16 Lab 2: Important: Yourlastname - Firstname - Lab01 - Questionnumber.M (Ex: Akgun - Ali - Lab01 - Q1B.M)Saqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- CE297 Ch3Document14 pagesCE297 Ch3PPLUISALAMOSNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- ME231 Syllabus Fall 2016Document3 pagesME231 Syllabus Fall 2016Saqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Write The Correct Comparison Symbol (, or ) in Each BoxDocument1 pageWrite The Correct Comparison Symbol (, or ) in Each BoxSaqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- HW 5 SolutionDocument2 pagesHW 5 SolutionSaqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- HW 2 SolutionDocument2 pagesHW 2 SolutionSaqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Midterm Exam 1: - October 27, 2010Document2 pagesMidterm Exam 1: - October 27, 2010Saqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- MT1 SolutionDocument3 pagesMT1 SolutionSaqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- MT1 SolutionDocument3 pagesMT1 SolutionSaqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Homework Assignment: ME 101 Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineering HW5Document1 pageHomework Assignment: ME 101 Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineering HW5Saqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Me101 HW 1Document2 pagesMe101 HW 1Saqib JabbarNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)