Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sickle Cell Complications
Uploaded by
LucykeshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sickle Cell Complications
Uploaded by
LucykeshCopyright:
Available Formats
Infections : increased
risk
especially
to
encapsulated
bacteria
because
of
autosplenectomy.
Hepatobiliary
complications:
Pigemented gallstones
due
to
increased
bilirubin from hemolysis.
Biliary sludge
Biliary cholic
Acute cholecystitis
Acute choledocolithiasis
Acute cholangitis
Acute
hepatic
sequestration
Acute
intrahepatic
cholestasis
Pain
from
vasoocclusion
Acute
chest
syndrome :
Presents with signs and
sx of lower resp tract
infection and has a new
pulmonary infiltrate on
radiograph .
Workup: CBC with diff.
blood and urine cx.
-if SOB, cough,
tachypnea, investigate
for acute chest
syndrome
Workup: LFTS, CBC with
retic, RUQ sono.
Splenic
-Hospitalize if high fever
and give abx therapy
Tx:
-surgery cholecystitis
-ERCP for cholangitis
-Exchnage transfusion
for Acute hepatic
sequestration and acute
intrahepatic cholestasis
Presents as acute onset
of pain in chest, back,
extremities. Triggers
stress, cold, and
infections
Dx: Xray , O2 sats
-CBC with diff and retic.
-blood cx.
-can develop sudden or
slow.
-#1 cause of death in
adult
Priapism: 1/3rd of men
Prevention:
Immunizations and ppx
antibotics until 5 years
old.
Treat mild pain with
NSAIDS If they tolerate
it. Narcotics for severe
pain.
*should also rule out
acute chest syndrome
and osteomyelitis.
(xray MRI)
Tx: Abx IV cephalosporin
and oral macrolide.
-Keep O2 sats > 95%
-give transfusion only if
rapid deteriorating or
the Hg has dropped
more than 1 unit from
baseline.
-Encourage incentive
spirometry
Need prompt treatment
because can cause
permanent erectile
dysfunction.
Elevated retic,
Tx: vigorous hydration
and analgesics.
-only transfuse if
surgery is required.
Tx:
sequestration:
nucleated RBCs and
decreased platelet.
Sudden drop 2 units Hg
from
baseline
and
enlargement of spleen.
Stroke:
-Kids ischemic stroke
-Adults
hemorrhagic
stroke
Multisystem
organ
failure.
Workup: CT
Comprehensive
metabolic panel . CBC
with diff.
1) splenic sequestration
with hypovolemia:
Immediate IV hydration
2) Splenic sequestration
with severe anemia.
Transfuse to raise Hg
but slowly because can
cause over transfusion
Tx: exchange
transfusion.
Tx: exchange
transfusion.
Presents
are
rapid
deterioration,
fever,
drop
in
Hg,
and
encephalopathy
42 years for males and 48 years for females.
Among those with sickle cell-hemoglobin C disease, the
median age at death was 60 years for males and 68 years
for females
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke causes and effects outlinedDocument25 pagesIschemic and hemorrhagic stroke causes and effects outlinedLucykesh100% (8)
- Immunology High Yield For STEP 1Document13 pagesImmunology High Yield For STEP 1Lucykesh100% (6)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Microbiology USMLE ReviewDocument9 pagesMicrobiology USMLE ReviewLaura TapiaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Pediatric Usmle NotesDocument14 pagesPediatric Usmle NotesLucykesh67% (3)
- Behavioural Science Notes UsmleDocument19 pagesBehavioural Science Notes UsmleLucykesh100% (3)
- Microbiology Step 1 Weird Exceptions and DetailDocument10 pagesMicrobiology Step 1 Weird Exceptions and DetailLucykesh100% (2)
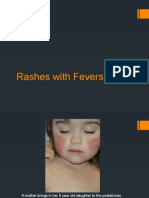
- Rashes and FeversDocument36 pagesRashes and FeversLucykeshNo ratings yet
- TB Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument4 pagesTB Diagnosis and TreatmentLucykeshNo ratings yet
- NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION TOXINS AND NEUROTRANSMITTERSDocument2 pagesNEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION TOXINS AND NEUROTRANSMITTERSLucykeshNo ratings yet